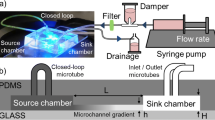
Abstract
Generation of concentration gradients of reactive molecules is of fundamental importance for many applications including biology, pharmaceutical and chemical engineering. By numerically simulating the flow behaviour, we reveal the possible factors that cause significant error in the gradients generated by the conventional universal microfluidic gradient generator (MGG) device reported previously. Based on these computational analyses, we optimize the geometrical design of the conventional 2-inlet MGG devices and improve the accuracy of the generated gradients. Moreover, we innovatively propose a 3-inlet MGG design showing desirable accuracy and versatility on creating various gradient profiles using the one single device. We further demonstrate our numerical simulation by fabricating the MGG devices by soft lithography and experimentally produce concentration gradients of diverse power functions. In general, the current study substantially improves the performance of universal MGG devices, which can serve as powerful tools for widespread applications in biology and chemistry.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe Y, Kamiya K, Osaki T, Sasaki H, Kawano R, Miki N, Takeuchi S (2015) Nonlinear concentration gradients regulated by the width of channels for observation of half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC 50) of transporter proteins. Analyst 140:5557–5562
Ahmed T, Shimizu TS, Stocker R (2010) Bacterial chemotaxis in linear and nonlinear steady microfluidic gradients. Nano Lett 10:3379–3385
Ahmed D, Chan CY, Lin SCS, Muddana HS, Nama N, Benkovic SJ, Huang TJ (2013) Tunable, pulsatile chemical gradient generation via acoustically driven oscillating bubbles. Lab Chip 13:328–331
Atencia J, Cooksey GA, Locascio LE (2012) A robust diffusion-based gradient generator for dynamic cell assays. Lab Chip 12:309–316
Brett ME, DeFlorio R, Stone DE, Eddington DT (2012) A microfluidic device that forms and redirects pheromone gradients to study chemotropism in yeast. Lab Chip 12:3127–3134
Chen CY, Wo AM, Jong DS (2012) A microfluidic concentration generator for dose-response assays on ion channel pharmacology. Lab Chip 12:794–801
Culbertson CT, Jacobson SC, Ramsey JM (2002) Diffusion coefficient measurements in microfluidic devices. Talanta 56:365–373
Dertinger SKW, Chiu DT, Jeon NL, Whitesides GM (2001) Generation of gradients having complex shapes using microfluidic networks. Anal Chem 73:1240–1246
Destgeer G, Im S, Ha BH, Jung JH, Ansari MA, Sung HJ (2014) Adjustable, rapidly switching microfluidic gradient generation using focused travelling surface acoustic waves. Appl Phys Lett 104:023506
Friedrich D, Please CP, Melvin T (2012) Design of novel microfluidic concentration gradient generators suitable for linear and exponential concentration ranges. Chem Eng J 193:296–303
Hu Y, Zhang X, Wang W (2011) Simulation of the generation of solution gradients in microfluidic systems using the lattice Boltzmann method. Ind Eng Chem Res 50:13932–13939
Irimia D, Geba DA, Toner M (2006) Universal microfluidic gradient generator. Anal Chem 78:3472–3477
Jain M, Yeung A, Nandakumar K (2010) Induced charge electro-osmotic concentration gradient generator. Biomicrofluidics 4:014110
Kim S, Kim HJ, Jeon NL (2010) Biological applications of microfluidic gradient devices. Integr Biol 2:584–603
Lin B, Levchenko A (2015) Spatial manipulation with microfluidics. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 3:39
Lin F, Saadi W, Rhee SW, Wang SJ, Mittal S, Jeon NL (2004) Generation of dynamic temporal and spatial concentration gradients using microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 4:164–167
Mazutis L, Gilbert J, Ung WL, Weitz DA, Griffiths AD, Heyman JA (2013) Single-cell analysis and sorting using droplet-based microfluidics. Nat Protoc 8:870–891
Saadi W, Rhee SW, Lin F, Vahidi B, Chung BG, Jeon NL (2007) Generation of stable concentration gradients in 2D and 3D environments using a microfluidic ladder chamber. Biomed Microdevices 9:627–635
Sackmann EK, Fulton AL, Beebe DJ (2014) The present and future role of microfluidics in biomedical research. Nature 507:181–189
Sahai R, Cecchini M, Klingauf M, Ferrari A, Martino C, Castrataro P, Lionetti V, Menciassi A, Beltram F (2011) Microfluidic chip for spatially and temporally controlled biochemical gradient generation in standard cell-culture Petri dishes. Microfluid Nanofluid 11:763–771
Sant S, Hancock MJ, Donnelly JP, Iyer D, Khademhosseini A (2010) Biomimetic gradient hydrogels for tissue engineering. Can J Chem Eng 88:899–911
Toh AGG, Wang ZP, Yang C, Nguyen NT (2014) Engineering microfluidic concentration gradient generators for biological applications. Microfluid Nanofluid 16:1–18
Wang H, Chen CH, Xiang Z, Wang M, Lee C (2015) A convection-driven long-range linear gradient generator with dynamic control. Lab Chip 15:1445–1450
Wu MH, Huang SB, Lee GB (2010) Microfluidic cell culture systems for drug research. Lab Chip 10:939–956
Xia Y, Whitesides GM (1998) Soft lithography. Annu Rev Mater Sci 28:153–184
Xu C, Poh YKC, Roes I, O’Cearbhaill ED, Matthiesen ME, Mu L, Seung YY, Nieves DM, Irimia D, Karp JM (2012) A portable chemotaxis platform for short and long term analysis. PLoS one 7:e44995
Yang CG, Wu YF, Xu ZR, Wang JH (2011) A radial microfluidic concentration gradient generator with high-density channels for cell apoptosis assay. Lab Chip 11:3305–3312
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51373153 and 51503208), National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2015CB057301), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (No. DUT15RC(3)113), the National Science Foundation (DMR-1310266) and the Harvard Materials Research Science and Engineering Center (DMR-1420570).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Z., Huang, X., Wang, P. et al. Optimization and development of a universal flow-based microfluidic gradient generator. Microfluid Nanofluid 20, 89 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-016-1749-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-016-1749-7