Abstract
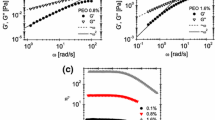
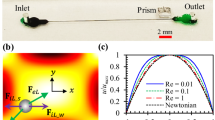
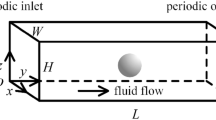
There has recently been a significantly increasing interest in the passive manipulation of particles in the flow of non-Newtonian fluids through microchannels. However, an accurate and comprehensive understanding of the various fluid rheological effects on particle migration is still largely missing. We present in this work a systematic experimental study of both the individual and the combined effects of fluid inertia, elasticity, and shear thinning on the motion of rigid spherical particles in a straight rectangular microchannel. We first study the sole effect of each of these rheological properties in a Newtonian fluid, purely elastic (i.e., Boger) fluid, and purely shear-thinning (i.e., pseudoplastic) fluid, respectively. We then study the combined effects of two or all of these rheological properties in a pseudoplastic fluid and two types of elastic shear-thinning fluids, respectively. We find that the fluid elasticity effect directs particles toward the centerline of the channel while the fluid shear-thinning effect causes particle migration toward both the centerline and corners. These two effects are combined with the fluid inertial effect to understand the particle migration in inertial pseudoplastic and viscoelastic fluid flows.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amini H, Lee W, Di Carlo D (2014) Inertial microfluidic physics. Lab Chip 14:2739–2761
Asghari M, Serhatlioglu M, Ortaç B, Solmaz ME, Elbuken C (2017) Sheathless microflow cytometry using viscoelastic fluids. Sci Rep 7:12342. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12558-2
Asmolov ES (1999) The inertial lift on a spherical particle in a plane Poiseuille flow at large channel Reynolds number. J Fluid Mech 381:63–87
Barnes HA, Hutton JF, Walters K (1989) An introduction to rheology. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Bird RB, Armstrong RC, Hassager O (1977) Dynamics of polymeric liquids, vol 1. Wiley-Interscience, Hoboken
Cheng NS (2008) Formula for the viscosity of a glycerol–water mixture. Ind Eng Chem Res 47:3285–3288
D’Avino G, Maffettone PL (2015) Particle dynamics in viscoelastic liquids. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 215:80–104
D’Avino G, Romeo G, Villone MM, Greco F, Netti PA, Maffettone PL (2012) Single line particle focusing induced by viscoelasticity of the suspending liquid: theory, experiments and simulations to design a micropipe flow-focuser. Lab Chip 12:1638–1645
D’Avino G, Greco F, Maffettone PL (2017) Particle migration due to viscoelasticity of the suspending liquid and its relevance in microfluidic devices. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 49:341–360
Del Giudice F, Romeo G, D’Avino G, Greco F, Netti PA, Maffettone PL (2013) Particle alignment in a viscoelastic liquid flowing in a square-shaped microchannel. Lab Chip 13:4263–4271
Del Giudice F, D’Avino G, Greco F, Netti PA, Maffettone PL (2015) Effect of fluid rheology on particle migration in a square-shaped microchannel. Microfluid Nanofluid 19:95–104
Del Giudice F, Sathish S, D’Avino G, Shen AQ (2017) “From the edge to the center”: viscoelastic migration of particles and cells in a strongly shear-thinning liquid flowing in a microchannel. Anal Chem 89:13146–13159
Di Carlo D (2009) Inertial microfluidics. Lab Chip 9:3038–3046
Di Carlo D, Edd JF, Humphry KJ, Stone HA, Toner M (2009) Particle segregation and dynamics in confined flows. Phy Rev Lett 102:094503
Gauthier F, Goldsmith HL, Mason SG (1971a) Particle motions in non-Newtonian media. Rheol Acta 10:344–364
Gauthier F, Goldsmith HL, Mason SG (1971b) Particle motions in non-Newtonian media. II. Poiseuille flow. Trans Soc Rheol 15:297–330
Hejazian M, Li W, Nguyen NT (2015) Lab on a chip for continuous-flow magnetic cell separation. Lab Chip 15:959–970
Ho BP, Leal LG (1974) Inertial migration of rigid spheres in two-dimensional unidirectional flows. J Fluid Mech 65:365–400
Ho BP, Leal LG (1976) Migration of rigid spheres in a two-dimensional unidirectional shear flow of a second-order fluid. J Fluid Mech 76:783–799
Huang PY, Joseph DD (2000) Effects of shear thinning on migration of neutrally buoyant particles in pressure driven flow of Newtonian and viscoelastic fluids. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 90:159–185
Huang L, Bian S, Cheng Y, Shi G, Liu P, Ye X, Wang W (2017) Microfluidics cell sample preparation for analysis: advances in efficient cell enrichment and precise single cell capture. Biomicrofluid 11:011501
James DF (2009) Boger fluids. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 41:129–142
Japper-Jaafar A, Escudier MP, Poole RJ (2010) Laminar, transitional and turbulent annular flow of drag-reducing polymer solutions. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 165:1357–1372
Kang K, Lee SS, Hyun K, Lee SJ, Kim JM (2013) DNA-based highly tunable particle focuser. Nat Commun 4:2567
Karimi A, Yazdi S, Ardekani AM (2013) Hydrodynamic mechanisms of cell and particle trapping in microfluidics. Biomicrofluid 7:021501
Karnis A, Mason SG (1966) Particle motions in sheared suspensions. XIX. Viscoelastic media. Trans Soc Rheol 10:571–592
Karnis A, Goldsmith HL, Mason SG (1963) Axial migration of particles in Poiseuille flow. Nature 200:159–160
Kayani AA, Khoshmanesh K, Ward SA, Mitchell A, Kalantar-Zadeh K (2012) Optofluidics incorporating actively controlled micro- and nano-particles. Biomicrofluid 6:031501
Kim B, Kim JM (2016) Elasto-inertial particle focusing under the viscoelastic flow of DNA solution in a square channel. Biomicrofluid 10:024111
Leal LG (1979) The motion of small particles in non-Newtonian fluids. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 5:33–78
Leal LG (1980) Particle motions in a viscous fluid. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 12:435–476
Lee DJ, Brenner H, Youn JR, Song YS (2013) Multiplex particle focusing via hydrodynamic force in viscoelastic fluids. Sci Rep 3:3258
Leshansky AM, Bransky A, Korin N, Dinnar U (2007) Tunable nonlinear viscoelastic “focusing” in a microfluidic device. Phys Rev Lett 98:234501
Li M, Li WH, Zhang J, Alici G, Wen W (2014) A review of microfabrication techniques and dielectrophoretic microdevices for particle manipulation and separation. J Phys D 47:063001
Li G, McKinley GH, Ardekani AM (2015) Dynamics of particle migration in channel flow of viscoelastic fluids. J Fluid Mech 785:486–505
Li D, Lu X, Xuan X (2016) Viscoelastic separation of particles by size in straight rectangular microchannels: a parametric study for a refined understanding. Anal Chem 88:12303–12309
Liang L, Zhu J, Xuan X (2011) Three-dimensional diamagnetic particle deflection in ferrofluid microchannel flows. Biomicrofluid 5:034110
Lim EJ, Ober TJ, Edd JF, Desai SP, Neal D, Bong KW, Doyle PS, McKinley GH, Toner M (2014a) Inertio-elastic focusing of bioparticles in microchannels at high throughput. Nat Commun 5:4120
Lim H, Nam J, Shin S (2014b) Lateral migration of particles suspended in viscoelastic fluids in a microchannel flow. Microfluid Nanofluid 17:683–692
Liu C, Hu G (2017) High-throughput particle manipulation based on hydrodynamic effects in microchannels. Micromachines 8:73
Liu C, Xue C, Chen X, Shan L, Tian Y, Hu G (2015a) Size-based separation of particles and cells utilizing viscoelastic effects in straight microchannels. Anal Chem 87:6041–6048
Liu C, Hu G, Jiang X, Sun J (2015b) Inertial focusing of spherical particles in rectangular microchannels over a wide range of Reynolds numbers. Lab Chip 15:1168–1177
Liu C, Ding B, Xue C, Tian Y, Hu G, Sun J (2016) Sheathless focusing and separation of diverse nanoparticles in viscoelastic solutions with minimized shear thinning. Anal Chem 88:12547–12553
Lu X, Xuan X (2015) Continuous microfluidic particle separation via elasto-inertial pinched flow fractionation. Anal Chem 87:6389–6396
Lu X, Zhu L, Hua RM, Xuan X (2015) Continuous sheath-free separation of particles by shape in viscoelastic fluids. Appl Phys Lett 107:264102
Lu X, Liu C, Hu G, Xuan X (2017) Particle manipulations in non-Newtonian microfluidics: a review. J Colloid Interface Sci 500:182–201
Martel JM, Toner M (2014) Inertial focusing in microfluidics. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 16:371–396
Nam J, Lee Y, Shin S (2011) Size-dependent microparticles separation through standing surface acoustic waves. Microfluid Nanofluid 11:317–326
Nam J, Tan JK, Khoo BL, Namgung B, Leo HL, Lim CT, Kim S (2015) Hybrid capillary-inserted microfluidic device for sheathless particle focusing and separation in viscoelastic flow. Biomicrofluid 9:064117
Nilsson J, Evander M, Hammarstrom B, Laurell T (2009) Review of cell and particle trapping in microfluidic systems. Anal Chim Acta 649:141–157
Poole RJ, Escudier MP (2004) Turbulent flow of viscoelastic liquids through an axisymmetric sudden expansion. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 117:25–46
Rodd LE, Scott TP, Boger DV, Cooper-White JJ, McKinley GH (2005) The inertio-elastic planar entry flow of low-viscosity elastic fluids in micro-fabricated geometries. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 129:1–22
Romeo G, D’Avino G, Greco F, Netti PA, Maffettone PL (2013) Viscoelastic flow-focusing in microchannels: scaling properties of the particle radial distributions. Lab Chip 13:2802–2807
Sajeesh P, Sen AK (2014) Particle separation and sorting in microfluidic devices: a review. Microfluid Nanofluid 17:1–52
Segre G, Silberberg A (1961) Radial particle displacements in Poiseuille flow of suspensions. Nature 189:209–210
Seo KW, Byeon HJ, Huh HK, Lee SJ (2014a) Particle migration and single-line particle focusing in microscale pipe flow of viscoelastic fluids. RSC Adv 4:3512–3520
Seo KW, Kang YJ, Lee SJ (2014b) Lateral migration and focusing of microspheres in a microchannel flow of viscoelastic fluids. Phys Fluids 26:063301
Seo KW, Ha YR, Lee SJ (2014c) Vertical focusing and cell ordering in a microchannel via viscoelasticity: applications for cell monitoring using a digital holographic microscopy. Appl Phys Lett 104:213702
Song HY, Lee SH, Salehiyan R, Hyun K (2016) Relationship between particle focusing and dimensionless numbers in elasto-inertial focusing. Rheol Acta 55:889–900
Tarn MD, Lopez-Martinez MJ, Pamme N (2014) On-chip processing of particles and cells via multilaminar flow streams. Anal Bioanal Chem 406:139–161
Villone MM, D’Avino G, Hulsen MA, Greco F, Maffettone PL (2013) Particle motion in square channel flow of a viscoelastic liquid: migration vs. secondary flows. J Non-Newton Fluid Mech 195:1–8
Xiang N, Dai Q, Ni Z (2016a) Multi-train elasto-inertial particle focusing in straight microfluidic channels. Appl Phys Lett 109:134101
Xiang N, Zhang X, Dai Q, Cheng J, Chen K, Ni Z (2016b) Fundamentals of elasto-inertial particle focusing in curved microfluidic channels. Lab Chip 16:2626–2635
Xuan X, Zhu J, Church C (2010) Particle focusing in microfluidic devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 9:1–16
Yan S, Zhang J, Yuan D, Li W (2017) Hybrid microfluidics combined with active and passive approaches for continuous cell separation. Electrophoresis 38:238–249
Yang S, Kim JY, Lee SJ, Lee SS, Kim JM (2011) Sheathless elasto-inertial particle focusing and continuous separation in a straight rectangular microchannel. Lab Chip 11:266–273
Yang S, Lee SS, Ahn SW, Kang K, Shim W, Lee G, Hyun K, Kim JM (2012) Deformability-selective particle entrainment and separation in a rectangular microchannel using medium viscoelasticity. Soft Matter 8:5011–5019
Yasuda K, Armstrong RC, Cohen RE (1981) Shear flow properties of concentrated solutions of linear and star branched polystyrenes. Rheol Acta 20:163–178
Yuan D, Zhang J, Yan S, Pan C, Alici G, Nguyen NT, Li W (2015) Dean-flow-coupled elasto-inertial three-dimensional particle focusing under viscoelastic flow in a straight channel with asymmetrical expansion–contraction cavity arrays. Biomicrofluid 9:044108
Yuan D, Zhao Q, Yan S, Tang SY, Alici G, Zhang J, Li W (2018) Recent progress of particle migration in viscoelastic fluids. Lab Chip. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7LC01076A
Zhang J, Yan S, Yuan D, Alici G, Nguyen NT, Warkiani ME, Li W (2016) Fundamentals and applications of inertial microfluidics: a review. Lab Chip 16:10–34
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by NSF under Grant CBET-1150670 and by Clemson University through a SEED Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Xuan, X. Fluid rheological effects on particle migration in a straight rectangular microchannel. Microfluid Nanofluid 22, 49 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-018-2070-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-018-2070-4