Abstract
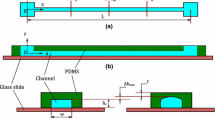
This paper presents a lab-on-a-chip development method that applies the Young–Laplace equation to design the geometries of a patterned water droplet, and then using the droplet as a mold to fabricate three-dimensional polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) channels. We demonstrate the method by designing and fabricating an on-chip funnel. We then subsequently trap beads of graded diameter in the tapered section of the funnel to make on-chip filters of controllable pore size. After packing the funnel with beads, the cutoff pore size of the fabricated filter agrees closely with our estimate. This approach provides a straightforward, low-cost, yet powerful way to design and fabricate microfluidic devices with 3D features.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abgrall P, Lattes C, Conédéra V, Dollat X, Colin S, Gué AM (2006) A novel fabrication method of flexible and monolithic 3D microfluidic structures using lamination of SU-8 films. J Micromech Microeng 16(1):113–121
Adamson AW, Gast AP (1997) Physical chemistry of surfaces, 6th edn. Wiley, New York
Andersson H, van der Wijngaart W, Enoksson P, Stemme G (2000) Micromachined flow-through filter-chamber for chemical reactions on beads. Sens Actuators B: Chem 67(1):203–208
Bae C-H, Seo C-T, Lee J-H (2003) Fabrication of cylinder type micro channel using photoresist reflow and isotropic etching. In: Microprocesses and nanotechnology conference. Digest of papers. 2003 International, pp 200–201
Ballard DH (1981) Generalizing the Hough transform to detect arbitrary shapes. Pattern Recognit 13(2):111–122
Brakke KA (1992) The surface evolver. Exp Math 1(2):141–165
Ceriotti L, de Rooij NF, Verpoorte E (2002) An integrated fritless column for on-chip capillary electrochromatography with conventional stationary phases. Anal Chem 74(3):639–647
Chan EY, Goncalves NM, Haeusler RA, Hatch AJ, Larson JW, Maletta AM, Yantz GR, Carstea ED, Fuchs M, Wong GG, Gullans SR, Gilmanshin R (2004) DNA mapping using microfluidic stretching and single-molecule detection of fluorescent site-specific tags. Genome Res 14(6):1137–1146
Chang S-I, Yoon J-B (2004) Shape-controlled, high fill-factor microlens arrays fabricated by a 3D diffuser lithography and plastic replication method. Opt Express 12(25):6366–6371
Chao S-H, Meldrum DR (2009) Spontaneous, oscillatory liquid transport in surface tension-confined microfluidics. Lab Chip 9(7):867–869
Chao S-H, Carlson R, Meldrum DR (2007) Rapid fabrication of microchannels using microscale plasma activated templating (μPLAT) generated water molds. Lab Chip 7(5):641–643
Crowley TA, Pizziconi V (2005) Isolation of plasma from whole blood using planar microfilters for lab-on-a-chip applications. Lab Chip 5(9):922–929
Hong JW, Studer V, Hang G, Anderson WF, Quake SR (2004) A nanoliter-scale nucleic acid processor with parallel architecture. Nat Biotechnol 22(4):435–439
Ikuta K, Maruo S, Fujisawa T, Yamada A (1999) Micro concentrator with opto-sense micro reactor for biochemical IC chip family. 3D composite structure and experimental verification. In: Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, 1999. MEMS’99. Twelfth IEEE International Conference on, 1999, pp 376–381
Jemere AB, Oleschuk RD, Harrison DJ (2003) Microchip-based capillary electrochromatography using packed beds. Electrophoresis 24(17):3018–3025
Laplace P-S (1825) Traité de mécanique céleste. Crapelet, Paris
Larson JW, Yantz GR, Zhong Q, Charnas R, D’Antoni CM, Gallo MV, Gillis KA, Neely LA, Phillips KM, Wong GG, Gullans SR, Gilmanshin R (2006) Single DNA molecule stretching in sudden mixed shear and elongational microflows. Lab Chip 6(9):1187–1199
Lee SA, Chung SE, Park W, Lee SH, Kwon S (2009) Three-dimensional fabrication of heterogeneous microstructures using soft membrane deformation and optofluidic maskless lithography. Lab Chip 9(12):1670
Lim CT, Zhang Y (2007) Bead-based microfluidic immunoassays: the next generation. Biosens Bioelectron 22(7):1197–1204
Lin L-I, Chao S-H, Meldrum DR (2009) Practical, microfabrication-free device for single-cell isolation. PLoS ONE 4(8):e6710
Liu X, Wang Q, Qin J, Lin B (2009) A facile ‘liquid-molding’ method to fabricate PDMS microdevices with 3-dimensional channel topography. Lab Chip 9(9):1200
Park JY, Hwang CM, Lee S-H (2008) Ice-lithographic fabrication of concave microwells and a microfluidic network. Biomed Microdev 11(1):129–133
Prince M, Ma X, Docker P, Ward M, Prewett P (2007) The development of a novel Bio-MEMS filtration chip for the separation of specific cells in fluid suspension. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part H-J Eng Med 22(H2):113–128
Romanato F, Tormen M, Businaro L, Vaccari L, Stomeo T, Passaseo A, Di Fabrizio E (2004) X-ray lithography for 3D microfluidic applications. Microelectron Eng 73:870–875
Shi X, Lin L-I, Chen S, Chao S-H, Zhang W, Meldrum DR (2011) Real-time PCR of single bacterial cells on an array of adhering droplets. Lab Chip 11(13):2276
Stephan K, Pittet P, Renaud L, Kleimann P, Morin P, Ouaini N, Ferrigno R (2007) Fast prototyping using a dry film photoresist: microfabrication of soft-lithography masters for microfluidic structures. J Micromech Microeng 17(10):N69–N74
Unger MA, Chou H-P, Thorsen T, Scherer A, Quake SR (2000) Monolithic microfabricated valves and pumps by multilayer soft lithography. Science 288(5463):113–116
Young T (1805) An essay on the cohesion of fluids. Philos Trans Royal Soc Lond 95:65–87
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge support from the National Human Genome Research Institute Grant No. 1 R01 HG01497 (PI: D. R. Meldrum) and Mr. Tao Peng’s public-domain MATLAB code for circle detection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goff, C.M., Chao, Sh., Johnson, R.H. et al. Surface tension-controlled three-dimensional water molds: theory and applications. Microfluid Nanofluid 13, 891–897 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-012-0997-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-012-0997-4