Abstract
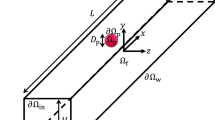
Thin deformable membranes are encountered in a number of microfluidics-based applications. These are often employed for enhancing sorting, mixing, cross-diffusion transport, etc. Microfluidic systems with deformable membranes can be better understood by employing simple models and efficient computational procedures. In this paper, we present a dissipative particle dynamics model to simulate the interaction between a deformable membrane and fluid flow in a two-dimensional microchannel. The membrane is modeled as a bead-spring system with both extensional and torsional springs to simulate extensional stiffness and bending rigidity, respectively. By performing detailed simulations on a membrane pinned at both ends and oriented parallel to the flow, we observe different steady state conformations. These membrane deflections are found to be relatively large for low bending stiffnesses and small for high stiffnesses. The membrane was found to exhibit a simple bowing out mode for high stiffness values and more complex conformations at lower stiffnesses.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertram CD (2008) Flow-induced oscillation of collapsed tubes and airway structures. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 163:256–265
Chakraborty D, Prakash JR, Friend J, Yeo L (2012) Fluid-structure interaction in deformable microchannels. Phys Fluids 24(102002):1–21
Charcosset C (2006) Membrane processes in biotechnology: an overview. Biotechnol Adv 24:482–492
Fan X, Phan-Thien N, Yong NT, Wu X, Xu D (2003) Microchannel flow of a macromolecular suspension. Phys Fluids 15:11–21
Goetz R, Lipowsky R (1998) Computer simulations of bilayer membranes: self-assembly and interfacial tension. J Chem Phys 108:7397–7409
Groot R, Warren P (1997) Dissipative particle dynamics: bridging the gap between atomistic and mesoscopic simulation. J Chem Phys 107:4423–4435
Heil M, Hazel AL (2011) Fluid-structure interaction in internal physiological flows. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 43(1):141–162
Heil M, Jensen OE (2003) Flows in deformable tubes and channels. Theoretical models and biological applications in flow past highly compliant boundaries and in collapsible tubes:15–50
Hoogerbrugge PG, Koelman JMVA (1992) Simulating microscopic hydrodynamic phenomena with dissipative particle dynamics. Europhys Lett 19:155–160
Huang L (2001) Viscous flutter of a finite elastic membrane in poiseuille flow. J Fluids Struct 15:1061–1088
Huh D, Matthews BD, Mammoto A, Montoya-Zavala M, Hsin HY, Ingber DE (2010) Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip. Science 328:1662–1668
Irving JH, Kirkwood JG (1950) The statistical mechanics of transport processes. IV. The equation of hydrodynamics. J Chem Phys 18:817
Jensen OE (1990) Instabilities of flow in a collapsed tube. J Fluid Mech 220:623–659
Kamm RD, Shapiro AH (1979) Unsteady flow in a collapsible tube subjected to external pressure or body forces. J Fluid Mech 95:1–78
Karniadakis GE, Beskok A (2002) Micro flows: fundamentals and simulation. Springer, New York
Krindel P, Silberberg A (1979) Flow through gel-walled tubes. J Colloid Interface Sci 71:39–50
Kumar A, Asaka Y, Nada EA, Manfred K, Faghri M (2009) From dissipative particle dynamics scales to physical scales: a course-graining study for water flow in micro channel. Microfluid-Nanofluid 7:467–477
Le DV, White J, Peraire J, Lim KM, Khoo BC (2009) An implicit immersed boundary method for three-dimensional fluid-membrane interactions. J Comput Phys 228:8427–8445
Liang SJ, Neitzeli GP, Aidun CK (1997) Finite element computations for unsteady fluid and elastic membrane interaction problems. Int J Numer Meth Fluids 24:1091–1110
Lipowsky R (1992) The physics of flexible membranes. Adv Solid State Phys 32:19–34
Luo XY, Pedley TJ (1996) A numerical simulation of unsteady flow in a 2-D collapsible channel. J Fluid Mech 314:191–225
Moeendarbary E, Ng TY, Zangeneh M (2009) Dissipative particle dynamics: introduction, methodology and complex fluid applications-a review. Int J of Appl Mech 1(4):737–763
Newman BG, Paidoussis MP (1991) The stability of two-dimensional membranes in streaming flow. J Fluids Struct 5:443–454
Noguchi H (2009) Membrane simulation models from nanometer to micrometer scale. J Phys Soc Jpn 78:041007
Paidoussis MP (2002) Fluid-structure interactions. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Pan W, Pivkin IV, Karniadakis GE (2008) Single-particle hydrodynamics in DPD: a new formulation. Europhys Lett 84:10012-p1–10012-p6
Pan W, Caswell B, Karniadakis GE (2010) A low-dimensional model for the red blood cell. Soft Matter 6(18):4366–4376. doi:10.1039/C0SM00183J
Pan W, Fedosov DA, Karniadakis GE, Caswell B (2008) Hydrodynamic interactions for single dissipative-particle-dynamics particles and their clusters and filaments. Phys Rev E 78(4):046706
Pedley TJ, Luo XY (1998) Modelling flow and oscillations in collapsible tubes. Theor Computat Fluid Dyn 10:277–294
Ranjith SK, Patnaik BSV, Vedantam S (2013a) No-slip boundary condition in finite-size dissipative particle dynamics. J Comput Phys 232:174–188
Ranjith SK, Patnaik BSV, Vedantam S (2013b) Hydrodynamics of the developing region in hydrophobic microchannels: a dissipative particle dynamics study. Phy Rev E 87(3):033303
Ranjith SK, Vedantam S, Patnaik BSV (2014a) Hydrodynamics of flow through microchannels with hydrophobic strips. Microfluid-Nanofluid 19:547–556
Ranjith SK, Patnaik BSV, Vedantam S (2014b) Transport of DNA in hydrophobic microchannels: a dissipative particle dynamics simulation. Soft Matter 10:4184–4191
Sajeesh P, Sen AK (2013) Particle separation and sorting in microfluidic devices: a review. Microfluid-Nanofluid 17:1–52
Shelley MJ, Zhang J (2010) Flapping and bending bodies interacting with fluid flows. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 43(1):449–465
Sygulski R (2007) Stability of membrane in low subsonic flow. Int J Nonlinear Mech 42:196–202
Thaokar RM, Kumaran V (2002) Stability of fluid flow past a membrane. J Fluid Mech 472:29–50
Whitesides G (2006) The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 442:368–373
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anand, D.V., Vedantam, S. & Patnaik, B.S.V. Dissipative particle dynamics simulation of shear flow in a microchannel with a deformable membrane. Microfluid Nanofluid 20, 161 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-016-1819-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-016-1819-x