Abstract
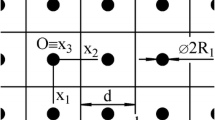
Based on the fundamental equations of the mechanics of solid continuum, the paper employs an analytical model for determination of elastic thermal stresses in isotropic continuum represented by periodically distributed spherical particles with different distributions in an infinite matrix, imaginarily divided into identical cells with dimensions equal to inter-particle distances, containing a central spherical particle with or without a spherical envelope on the particle surface. Consequently, the multi-particle-(envelope)-matrix system, as a model system regarding the analytical modelling, is applicable to four types of multi-phase materials. As functions of the particle volume fraction v, the inter-particle distances d 1, d 2, d 3 along three mutually perpendicular axes, and the particle and envelope radii, R 1 and R 2, respectively, the thermal stresses within the cell, are originated during a cooling process as a consequence of the difference in thermal expansion coefficients of phases represented by the matrix, envelope and particle. Analytical-(experimental)-computational lifetime prediction methods for multi-phase materials are proposed, which can be used in engineering with appropriate values of parameters of real multi-phase materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mizutani T. (1996). Residual strain energy in composites containing particles. J. Mater. Res. 11: 483–494
Ceniga L. (2004). Thermal stresses in isotropic cell-divided particle-matrix system: Spherical and cubic cells. J. Therm. Stress. 27: 425–432
Brdička M., Samek L. and Sopko B. (2000). Mechanics of Continuum, 1st edn. Academia, Prague
Rektorys K. (1973). Review of Applied Mathematics, 2nd edn. SNTL, Prague
Skočovský P., Bokůvka O. and Palček P. (1996). Materials Science, 1st edn. EDIS, Žilina
Bhadeshia H.K.D.H., Strang A. and Gooch D.J. (1998). Ferritic power plant steels: remanent life assessment and approach to equilibrium. Int. Mater. Rev. 43: 45–53
Výrostková A., Kroupa A., Janovec J. and Svoboda M. (1998). Carbide reactions and phase equilibria in low alloy Cr-Mo-V steels tempered at 773–993 K. Part I: Experimental measurements. Acta Mater. 46: 31–38
Homolová V., Janovec J., Záhumenský P. and Výrostková A. (2003). Influence of thermal-deformation history on evolution of secondary phases in P91 steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 349: 306–312
Dimmler G., Weinert P., Kozeschnik E. and Cerjak H. (2003). Quantification of the laves phase in advanced 9-12% Cr steels using a standard SEM. Mater. Character. 51: 341–352
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The English text was polished by Keren Wang.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ceniga, L. A new analytical model for thermal stresses in multi-phase materials and lifetime prediction methods. Acta Mech. Sin. 24, 189–206 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-007-0132-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-007-0132-z