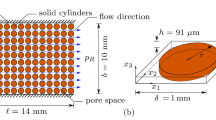
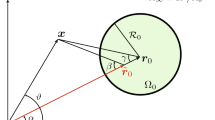
Abstract
For tight porous media, the permeability measured from the Darcy test is only an apparent permeability because the Klinkenberg effect occurs when the Knudsen number is high. To determine the intrinsic permeability, we need a simple and rigorous permeability correction that is valid in the entire flow regime. Thus, introducing a non-Maxwellian slip boundary condition, we develop the bivelocity hydrodynetics in this paper. The bivelocity hydrodynetics is defined by combining bivelocity hydrodynamics with kinetic theories. In the framework of the bivelocity hydrodynetics, we derive a simple and rigorous permeability correction based on the analytical solutions of rarefied gas flows in micro- and nano-tubes. After compared with conventional solutions and experiments, the present solutions are validated in the entire flow regime. Moreover, the validation is also a clear proof for the bivelocity theories.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beskok A, Karniadakis GE (1999) A model for flows in channels, pipes, and ducts at micro and nano scales. Microscale Thermophys Eng 3:43–77. doi:10.1080/108939599199864
Brenner H (2005) Kinematics of volume transport. Phys A 349:11–59. doi:10.1016/j.physa.2004.10.033
Brenner H (2011) Beyond the no-slip boundary condition. Phys Rev E 84:046309. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.84.046309
Brenner H (2012) Beyond Navier–Stokes. Int J Eng Sci 54:67–98. doi:10.1016/j.ijengsci.2012.01.006
Burnett D (1936) The distribution of molecular velocities and the mean motion in a non-uniform gas. Proc Lond Math Soc 2:382–435. doi:10.1112/plms/s2-40.1.382
Cercignani C, Sernagiotto F (1966) Cylindrical Poiseuille flow of a rarefied gas. Phys Fluids 9:40–44. doi:10.1063/1.1761530
Chakraborty S, Durst F (2007) Derivations of extended Navier–Stokes equations from upscaled molecular transport considerations for compressible ideal gas flows: towards extended constitutive forms. Phys Fluids 19:088104. doi:10.1063/1.2759531
Civan F (2010) Effective correlation of apparent gas permeability in tigh porous media. Transp Porous Med 82:375–384. doi:10.1007/s11242-009-9432-z
Dadzie SK, Brenner H (2012) Predicting enhanced mass flow rates in gas microchannels using nonkinetic models. Phys Rev E 86:036318. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.86.036318
Dadzie SK, Reese JM (2012) Analysis of the thermomechanical inconsistency of some extended hydrodynamic models at high Knudsen number. Phys Rev E 85:088104. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.85.041202
Darcy H (1856) Les fontaines publiques de la ville de Dijon. Victor Dalmont, Paris
Dongari N, Durst F, Chakraborty S (2010) Predicting microscale gas flows and rarefaction effects through extended Navier–Stokes–Fourier equations from phoretic transport considerations. Microfluid Nanofluid 9:831–846. doi:10.1007/s10404-010-0604-5
Freytag I, Roque WL (2013) Influence of granular packing on porosity and tortuosity. Phys Rev E 88:023011. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.88.023011
Grad H (1949) On the kinetic theory of rarefied gases. Commun Pure Appl Math 2:331–407. doi:10.1002/cpa.3160020403
Graur IA, Méeolans JG, Zeitoun DE (2006) Analytical and numerical description for isothermal gas flows in microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 2:64–77. doi:10.1007/s10404-005-0055-6
Green MS (1954) Markoff random processes and the statistical mechanics of time-dependent phenomena. II. Irreversible processes in fluids. J Chem Phys 22:398–413. doi:10.1063/1.1740082
Greenshields CJ, Reese JM (2007) The structure of shock waves as a test of brenner’s modifications to the Navier–Stokes equations. J Fluid Mech 580:407–429. doi:10.1017/S0022112007005575
Klinkenberg LJ (1941) The permeability of porous media to liquid and gases. API Drilling and Production Practices, New York, pp 200–213
Knudsen M (1909) Die gesetze der molekularströmung und der inneren reibungsströmung der gase durch röhren. Ann Phys 333:75–130. doi:10.1002/andp.19093330106
Kubo R (1957) Statistical-mechanical theory of irreversible processes. I. General theory and simple applications to magnetic and conduction problems. J Phys Soc Jpn 12:570–586. doi:10.1143/JPSJ.12.570
Lo SS, Loyalka SK (1982) An efficient computation of near-continuum rarefied gas flows. J Appl Math Phys (ZAMP) 33:419–424. doi:10.1007/BF00944451
Loeb LB (1927) The kinetic theory of gases. McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc., New York
Loyalka SK, Hamoodi SA (1990) Poiseuille flow of a rarefied gas in a cylindrical tube: solution of linearized Boltzmann equation. Phys Fluids A 2:2061–2065. doi:10.1063/1.857681
Lv Q, Liu X, Wang E, Wang S (2013) Analytical solution to predicting gaseous mass flow rates of microchannels in a wide range of Knudsen numbers. Phys Rev E 88:013007. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.88.013007
Marino L (2009) Experiments on rarefied gas flows through tubes. Microfluid Nanofluid 6:109–119. doi:10.1007/s10404-008-0311-7
Maxwell JC (1879) On stresses in rarefied gases arising from inequalities of temperature. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 170:231–256. doi:10.1098/rstl.1879.0067
Pollard WG, Present RD (1948) On gaseous self-diffusion in long capillary tubes. Phys Rev 73:762–774. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.73.762
Reynolds O (1879) On certain dimensional properties of matter in the gaseous state. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 170:727–845. doi:10.1098/rstl.1879.0078
Siewert CE (2000) Poiseuille and thermal-creep flow in a cylindrical tube. J Comput Phys 160:470–480. doi:10.1006/jcph.2000.6464
Struchtrup H, Torrilhon M (2003) Regularization of Grads 13 moment equations: derivation and linear analysis. Phys Fluids 15:2668–2680. doi:10.1063/1.1597472
Tang GH, Tao WQ, He YL (2005) Gas slippage effect on microscale porous flow using the lattice Boltzmann method. Phys Rev E 72:056301. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.72.056301
Tison SA (1993) Experimental data and theoretical modeling of gas flows through metal capillary leaks. Vacuum 44:1171–1175. doi:10.1016/0042-207X(93)90342-8
Velasco AE, Friedman SG, Pevarnik M, Siwy ZS, Taborek P (2012) Pressure-driven flow through a single nanopore. Phys Rev E 86:025302R. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.86.025302
Ziarani AS, Aguilera R (2012) Knudsen’s permeability correction for tight porous media. Transp Porous Med 91:239C260. doi:10.1007/s11242-011-9842-6
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. A. E. Velasco and Prof. P. Taborek for providing the experimental data, some of which are unpublished.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Q., Wang, E., Liu, X. et al. Determining the intrinsic permeability of tight porous media based on bivelocity hydrodynetics. Microfluid Nanofluid 16, 841–848 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-014-1332-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-014-1332-z