Abstract
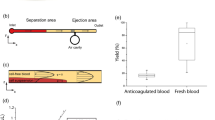
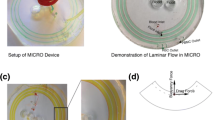
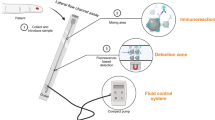
Red blood cell aggregation is an intrinsic property of red blood cells that form reversible stacked structures, also called rouleaux, under low shear rates. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), commonly performed in clinics, is an indirect inflammation screener and a prognostic test for diseases. We have recently developed a microfluidic system for rapid measurement of ESR from 40 µl whole blood employing the aggregation dynamics. In this work, we propose the use of an aggregation inducer, dextran polyglucose, for the preparation of multiple blood samples with differing aggregation dynamics. Using these samples, we characterized the performance of the system with three aggregation indices and under varying experimental conditions. Additionally, using the same underlying principle, we improved the system for ESR measurement using both venipuncture and fingerprick whole blood samples depending on the user needs. The results demonstrate that the system performs equally well with both samples, which validates the compatibility of the system for both laboratory and point-of-care applications where venous and capillary blood are the primary samples, respectively. The detailed characterization presented in this study legitimates the feasibility of the system for ultrafast and facile measurement of ESR in clinics and diverse off-laboratory settings.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand M, Rajagopal K (2004) A shear-thinning viscoelastic fluid model for describing the flow of blood. Int J Cardiovasc Med Sci 4:59–68
Andresdottir MB, Sigfusson N, Sigvaldason H, Gudnason V (2003) Erythrocyte sedimentation rate, an independent predictor of coronary heart disease in men and women the Reykjavik study. Am J Epidemiol 158:844–851
Andrews DA, Low PS (1999) Role of red blood cells in thrombosis. Curr Opin Hematol 6:76
Armstrong JK, Meiselman HJ, Wenby RB, Fisher TC (2001) Modulation of red blood cell aggregation and blood viscosity by the covalent attachment of Pluronic copolymers. Biorheology 38:239–247
Asakura S, Oosawa F (1954) On interaction between two bodies immersed in a solution of macromolecules. J Chem Phys 22:1255–1256
Barshtein G, Tamir I, Yedgar S (1998) Red blood cell rouleaux formation in dextran solution: dependence on polymer conformation. Eur Biophys J 27:177–181
Baskurt OK, Meiselman HJ (2013) Erythrocyte aggregation: basic aspects and clinical importance. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 53:23–37
Baskurt OK, Meiselman H, Kayar E (1998) Measurement of red blood cell aggregation in a “plate–plate” shearing system by analysis of light transmission. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 19:307–314
Baskurt OK, Uyuklu M, Hardeman MR, Meiselman HJ (2009) Photometric measurements of red blood cell aggregation: light transmission versus light reflectance. J Biomed Opt 14:054044
Baskurt OK, Uyuklu M, Meiselman HJ (2010) Time course of electrical impedance during red blood cell aggregation in a glass tube: comparison with light transmittance. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57:969–978
Baskurt O, Neu B, Meiselman HJ (2011a) Red blood cell aggregation. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Baskurt OK, Uyuklu M, Ozdem S, Meiselman HJ (2011b) Measurement of red blood cell aggregation in disposable capillary tubes. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 47:295–305
Bishop JJ, Popel AS, Intaglietta M, Johnson PC (2001) Rheological effects of red blood cell aggregation in the venous network: a review of recent studies. Biorheology 38:263–274
Bull BS, Brailsford JD (1972) The zeta sedimentation ratio. Blood 40:550–559
Cai D, Neyer A (2010) Cost-effective and reliable sealing method for PDMS (PolyDiMethylSiloxane)-based microfluidic devices with various substrates. Microfluid Nanofluidics 9:855–864
Carreau PJ, MacDonald IF, Bird RB (1968) A nonlinear viscoelastic model for polymer solutions and melts—II. Chem Eng Sci 23:901–911
Chien S (1975) Biophysical behavior of red cells in suspensions. Red Blood Cell 2:1031–1133
Chien S, Jan KM (1973) Red cell aggregation by macromolecules: roles of surface adsorption and electrostatic repulsion. J Supramol Struct 1:385–409
Chien S, Usami S, Dellenback RJ, Gregersen MI, Nanninga LB, Guest MM (1967) Blood viscosity: influence of erythrocyte aggregation. Science 157:829–831
Chin CD, Linder V, Sia SK (2007) Lab-on-a-chip devices for global health: past studies and future opportunities. Lab Chip 7:41–57
Chin CD, Linder V, Sia SK (2012) Commercialization of microfluidic point-of-care diagnostic devices. Lab Chip 12:2118–2134
Cokelet G (1987) The rheology and tube flow of blood. In: Skalak R, Chien S (eds) Handbook of bioengineering, vol 14. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 14.1–14.7
Cross MM (1965) Rheology of non-Newtonian fluids: a new flow equation for pseudoplastic systems. J Colloid Sci 20:417–437
Deng L, Barbenel J, Lowe G (1993) Influence of hematocrit on erythrocyte aggregation kinetics for suspensions of red blood cells in autologous plasma. Biorheology 31:193–205
Dima A, Opris D, Jurcut C, Baicus C (2016) Is there still a place for erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein in systemic lupus erythematosus? Lupus 25:1173–1179
Gambaruto AM, Janela J, Moura A, Sequeira A (2011) Sensitivity of hemodynamics in a patient specific cerebral aneurysm to vascular geometry and blood rheology. Math Biosci Eng MBE 8:409–423
Gillum RF, Mussolino ME, Makuc DM (1995) Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and coronary heart disease: the NHANES I epidemiologic follow-up study. J Clin Epidemiol 48:353–361
Gilmour D, Sykes A (1951) Westergren and Wintrobe methods of estimating ESR compared. Br Med J 2:1496
Hardwicke J, Squire J (1952) The basis of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Clin Sci 11:333–355
Hong T-F, Ju W-J, Wu M-C, Tai C-H, Tsai C-H, Fu L-M (2010) Rapid prototyping of PMMA microfluidic chips utilizing a CO2 laser. Microfluid Nanofluidics 9:1125–1133
Hysi E, Saha RK, Kolios MC (2012) On the use of photoacoustics to detect red blood cell aggregation. Biomed Opt Express 3:2326–2338
Isiksacan Z, Erel O, Elbuken C (2016a) A portable microfluidic system for rapid measurement of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Lab Chip 16:4682–4690
Isiksacan Z, Guler MT, Aydogdu B, Bilican I, Elbuken C (2016b) Rapid fabrication of microfluidic PDMS devices from reusable PDMS molds using laser ablation. J Micromech Microeng 26:035008
Jan K-M, Chien S (1973) Role of surface electric charge in red blood cell interactions. J Gen Physiol 61:638–654
Jiang H, Weng X, Li D (2011) Microfluidic whole-blood immunoassays. Microfluid Nanofluidics 10:941–964
Johansson JE, Sigurdsson T, Holmberg L, Bergstrom R (1992) Erythrocyte sedimentation rate as a tumor marker in human prostatic cancer. An analysis of prognostic factors in 300 population-based consecutive cases. Cancer 70:1556–1563
Li C, Liu C, Xu Z, Li J (2012) A power-free deposited microbead plug-based microfluidic chip for whole-blood immunoassay. Microfluid Nanofluidics 12:829–834
Lim H-J, Lee Y-J, Nam J-H, Chung S, Shin S (2010) Temperature-dependent threshold shear stress of red blood cell aggregation. J Biomech 43:546–550
Lominadze D, Joshua IG, Schuschke DA (1998) Increased erythrocyte aggregation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Hypertens 11:784–789
Manage DP, Morrissey YC, Stickel AJ, Lauzon J, Atrazhev A, Acker JP, Pilarski LM (2011) On-chip PCR amplification of genomic and viral templates in unprocessed whole blood. Microfluid Nanofluidics 10:697–702
Mehri R, Mavriplis C, Fenech M (2014) Design of a microfluidic system for red blood cell aggregation investigation. J Biomech Eng 136:064501
Merrill EW (1969) Rheology of blood. Physiol Rev 49:863–888
Mimouni Z (2016) The rheological behavior of human blood—comparison of two models open. J Biophys 6:29
Mogensen KB, Kutter JP (2009) Optical detection in microfluidic systems. Electrophoresis 30:S92–S100
Myers FB, Lee LP (2008) Innovations in optical microfluidic technologies for point-of-care diagnostics. Lab Chip 8:2015–2031
Nash GB, Meiselman HJ (1983) Effects of dextran and polyvinylpyrrolidone on red cell geometry and membrane elasticity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 416:255–262
Neu B, Meiselman HJ (2007) Red blood cell aggregation. In: Baskurt OK, Hardeman MR, Rampling MW, Meiselman HJ (eds) Handbook of hemorheology and hemodynamics, vol 69. IOS Press, Amsterdam, pp 114–136
Neu B, Wenby R, Meiselman HJ (2008) Effects of dextran molecular weight on red blood cell aggregation. Biophys J 95:3059–3065
Plebani M, De Toni S, Sanzari MC, Bernardi D, Stockreiter E (1998) The TEST 1 automated system: a new method for measuring the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Am J Clin Pathol 110:334–340
Rampling M, Meiselman H, Neu B, Baskurt O (2004) Influence of cell-specific factors on red blood cell aggregation. Biorheology 41:91–112
Shin S, Nam J-H, Hou J-X, Suh J-S (2009) A transient, microfluidic approach to the investigation of erythrocyte aggregation: the threshold shear-stress for erythrocyte disaggregation. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 42:117–125
Sia SK, Kricka LJ (2008) Microfluidics and point-of-care testing. Lab Chip 8:1982–1983
Singh AS, Atam V, Yathish BE, Das L, Koonwar S (2014) Role of erythrocyte sedimentation rate in ischemic stroke as an inflammatory marker of carotid atherosclerosis. J Neurosci Rural Pract 5:40
Sox HC, Liang MH (1986) Diagnostic decision: the erythrocyte sedimentation rate: guidelines for rational use. Ann Intern Med 104:515–523
Stokes GG (1851) On the effect of the internal friction of fluids on the motion of pendulums, vol 9. Pitt Press, Cambridge
Tilted E, Short E (1999) Clinical utility of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Am Fam Physician 60:1443–1450
Tuma RF, Durán WN, Ley K (2011) Microcirculation. Academic Press, London
Uyuklu M, Canpolat M, Meiselman HJ, Baskurt OK (2011) Wavelength selection in measuring red blood cell aggregation based on light transmittance. J Biomed Opt 16:117006–1170069
Viero Y, He Q, Mazenq L, Ranchon H, Fourniols J, Bancaud A (2012) Efficient prototyping of large-scale pdms and silicon nanofluidic devices using pdms-based phase-shift lithography. Microfluid Nanofluidics 12:465–473
Walburn FJ, Schneck DJ (1976) A constitutive equation for whole human blood. Biorheology 13:201–210
Westergren A (1921) Studies of the suspension stability of the blood in pulmonary tuberculosis1. Acta Med Scand 54:247–282
Wintrobe MM, Landsberg JW (1935) A standardized technique for the blood sedimentation test. Am J Med Sci 189:102–114
Xu X, Yu L, Chen Z (2008) Effect of erythrocyte aggregation on hematocrit measurement using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 55:2753–2758
Yager P, Domingo GJ, Gerdes J (2008) Point-of-care diagnostics for global health. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 10:107–144
Yang Y-A, Lin C-H, Wei Y-C (2014) Thread-based microfluidic system for detection of rapid blood urea nitrogen in whole blood. Microfluid Nanofluidics 16:887–894
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge support from The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey (TUBITAK project no. 213S127).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the topical collection “2016 International Conference of Microfluidics, Nanofluidics and Lab-on-a-Chip, Dalian, China” guest edited by Chun Yang, Carolyn Ren and Xiangchun Xuan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Isiksacan, Z., Asghari, M. & Elbuken, C. A microfluidic erythrocyte sedimentation rate analyzer using rouleaux formation kinetics. Microfluid Nanofluid 21, 44 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-017-1878-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-017-1878-7