Abstract
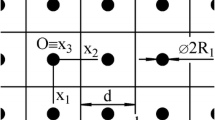
The paper deals with analytical models of the elastic energy gradient W sq representing an energy barrier. The energy barrier is a surface integral of the elastic energy density w q . The elastic energy density is induced by thermal stresses acting in an isotropic spherical particle (q = p) with the radius R and in a cubic cell of an isotropic matrix (q = m). The spherical particle and the matrix are components of a multi-particle-matrix system representing a model system applicable to a real two-component material of a precipitation-matrix type. The multi-particle-matrix system thus consists of periodically distributed isotropic spherical particles and an isotropic infinite matrix. The infinite matrix is imaginarily divided into identical cubic cells with a central spherical particle in each of the cubic cells. The dimension d of the cubic cell then corresponds to an inter-particle distance. The parameters R, d along with the particle volume fraction v = v(R,d) as a function of R, d represent microstructural characteristics of a real two-component material. The thermal stresses are investigated within the cubic cell, and accordingly are functions of the microstructural characteristics. The thermal stresses originate during a cooling process as a consequence of the difference α m − α p in thermal expansion coefficients between the matrix and the particle, α m and α p , respectively. The energy barrier W sq is used for the determination of the thermal-stress induced strengthening σ q . The strengthening represents resistance against compressive or tensile mechanical loading for α m − α p > 0 or α m − α p < 0, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ceniga, L.: Thermal-stress induced phenomena in two-component material. Part I. Acta Mech. Sinica 25(6) (2009)
Ceniga L.: Thermal stresses in isotropic cell-divided particle-matrix system: spherical and cubic cells. J. Thermal Stress. 27, 425–432 (2004)
Ceniga L.: A new analytical model for thermal stresses in multi-phase materials and lifetime prediction methods. Acta Mech. Sinica 24, 189–206 (2008)
Skočovský P., Bokůvka O., Palček P.: Materials Science, 1st edn. EDIS, Žilina (1996)
Brdička M., Samek L., Sopko B.: Continuum Mechanics, 1st edn. Academia, Prague (2000)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ceniga, L. Thermal-stress induced phenomena in two-component material: Part II. Acta Mech Sin 26, 101–106 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-009-0317-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-009-0317-8