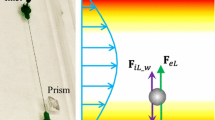
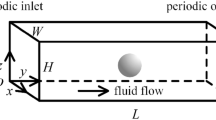
Abstract
Micro-/nanoparticle-based systems are regarded as one of the possible candidates due to the engineerability and multifunctionality to maximize the accumulation of the nano-/microparticle-based drug delivery system on the target. Recent advances in nanotechnology enable the fabrication of diverse particle shapes from simple spherical particles to more complex shapes. The particle dynamics in blood flow and endocytosis characteristics of non-spherical particles change as the non-sphericity effect increases. We used a numerical approach to investigate the particle dynamics in linear shear flow near a wall. We examined the dynamics of slender cylindrical particles with aspect ratio γ = 5.0 in terms of particle trajectory, velocity, and force variation for different Stokes numbers over time. We identified the rotating inertia of particle near a wall as the source of inertial migration toward the wall. The drift velocity of slender cylindrical particles is comparable to that of discoidal particles. We discuss the possibilities and limitations of using slender cylindrical particles as a drug delivery system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriani G, de Tullio MD, Ferrari M, Hussain F, Pascazio G, Liu X, Decuzzi P (2012) The preferential targeting of the diseased microvasculature by disk-like particles. Biomaterials 33:5504–5513
Carlos TM, Harlan JM (1994) Leukocyte-endothelial adhesion molecules. Blood 84:2068
Champion JA, Mitragotri S (2006) Role of target geometry in phagocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:4930–4934
Charoenphol P, Huang RB, Eniola-Adefeso O (2010) Potential role of size and hemodynamics in the efficacy of vascular-targeted spherical drug carriers. Biomaterials 31:1392–1402
Charoenphol P, Onyskiw PJ, Carrasco-Teja M, Eniola-Adefeso O (2012) Particle-cell dynamics in human blood flow: implications for vascular-targeted drug delivery. J Biomech 45:2822–2828
de Faria PCB, dos Santos LI, Coelho JP, Ribeiro HB, Pimenta MA, Ladeira LO, Gomes DA, Furtado CA, Gazzinelli RT (2014) Oxidized multiwalled carbon nanotubes as antigen delivery system to promote superior CD8(+) T cell response and Protection against cancer. Nano Lett 14:5458–5470
Decuzzi P, Gentile F, Granaldi A, Curcio A, Causa F, Indolfi C, Netti P, Ferrari M (2007) Flow chamber analysis of size effects in the adhesion of spherical particles. Int J Nanomed 2:689–696
Decuzzi P, Pasqualini R, Arap W, Ferrari M (2009) Intravascular delivery of particulate systems: Does geometry really matter? Pharm Res 26:235–243
Decuzzi P, Godin B, Tanaka T, Lee SY, Chiappini C, Liu X, Ferrari M (2010) Size and shape effects in the biodistribution of intravascularly injected particles. J Control Release 141:320–327
Einarsson J, Candelier F, Lundell F, Angilella J, Mehlig B (2015) Effect of weak fluid inertia upon Jeffery orbits. Phys Rev E 91:041002
Ferrari M (2005) Cancer nanotechnology: opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Cancer 5:161–171
Gavze E, Shapiro M (1997) Particles in a shear flow near a solid wall: effect of nonsphericity on forces and velocities. Int J Multiph Flow 23:155–182
Gentile F, Chiappini C, Fine D, Bhavane RC, Peluccio MS, Cheng MM, Liu X, Ferrari M, Decuzzi P (2008) The effect of shape on the margination dynamics of non-neutrally buoyant particles in two-dimensional shear flows. J Biomech 41:2312–2318
Godin B, Driessen WHP, Proneth B, Lee SY, Srinivasan S, Rumbaut R, Arap W, Pasqualini R, Ferrari M, Decuzzi P (2010) An integrated approach for the rational design of nanovectors for biomedical imaging and therapy. Tissue Specifc Vasc Endothel Signals Vector Targeting Pt B 69:31–64
Goldman AJ, Cox GR, Brenner H (1967a) Slow viscous motion of a sphere parallel to a plane wall I. Motion through a quiescent fluid. Chem Eng Sci 22:637–651
Goldman AJ, Cox GR, Brenner H (1967b) Slow viscous motion of a sphere parallel to a plane wall II. Couette flow. Chem Eng Sci 22:653–660
Gratton SE, Ropp PA, Pohlhaus PD, Luft JC, Madden VJ, Napier ME, DeSimone JM (2008) The effect of particle design on cellular internalization pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:11613–11618
Gu F, Zhang L, Teply BA, Mann N, Wang A, Radovic-Moreno AF, Langer R, Farokhzad OC (2008) Precise engineering of targeted nanoparticles by using self-assembled biointegrated block copolymers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:2586–2591
Herant M, Heinrich V, Dembo M (2006) Mechanics of neutrophil phagocytosis: experiments and quantitative models. J Cell Sci 119:1903–1913
Hossain SS, Zhang Y, Liang X, Hussain F, Ferrari M, Hughes TJ, Decuzzi P (2013) In silico vascular modeling for personalized nanoparticle delivery. Nanomedicine (Lond) 8:343–357
Huang RB, Eniola-Adefeso O (2012) Shear stress modulation of IL-1beta-induced E-selectin expression in human endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 7:e31874
Hyun JY, Lee SY (2015) A numerical study on the dynamics of nano/micro-sized prismatic particles in linear shear flow near a wall. J Comput Theor Nanosci 12:5685–5692
Karimi M, Solati N, Amiri M, Mirshekari H, Mohamed E, Taheri M, Hashemkhani M, Saeidi A, Estiar MA, Kiani P, Ghasemi A, Basri SM, Aref AR, Hamblin MR (2015) Carbon nanotubes part I: preparation of a novel and versatile drug-delivery vehicle. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 12:1071–1087
Lee SY, Ferrari M, Decuzzi P (2009a) Design of bio-mimetic particles with enhanced vascular interaction. J Biomech 42:1885–1890
Lee SY, Ferrari M, Decuzzi P (2009b) Shaping nano-/micro-particles for enhanced vascular interaction in laminar flows. Nanotechnology 20:495101
Lee TR, Choi M, Kopacz AM, Yun SH, Liu WK, Decuzzi P (2013) On the near-wall accumulation of injectable particles in the microcirculation: smaller is not better. Sci Rep 3:2079
Ley K, Laudanna C, Cybulsky MI, Nourshargh S (2007) Getting to the site of inflammation: the leukocyte adhesion cascade updated. Nat Rev Immunol 7:678–689
Onyskiw PJ, Eniola-Adefeso O (2013) Effect of PEGylation on ligand-based targeting of drug carriers to the vascular wall in blood flow. Langmuir 29:11127–11134
Perry JL, Reuter KG, Kai MP, Herlihy KP, Jones SW, Luft JC, Napier M, Bear JE, DeSimone JM (2012) PEGylated PRINT nanoparticles: the impact of PEG density on protein binding, macrophage association, biodistribution, and pharmacokinetics. Nano Lett 12:5304–5310
Pozrikidis C (2006) Flipping of an adherent blood platelet over a substrate. J Fluid Mech 568:161–172
Rieger C, Kunhardt D, Kaufmann A, Schendel D, Huebner D, Erdmann K, Propping S, Wirth MP, Schwenzer B, Fuessel S, Hampel S (2015) Characterization of different carbon nanotubes for the development of a mucoadhesive drug delivery system for intravesical treatment of bladder cancer. Int J Pharm 479:357–363
Rolland JP, Maynor BW, Euliss LE, Exner AE, Denison GM, DeSimone JM (2005) Direct fabrication and harvesting of monodisperse, shape-specific nanobiomaterials. J Am Chem Soc 127:10096–10100
Rosén T, Lundell F, Aidun C (2014) Effect of fluid inertia on the dynamics and scaling of neutrally buoyant particles in shear flow. J Fluid Mech 738:563–590
Rosén T, Do-Quang M, Aidun C, Lundell F (2015) The dynamical states of a prolate spheroidal particle suspended in shear flow as a consequence of particle and fluid inertia. J Fluid Mech 771:115–158
Sakamoto J, Annapragada A, Decuzzi P, Ferrari M (2007) Antibiological barrier nanovector technology for cancer applications. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 4:359–369
Schipper ML, Iyer G, Koh AL, Cheng Z, Ebenstein Y, Aharoni A, Keren S, Bentolila LA, Li J, Rao J, Chen X, Banin U, Wu AM, Sinclair R, Weiss S, Gambhir SS (2009) Particle size, surface coating, and PEGylation influence the biodistribution of quantum dots in living mice. Small 5:126–134
Serda RE, Gu J, Burks JK, Ferrari K, Ferrari C, Ferrari M (2009) Quantitative mechanics of endothelial phagocytosis of silicon microparticles. Cytom A 75:752–760
Shapiro M, Gavze E (1998) Motion of inertial spheroidal particles in a shear flow near a solid wall with special application to aerosol transport in microgravity. J Fluid Mech 371:59–79
Shinde Patil VR, Campbell CJ, Yun YH, Slack SM, Goetz DJ (2001) Particle diameter influences adhesion under flow. Biophys J 80:1733–1743
Tasciotti E, Liu XW, Bhavane R, Plant K, Leonard AD, Price BK, Cheng MMC, Decuzzi P, Tour JM, Robertson F, Ferrari M (2008) Mesoporous silicon particles as a multistage delivery system for imaging and therapeutic applications. Nat Nanotechnol 3:151–157
Thompson AJ, Mastria EM, Eniola-Adefeso O (2013) The margination propensity of ellipsoidal micro/nanoparticles to the endothelium in human blood flow. Biomaterials 34:5863–5871
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D.K., Hyun, J.Y., Kim, S.C. et al. Inertial effects on cylindrical particle migration in linear shear flow near a wall. Microfluid Nanofluid 20, 75 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-016-1742-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-016-1742-1