Abstract
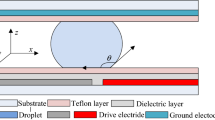
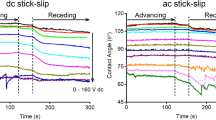
Electrowetting on dielectric is a phenomenon in which the shape and apparent contact angle of a droplet changes when an electric field is applied across the droplet interface. If the field is asymmetric with respect to the droplet, then a net force can be applied to the droplet. In this work, we have measured the electrowetting force by confining the droplet shape beneath a glass plate and measuring the force on the plate. The force was measured as a function of voltage for a range of fluids with different surface energy. Measured forces show excellent agreement with predictions based on the Young–Lippmann equation with measured contact angles. Results also show that the electrowetting force is independent of fluid surface energy below saturation but that the peak force is proportional to the surface tension. This work shows that lowering the surface energy of the fluid can induce larger contact angle change under the same voltage, but it has no beneficial impact on the actuation force in droplet-based actuators. In contrast, velocity tests with deformable droplets show higher speeds for lower surface energy fluids, even above their saturation voltage. However, when the droplet’s shape is restrained, the highest velocity is achieved with high surface energy fluids due to the larger electrowetting actuation forces applied.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
’t Mannetje D, Banpurkar A, Koppelman H, Duits MHG, van den Ende D, Mugele F (2013) Electrically tunable wetting defects characterized by a simple capillary force sensor. Langmuir ACS J Surf Colloids 29(31):9944–9949. doi:10.1021/la4015724
Banpurkar AG, Nichols KP, Mugele F (2008) Electrowetting-based microdrop tensiometer. Langmuir ACS J Surf Colloids 24(19):10549–10551. doi:10.1021/la801549p
Berthier J, Dubois P, Clementz P, Claustre P, Peponnet C, Fouillet Y (2007) Actuation potentials and capillary forces in electrowetting based microsystems. Sens Actuators A 134(2):471–479. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2006.04.050
Blake TD (2006) The physics of moving wetting lines. J Colloid Interface Sci 299(1):1–13. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2006.03.051
Blake TD, Clarke A, Stattersfield EH (2000) An investigation of electrostatic assist in dynamic wetting. Langmuir 16(6):2928–2935. doi:10.1021/la990973g
Chen JH, Hsieh WH (2006) Electrowetting-induced capillary flow in a parallel-plate channel. J Colloid Interface Sci 296(1):276–283. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2005.08.048
Chevalliot S, Kuiper S, Heikenfeld J (2012) Experimental validation of the invariance of electrowetting contact angle saturation. J Adhes Sci Technol. doi:10.1163/156856111X599580
Cho SK, Moon H, Kim C-J (2003) Creating, transporting, cutting, and merging liquid droplets by electrowetting-based actuation for digital microfluidic circuits. J Microelectromech Syst 12(1):70–80. doi:10.1109/JMEMS.2002.807467
Crane NB, Mishra P, Volinsky AA (2010) Characterization of electrowetting processes through force measurements. Rev Sci Instrum 81(4):043902. doi:10.1063/1.3373945
Decamps C, De Coninck J (2000) Dynamics of spontaneous spreading under electrowetting conditions. Langmuir 16(26):10150–10153. doi:10.1021/la000590e
Guan L, Qi G, Liu S, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Yang Y, Wang C (2009) Nanoscale electrowetting effects studied by atomic force microscopy. J Phys Chem C 113(2):661–665. doi:10.1021/jp806538r
Hayes RA, Feenstra BJ (2003) Video-speed electronic paper based on electrowetting. Nature 425(6956):383–385. doi:10.1038/nature01988
Jones TB (2005) An electromechanical interpretation of electrowetting. J Micromech Microeng 15(6):1184–1187. doi:10.1088/0960-1317/15/6/008
Jones TB (2009) More about the electromechanics of electrowetting. Mech Res Commun 36(1):2–9. doi:10.1016/j.mechrescom.2008.08.012
Jones TB, Fowler JD, Chang YS, Kim C-J (2003) Frequency-based relationship of electrowetting and dielectrophoretic liquid microactuation. Langmuir 19(18):7646–7651. doi:10.1021/la0347511
Khodayari M, Carballo J, Crane NB (2012) A material system for reliable low voltage anodic electrowetting. Mater Lett 69(February):96–99. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2011.11.060
Lu H-W, Glasner K, BertozzI AL, Kim C-J (2007) A diffuse-interface model for electrowetting drops in a Hele-Shaw cell. J Fluid Mech 590:411–35. http://journals.cambridge.org/abstract_S0022112007008154
Manjeet D, Heikenfeld J, Weekamp W, Kuiper S (2011) Electrowetting without electrolysis on self-healing dielectrics. Langmuir ACS J Surf Colloids 27(9):5665–5670. doi:10.1021/la1051468
Mugele F, Baret J-C (2005) Electrowetting: from basics to applications. J Phys Condens Matter 17(28):R705–R774. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/17/28/R01
Nelson WC, Kim C-JCJ (2012) Droplet actuation by electrowetting-on-dielectric (EWOD): a review. J Adhes Sci Technol 26(12–17):1747–1771. doi:10.1163/156856111X599562
Nelson WC, Sen P, Kim C-JCJ (2011) Dynamic contact angles and hysteresis under electrowetting-on-dielectric. Langmuir ACS J Surf Colloids 27(16):10319–10326. doi:10.1021/la2018083
Papathanasiou AG, Boudouvis AG (2005) Manifestation of the connection between dielectric breakdown strength and contact angle saturation in electrowetting. Appl Phys Lett 86(16):164102. doi:10.1063/1.1905809
Ren Hong, Fair Richard B, Pollack Michael G, Shaughnessy Edward J (2002) Dynamics of electro-wetting droplet transport. Sens Actuators B Chem 87(1):201–206. doi:10.1016/S0925-4005(02)00223-X
Sen P (2009) A fast liquid-metal droplet microswitch using EWOD-driven contact-line sliding. J Microelectromech Syst 18(1):174–185. doi:10.1109/JMEMS.2008.2008624
Shabani Roxana, Cho HJ (2013) Flow rate analysis of an EWOD-based device: How important are wetting-line pinning and velocity effects? Microfluid Nanofluid 15(5):587–597. doi:10.1007/s10404-013-1184-y
Shikhmurzaev YD (1993) The moving contact line on a smooth solid surface. Int J Multiph Flow 19(4):589–610. doi:10.1016/0301-9322(93)90090-H
Smith NR, Abeysinghe DC, Haus JW, Heikenfeld J (2006) Agile wide-angle beam steering with electrowetting microprisms. Opt Express 14(14):6557. doi:10.1364/OE.14.006557
Snoeijer JH, Andreotti B (2013) Moving contact lines: scales, regimes, and dynamical transitions. Annu Rev Fluid Mech 45(1):269–292. doi:10.1146/annurev-fluid-011212-140734
Song JH, Evans R, Lin Y-Y, Hsu B-N, Fair RB (2008) A scaling model for electrowetting-on-dielectric microfluidic actuators. Microfluid Nanofluid 7(1):75–89. doi:10.1007/s10404-008-0360-y
Takei A, Matsumoto K, Shomoyama I (2010) Capillary motor driven by electrowetting. Lab Chip 10(14):1781–1786. doi:10.1039/c001211d
Vasudev A, Zhe J (2008) A capillary microgripper based on electrowetting. Appl Phys Lett 93(10):103503. doi:10.1063/1.2978402
Verheijen HJJ, Prins MWJ (1999) Contact angles and wetting velocity measured electrically. Rev Sci Instrum 70(9):3668. doi:10.1063/1.1149976
Yoon E (2001) A micropump driven by continuous electrowetting actuation for low voltage and low power operations. In: Technical digest. MEMS 2001. 14th IEEE international conference on micro electro mechanical systems (Cat. No. 01CH37090), IEEE, pp 487–490. doi:10.1109/MEMSYS.2001.906585
Acknowledgments
The work is supported in part by the National Science Foundation thorough Grant No. CMMI-113075.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, Q., Capecci, D.E. & Crane, N.B. Electrowetting force and velocity dependence on fluid surface energy. Microfluid Nanofluid 19, 181–189 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1563-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-015-1563-7