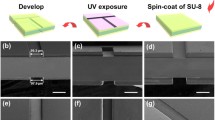
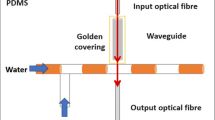
Abstract
Vertical optofluidic biosensors based on refractive index sensing promise highest sensitivities at smallest area footprint. Nevertheless, when it comes to large-scale fabrication and application of such sensors, cheap and robust platforms for sample preparation and supply are needed—not to mention the expected ease of use in application. We present an optofluidic sensor system using a cyclic olefin copolymer microfluidic chip as carrier and feeding supply for a complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor compatibly fabricated Ge PIN photodetector. Whereas typically only passive components of a sensor are located within the microfluidic channel, here the active device is directly exposed to the fluid, enabling top-illumination. The capability for detecting different refractive indices was verified by different fluids with subsequent recording of the optical responsivity. All components excel in their capability to be transferred to large-scale fabrication and further integration of microfluidic and sensing systems. The photodetector itself is intended to serve as a platform for further sophisticated collinear sensing approaches.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Augel L, Fischer IA, Dunbar LA, Bechler S, Berrier A, Etezadi D, Hornung F, Kostecki K, Ozdemir CI, Soler M, Altug H, Schulze J (2016) Plasmonic nanohole arrays on Si-Ge heterostructures: an approach for integrated biosensors. In: Proceedings SPIE 9724, plasmonics in biology and medicine XIII, 97240M. doi:10.1117/12.2212650
Beals M, Michel J, Liu JF, Ahn DH, Sparacin D, Sun R, Hong CY, Kimerling LC, Pomerene A, Carothers D, Beattie J, Kopa A, Apsel A, Rasras MS, Gill DM, Patel SS, Tu KY, Chen YK, White AE (2008) Process flow innovations for photonic device integration in CMOS. In: Proceedings SPIE 6898, silicon photonics III, 689804. doi:10.1117/12.774576
Blanco FJ, Agirregabiria M, Berganzo J, Mayora K, Elizalde J, Calle A, Dominguez C, Lechuga LM (2006) Microfluidic-optical integrated CMOS compatible devices for label-free biochemical sensing. J Micromech Microeng 16:1006–1016. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/16/5/018
Brolo AG, Gordon R, Leathem B, Kavanagh KL (2004) Surface plasmon sensor based on the enhanced light transmission through arrays of nanoholes in gold films. Langmuir 20:4813–4815. doi:10.1021/la0493621
Canalejas-Tejero V, Herranz S, Bellingham A, Moreno-Bondi MC, Barrios CA (2014) Passivated aluminum nanohole arrays for label-free biosensing applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:1005–1010. doi:10.1021/am404509f
Cetin AE, Coskun AF, Galarreta BC, Huang M, Herman D, Ozcan A, Altug H (2014) Handheld high-throughput plasmonic biosensor using computational on-chip imaging. Light Sci Appl 3:e122. doi:10.1038/lsa.2014.3
Chen S, Svedendahl M, Van Duyne RP, Käll M (2011) Plasmon-enhanced colorimetric ELISA with single molecule sensitivity. Nano Lett 11:1826–1830. doi:10.1021/nl2006092
Damborský P, Švitel J, Katrlík J (2016) Optical biosensors. Essays Biochem 60:91–100. doi:10.1042/EBC20150010
De Vos K, Bartolozzi I, Schacht E, Bienstman P, Baets R (2007) Silicon-on-Insulator microring resonator for sensitive and label-free biosensing. Opt Express 15:7610. doi:10.1364/OE.15.007610
Erickson D, Mandal S, Yang AHJ, Cordovez B (2008) Nanobiosensors: optofluidic, electrical and mechanical approaches to biomolecular detection at the nanoscale. Microfluid Nanofluid 4:33–52. doi:10.1007/s10404-007-0198-8
Escobedo C, Brolo AG, Gordon R, Sinton D (2010) Flow-through vs flow-over: analysis of transport and binding in nanohole array plasmonic biosensors. Anal Chem 82:10015–10020. doi:10.1021/ac101654f
Fischer IA, Augel L, Kropp T, Jitpakdeebodin S, Franz N, Oliveira F, Rolseth E, Maß T, Taubner T, Schulze J (2016) Ge-on-Si PIN-photodetectors with Al nanoantennas: the effect of nanoantenna size on light scattering into waveguide modes. Appl Phys Lett 108:071108. doi:10.1063/1.4942393
Guyot L, Blanchard-Dionne A-P, Patskovsky S, Meunier M (2011) Integrated silicon-based nanoplasmonic sensor. Opt Express 19:9962. doi:10.1364/OE.19.009962
Kasper E, Lyutovich K, Bauer M, Oehme M (1998) New virtual substrate concept for vertical MOS transistors. Thin Solid Films 336:319–322. doi:10.1016/S0040-6090(98)01317-0
Laplatine L, Al’Mrayat O, Luan E, Fang C, Rezaiezadeh S, Ratner DM, Cheung K, Dattner Y, Chrostowski L (2017) System-level integration of active silicon photonic biosensors. In: Proceedings SPIE 10061, microfluidics, bioMEMS, and medical microsystems XV, 100610I. doi:10.1117/12.2256068
Mazzotta F, Wang G, Hägglund C, Höök F, Jonsson MP (2010) Nanoplasmonic biosensing with on-chip electrical detection. Biosens Bioelectron 26:1131–1136. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2010.07.008
Patskovsky S, Meunier M (2013) Integrated Si-based nanoplasmonic sensor with phase-sensitive angular interrogation. Ann Phys 525:431–436. doi:10.1002/andp.201300078
Perino M, Pasqualotto E, De Toni A, Garoli D, Scaramuzza M, Zilio P, Ongarello T, Paccagnella A, Romanato F (2014) Development of a complete plasmonic grating-based sensor and its application for self-assembled monolayer detection. Appl Opt 53:5969. doi:10.1364/AO.53.005969
TOPAS Advanced Polymers (2017) Displays | TOPAS. http://www.topas.com/markets/optical/displays. Accessed 21 June 2017
Zang K, Zhang D, Huo Y, Chen X, Lu C-Y, Fei ET, Kamins TI, Feng X, Huang Y, Harris JS (2015) Microring bio-chemical sensor with integrated low dark current Ge photodetector. Appl Phys Lett 106:101111. doi:10.1063/1.4915094
Acknowledgements
This work was supported through funding by the University of Stuttgart and the Ministry of Science and Education of Baden-Wuerttemberg (RiSC). Furthermore, we appreciate the support by the Institute of Electron Devices and Circuits at Ulm University especially from S. Jenisch and S. Strehle.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Augel, L., Berkmann, F., Latta, D. et al. Optofluidic sensor system with Ge PIN photodetector for CMOS-compatible sensing. Microfluid Nanofluid 21, 169 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-017-2007-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-017-2007-3