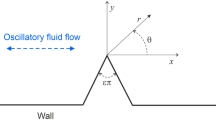
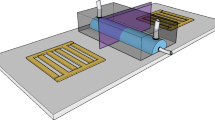
Abstract
Acoustic streaming can be generated in microchannels by low-frequency acoustic transducer in the vicinity of sharp structures. Close to the tip, the strong curvature induces bent trajectories on the time-periodic acoustic flow, locally enhancing the streaming-generating force. In this study, we investigate the influence of the sharp structure and vibration velocity on the streaming flow. The vibration velocities are characterized by directly visualizing the displacement of tracing particles and the generated acoustic streaming is observed using particle image velocimetry, under various operating conditions. By measuring the concentration of a fluorescence dye, we evaluate the mixing performance for different values of tip angle, vibration amplitude, and flow rate through the microchannel. Our results confirm that intense streaming is generated under low-frequency (2.5 kHz) acoustic condition when the local curvature of the boundary is close to or smaller than the viscous boundary-layer thickness. It is shown that the sharpest the edge tip, the largest the vortices size and the spatial extent of the induced streaming, therefore greatly enhancing the mixing between two miscible liquids. The mixing index, linearly characterizing the mixing degree between 1 (totally separated) and 0 (perfectly mixed), jumps from 0.73 (without acoustic excitation) to 0.38 (with acoustic excitation), resulting in a highly mixed homogeneous fluid just after the sharp edge. This emphasizes the promising potential of acoustic streaming to enhance mass transfer inside microchannels which is usually limited by the laminar flow conditions.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambreen T, Kim M-H (2018) Effect of fin shape on the thermal performance of nanofluid-cooled micro pin-fin heat sinks. Int J Heat Mass Transf 126:245–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJHEATMASSTRANSFER.2018.05.164
Bachman H, Huang P-H, Zhao S et al (2018) Acoustofluidic devices controlled by cell phones. Lab Chip 18:433–441. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7LC01222E
Barnkob R, Augustsson P, Laurell T, Bruus H (2012) Acoustic radiation- and streaming-induced microparticle velocities determined by microparticle image velocimetry in an ultrasound symmetry plane. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys 86:056307. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevE.86.056307
Boluriaan S, Morris P (2003) Acoustic streaming: from Rayleigh to today. Int J Aeroacoustics 2:255–292. https://doi.org/10.1260/147547203322986142
Bruus H (2012) Acoustofluidics 2: perturbation theory and ultrasound resonance modes. Lab Chip 12:20–28. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1lc20770a
Cao Z, Lu C (2016) A microfluidic device with integrated sonication and immunoprecipitation for sensitive epigenetic assays. Anal Chem 88:1965–1972. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04707
Chen J, Stefanov SK, Baldas L, Colin S (2016) Analysis of flow induced by temperature fields in ratchet-like microchannels by Direct Simulation Monte Carlo. Int J Heat Mass Transf 99:672–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJHEATMASSTRANSFER.2016.04.023
Chiu H-C, Hsieh R-H, Wang K et al (2017) The heat transfer characteristics of liquid cooling heat sink with micro pin fins. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 86:174–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ICHEATMASSTRANSFER.2017.05.027
Dong Z, Zhao S, Zhang Y et al (2017) Mixing and residence time distribution in ultrasonic microreactors. AIChE J 63:1404–1418. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.15493
Eckart C (1948) Vortices and streams caused by sound waves. Phys Rev 73:68–76. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.73.68
Elvira KS, I Solvas XC, Wootton RCR, Demello AJ (2013) The past, present and potential for microfluidic reactor technology in chemical synthesis. Nat Chem 5:905–915
Faraday M (1831) On a peculiar class of acoustical figures; and on certain forms assumed by groups of particles upon vibrating elastic surfaces. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 121:299–340. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstl.1831.0018
Franke K, Ross-Messemer M, Menck A et al (2003) The highly sensitive optical measurement of absolute SAW amplitudes for power flow analysis. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 50:77–80. https://doi.org/10.1109/TUFFC.2003.1176527
Gopinath A, Mills AF (1994) Convective heat transfer due to acoustic streaming across the ends of a Kundt tube. J Heat Transfer 116:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2910882
Guo X, Fan Y, Luo L (2013) Mixing performance assessment of a multi-channel mini heat exchanger reactor with arborescent distributor and collector. Chem Eng J 227:116–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.08.068
Guo X, Fan Y, Luo L (2014) Multi-channel heat exchanger-reactor using arborescent distributors: a characterization study of fluid distribution, heat exchange performance and exothermic reaction. Energy 69:728–741. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.03.069
Guo X, Fan Y, Luo L (2018) Residence time distribution on flow characterisation of multichannel systems: modelling and experimentation. Exp Therm Fluid Sci 99:407–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2018.08.016
Huang P-H, Xie Y, Ahmed D et al (2013a) An acoustofluidic micromixer based on oscillating sidewall sharp-edges. Lab Chip 13:3847. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3lc50568e
Huang PH, Xie Y, Ahmed D et al (2013b) An acoustofluidic micromixer based on oscillating sidewall sharp-edges. Lab Chip 13:3847–3852. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3lc50568e
Huang P-H, Nama N, Mao Z et al (2014) A reliable and programmable acoustofluidic pump powered by oscillating sharp-edge structures. Lab Chip 14:4319–4323. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4LC00806E
Huang P-H, Chan CY, Li P et al (2015a) A spatiotemporally controllable chemical gradient generator via acoustically oscillating sharp-edge structures. Lab Chip 15:4166–4176. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5LC00868A
Huang PH, Ren L, Nama N et al (2015b) An acoustofluidic sputum liquefier. Lab Chip 15:3125–3131. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5lc00539f
Huang P-H, Chan CY, Li P et al (2018a) A sharp-edge-based acoustofluidic chemical signal generator. Lab Chip 18:1411–1421. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8LC00193F
Huang PH, Chan CY, Li P et al (2018b) A sharp-edge-based acoustofluidic chemical signal generator. Lab Chip 18:1411–1421. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8lc00193f
Lee Dong-Ryul, Loh Byoung-Gook (2007) Smart cooling technology utilizing acoustic streaming. IEEE Trans Compon Packag Technol 30:691–699. https://doi.org/10.1109/tcapt.2007.901756
Legay M, Simony B, Boldo P et al (2012) Improvement of heat transfer by means of ultrasound: application to a double-tube heat exchanger. Ultrason Sonochem 19:1194–1200. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ULTSONCH.2012.04.001
Lei J, Glynne-Jones P, Hill M (2013) Acoustic streaming in the transducer plane in ultrasonic particle manipulation devices. Lab Chip 13:2133. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3lc00010a
Leibacher I, Hahn P, Dual J (2015) Acoustophoretic cell and particle trapping on microfluidic sharp edges. Microfluid Nanofluidics 19:923–933. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1621-1
Lighthill SIRJ (1978) ACOUSTIC STREAMINGt. J Sound Vib 61:391–418
Nama N, Huang P-H, Huang TJ, Costanzo F (2014a) Investigation of acoustic streaming patterns around oscillating sharp edges. Lab Chip 14:2824–2836. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4LC00191E
Nama N, Huang PH, Huang TJ, Costanzo F (2014b) Investigation of acoustic streaming patterns around oscillating sharp edges. Lab Chip 14:2824–2836. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4lc00191e
Nyborg WL (1953) Acoustic streaming due to attenuated plane waves. J Acoust Soc Am 25:68–75. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.1907010
Ovchinnikov M, Zhou J, Yalamanchili S (2014) Acoustic streaming of a sharp edge. J Acoust Soc Am 136:22–29. https://doi.org/10.1121/1.4881919
Ozcelik A, Nama N, Huang P-H et al (2016) Acoustofluidic rotational manipulation of cells and organisms using oscillating solid structures. Small 12:5120–5125. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201601760
Rayleigh JWS (2013) The theory of sound, vol One. Dover Publications, New York
Schneider C, Rasband W, Eliceiri K (2012) ImageJ. Nat Methods 9:671–675
Squires TM, Quake SR (2005) Microfluidics: fluid physics at the nanoliter scale. Rev Mod Phys 77:977–1026. https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.77.977
Stuart JT (1966) Double boundary layers in oscillatory viscous flow. J Fluid Mech 24:673. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022112066000910
Thielicke W, Stamhuis EJ (2014) PIVlab—towards user-friendly, affordable and accurate digital particle image velocimetry in MATLAB. J Open Res Softw. https://doi.org/10.5334/jors.bl
Tobias J, Karlsen JT, Bruus H (2015) Forces acting on a small particle in an acoustical field in a thermoviscous fluid Forces acting on a small particle in an acoustical field in a thermoviscous fluid. Phys Rev E. https://doi.org/10.1103/physreve.92.043010
Uchida T, Suzuki T, Shiokawa S (1995) Investigation of acoustic streaming excited by surface acoustic waves. In: IEEE ultrasonics symposium. proceedings. An international symposium. IEEE, pp 1081–1084
Wang C, Jalikop SV, Hilgenfeldt S (2012) Efficient manipulation of microparticles in bubble streaming flows. Biomicrofluidics 6:012801. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3654949
Wang X, Zhang Z, Zhang W et al (2019) Numerical simulation of thermal edge flow in ratchet-like periodically patterned micro-channels. Int J Heat Mass Transf 135:1023–1038. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJHEATMASSTRANSFER.2019.02.006
Whitesides GM (2006) The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 442:368–373. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05058
Wiklund M, Green R, Ohlin M (2012) Acoustofluidics 14: applications of acoustic streaming in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 12:2438. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2lc40203c
Zacharias J, Ohl C-D (2013) Fluid dynamics, cavitation, and tip-to-tissue interaction of longitudinal and torsional ultrasound modes during phacoemulsification. J Cataract Refract Surg 39:611–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrs.2012.10.050
Zhao S, He W, Ma Z et al (2019) On-chip stool liquefaction via acoustofluidics. Lab Chip 19:941–947. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8LC01310A
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the scholarship support from the CSC (China Scholarship Council). Eric Falcon is acknowledged for his help in the measurement of the vibration velocity with the laser vibrometer. They would like to thank the MSC and LIED lab members for their daily support and discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MP4 8218 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Guo, X., Brunet, P. et al. Acoustic streaming near a sharp structure and its mixing performance characterization. Microfluid Nanofluid 23, 104 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-019-2271-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-019-2271-5