Abstract
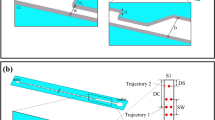
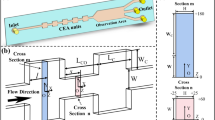
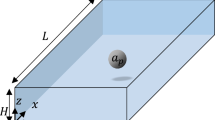
To enhance focusing performance, we proposed an integrated microchannel with expansion–contraction arrays (ECA) on the inner wall of the curved microchannel (CIECA) and compared it with a straight microchannel with ECA (SECA) as well as the traditional integrated microchannel of ECA on the outer wall of the curved channel (COECA). We investigated the particle-focusing mechanisms in these microchannels through a combination of experiments and numerical simulations. The proposed integrated microchannel demonstrates significant improvements in focusing performance compared to SECA and COECA, which is attributed to its consistent Dean flow. In contrast, COECA shows the poorest performance because of inconsistent Dean flow. The focusing width in the proposed integrated microchannel is reduced to 1/3 of that in COECA and 1/2 of that in SECA. Furthermore, the focusing performance of CIECA improves as the Reynolds number increases, eventually forming a single trajectory when the Reynolds number (at contraction) reaches 83.33. Finally, the impact of particle size on focusing performance was investigated through numerical simulations. The focusing performance of the CIECA is the best in these three microchannels. In CIECA, as the particle size increases, the focusing width initially decreases and then increases. Among them, 8 and 10 μm particles can achieve complete focusing. This study serves as a crucial reference for comprehending and enhancing particle focusing through the synergy of multi-Dean flow.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary material.
References
Abdulla A, Liu W, Gholamipour-Shirazi A et al (2018) High-throughput isolation of circulating tumor cells using cascaded inertial focusing microfluidic channel. Anal Chem 90:4397–4405. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04210
Augustsson P, Magnusson C, Nordin M et al (2012) Microfluidic, label-free enrichment of prostate cancer cells in blood based on acoustophoresis. Anal Chem 84:7954–7962. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac301723s
Bhagat AAS, Kuntaegowdanahalli SS, Papautsky I (2008) Enhanced particle filtration in straight microchannels using shear-modulated inertial migration. Phys Fluids 20:101702. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2998844
Bhagat AAS, Kuntaegowdanahalli SS, Kaval N et al (2010) Inertial microfluidics for sheath-less high-throughput flow cytometry. Biomed Microdevices 12:187–195. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-009-9374-9
Çetin B, Li D (2011) Dielectrophoresis in microfluidics technology. Electrophoresis 32:2410–2427. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201100167
Di Carlo D (2009) Inertial microfluidics. Lab Chip 9:3038. https://doi.org/10.1039/b912547g
Fan L-L, Wu X, Zhang H et al (2019) Continuous sheath-free focusing of microparticles in viscoelastic and Newtonian fluids. Microfluid Nanofluidics 23:117. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-019-2281-3
Forbes TP, Forry SP (2012) Microfluidic magnetophoretic separations of immunomagnetically labeled rare mammalian cells. Lab Chip 12:1471. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2lc40113d
Gou Y, Zhang S, Sun C et al (2020) Sheathless inertial focusing chip combining a spiral channel with periodic expansion structures for efficient and stable particle sorting. Anal Chem 92:1833–1841. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b03692
Guan G, Wu L, Bhagat AA et al (2013) Spiral microchannel with rectangular and trapezoidal cross-sections for size based particle separation. Sci Rep 3:1475. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep01475
Jin C, McFaul SM, Duffy SP et al (2014) Technologies for label-free separation of circulating tumor cells: from historical foundations to recent developments. Lab Chip 14:32–44. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3LC50625H
Kim YW, Yoo JY (2008) The lateral migration of neutrally-buoyant spheres transported through square microchannels. J Micromech Microeng 18:065015. https://doi.org/10.1088/0960-1317/18/6/065015
Lee MG, Choi S, Park J-K (2009) Three-dimensional hydrodynamic focusing with a single sheath flow in a single-layer microfluidic device. Lab Chip 9:3155. https://doi.org/10.1039/b910712f
Lee MG, Choi S, Park J-K (2011) Inertial separation in a contraction–expansion array microchannel. J Chromatogr A 1218:4138–4143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2010.11.081
Li M, Muñoz HE, Schmidt A et al (2016) Inertial focusing of ellipsoidal Euglena gracilis cells in a stepped microchannel. Lab Chip 16:4458–4465. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6LC01118G
Lim EJ, Ober TJ, Edd JF et al (2012) Visualization of microscale particle focusing in diluted and whole blood using particle trajectory analysis. Lab Chip 12:2199. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2lc21100a
Liu C, Hu G, Jiang X, Sun J (2015) Inertial focusing of spherical particles in rectangular microchannels over a wide range of Reynolds numbers. Lab Chip 15:1168–1177. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4LC01216J
Liu C, Xue C, Sun J, Hu G (2016) A generalized formula for inertial lift on a sphere in microchannels. Lab Chip 16:884–892. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5LC01522G
Lu X, Liu C, Hu G, Xuan X (2017) Particle manipulations in non-Newtonian microfluidics: a review. J Colloid Interface Sci 500:182–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.04.019
Morsi SA, Alexander AJ (1972) An investigation of particle trajectories in two-phase flow systems. J Fluid Mech 55:193. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112072001806
Nasiri R, Shamloo A, Akbari J et al (2020) Design and simulation of an integrated centrifugal microfluidic device for CTCs separation and cell lysis. Micromachines 11:699. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11070699
Prohm C, Stark H (2014) Feedback control of inertial microfluidics using axial control forces. Lab Chip 14:2115. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4lc00145a
Qin J, Wang Z, Chen Y et al (2023) Thermocapillary flow-induced core release from double-emulsion droplets in microchannels. Droplet 2:54. https://doi.org/10.1002/DRO2.54
Roper MG (2016) Cellular analysis using microfluidics. Anal Chem 88:381–394. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04532
Segré G, Silberberg A (1961) Radial particle displacements in Poiseuille flow of suspensions. Nature 189:209–210. https://doi.org/10.1038/189209a0
Shamloo A, Abdorahimzadeh S, Nasiri R (2019) Exploring contraction–expansion inertial microfluidic-based particle separation devices integrated with curved channels. AIChE J 65:16741. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.16741
Shen S, Tian C, Li T et al (2017) Spiral microchannel with ordered micro-obstacles for continuous and highly-efficient particle separation. Lab Chip 17:3578–3591. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7LC00691H
Shen S, Zhang F, Wang S et al (2019) Ultra-low aspect ratio spiral microchannel with ordered micro-bars for flow-rate insensitive blood plasma extraction. Sens Actuators B Chem 287:320–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.02.066
Shiriny A, Bayareh M (2021) Inertial focusing of CTCs in a novel spiral microchannel. Chem Eng Sci 229:116102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2020.116102
Tang W, Zhu S, Jiang D et al (2020) Channel innovations for inertial microfluidics. Lab Chip 20:3485–3502. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0LC00714E
Wang Z, Li S, Chen R et al (2018) Numerical study on dynamic behaviors of the coalescence between the advancing liquid meniscus and multi-droplets in a microchannel using CLSVOF method. Comput Fluid 170:341–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compfluid.2018.05.014
Wang R, Sun S, Wang W, Zhu Z (2019) Investigation on the thermophoretic sorting for submicroparticles in a sorter with expansion–contraction microchannel. Int J Heat Mass Transf 133:912–919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.12.126
Wang Z, Zhen T, Wu F et al (2023) Enhanced particle focusing and sorting by multiple sheath stream in contraction–expansion microchannel. Microfluid Nanofluidics 27:16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-022-02620-5
Wang Z, Li Z, Jia L et al (2024) Numerical investigation on heat transfer characteristics of microencapsulated phase change material slurry in a rectangular minichannel. J Therm Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11630-024-1860-0
Xiang N, Wang J, Li Q et al (2019) Precise size-based cell separation via the coupling of inertial microfluidics and deterministic lateral displacement. Anal Chem 91:10328–10334. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b02863
Zhang J, Yan S, Yuan D et al (2016) Fundamentals and applications of inertial microfluidics: a review. Lab Chip 16:10–34. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5LC01159K
Zhao Q, Yuan D, Zhang J, Li W (2020) A review of secondary flow in inertial microfluidics. Micromachines 11:461. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi11050461
Zhou J, Papautsky I (2013) Fundamentals of inertial focusing in microchannels. Lab Chip 13:1121. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2lc41248a
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Key Laboratory of Low-grade Energy Utilization Technologies and Systems (No. LLEUTS-202312), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52106212, U20A20299, 51806038), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2019A1515012119).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RZ: methodology, formal analysis, investigation, writing—review and editing. KS: formal analysis, investigation, writing—review and editing. ZW: methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, writing—review and editing. GC: methodology, validation, formal analysis, writing—review and editing. YC: conceptualization, methodology, supervision. LJ: formal analysis, validation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhuang, R., Song, K., Wang, Z. et al. Curved microchannels with inner wall expansion–contraction array for particle focusing. Microfluid Nanofluid 28, 20 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-024-02715-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-024-02715-1