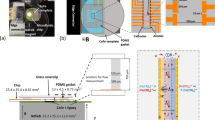
Abstract
A micropump based on strong polarization of ion-exchange beads and corresponding actuation by electroosmosis of the second kind was designed and fabricated. Experimental results from operation with AC and DC voltage showed a close to second order relationship between flow and voltage, in good agreement with theory. The difference between experimental and theoretical flow rates and pressures is attributed to the hydrodynamic resistance of the channel network. A modified pump design which should yield higher flow rates and pressures was suggested.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajdari A (2000) Pumping liquids using asymmetric electrode arrays. Phys Rev E 61:R45–R48
Barinova NO, Mishchuk NA (2008) Electroosmosis in system of ion-exchange granules. Colloid J 70:743–747
Belova EI, Lopatkova GYu, Pismenskaya ND, Nikonenko VV, Larchet C, Pourcelly G (2006) Effect of anion-exchange membrane surface properties on mechanisms of overlimiting mass transfer. J Phys Chem B 110:13458–13469
Ben Y, Chang HC (2002) Nonlinear Smoluchowski slip velocity and vortex generation. J Fluid Film 461:229–238
Bhattacharyya A, Masliyah JH, Yang J (2003) Oscillating laminar electrokinetic flow in infinitely extended circular microchannels. J Colloid Interface Sci 261:12–20
Colon LA, Burgos G, Maloney TD, Cintron JM, Rodriguez RL (2000) Recent progress in capillary electrochromatography. Electrophoresis 21:3965–3993
Debesset S, Hayden CJ, Dalton C, Eijkel JCT, Manz A (2004) An AC electroosmotic micropump for circular chromatographic applications. Lab on a Chip 4:396–400
Dukhin AS, Dukhin SS (2005) Aperiodic capillary electrophoresis method using an alternating current for separation of macromolecules. Electrophoresis 26:2149–2153
Dukhin SS, Mishchuk NA (1988a) Unrestricted increase in the current through a granule of an ion exchanger. Colloids J (USSR) 49:1047–1049
Dukhin SS, Mishchuk NA (1988b) Strong concentration polarization of thin double layer of spherical particle at external electric field. Colloid J (USSR) 50:208–214
Dukhin SS, Mishchuk NA (1993) Intensification of electrodialysis based on the electroosmosis of the second kind. J Membr Sci 79:199–210
Dukhin SS, Mishchuk NA, Tarovsky AA, Baran AA (1987) Electrophoresis of the second kind. Colloid J (USSR) 49:616–617
Eckstein Yu, Yossifon G, Seifert A, Miloh T (2009) Nonlinear electrokinetic phenomena around nearly insulated sharp tips in microflows. J Colloid Interface Sci 338:243–249
Gnusin NP, Grebenyuk VD (1972) Electrochemistry of granulated ionites. Naukova Dumka, Kiev
Holtzel A, Tallarek U (2007) Ionic conductance of nanopores in microscale analysis systems: where microfluidics meets nanofluidics. J Sep Sci 30:1398–1419
Hu G, Li D (2007) Multiscale phenomena in microfluidics and nanofluidics. Chem Eng Sci 62:3443–3454
Kivanc FC, Litster S (2011) Pumping with electroosmosis of the second kind in mesoporous skeletons. Sens Actuators B 151:394–401
Lastochkin D, Zhou R, Wang P, Ben Y, Chang H-C (2004) Electrokinetic micropump and micromixer design based on AC faradaic polarization. J Appl Phys 96:1730–1734
Leinweber FC, Tallarek U (2005) Concentration polarization-based nonlinear electrokinetics in porous media: induced-charge electroosmosis. J Phys Chem B 109:21481–21485
Listovnichij AV (1991) Concentration polarization of system ion-exchange membrane at overlimiting mode. Russ J Electrochem 27:316–323
Lojtsjanskij LG (1973) Mechanic of liquid and gas. Nauka, Moscow
Minor M, van der Linde AJ, van Leeuwen H, Lyklema J (1997) Dynamic aspects of electrophoresis and electroosmosis: a new fast method for measuring particle mobilities. J Colloid Interface Sci 189:370–375
Mishchuk NA (1996) Electrokinetic phenomena at strong concentration polarization of interface. Dr. Sc. thesis, ICCWC, Kiev
Mishchuk NA (1998a) Electroosmosis of the second kind near the heterogeneous ion-exchange membrane. Colloids Surf A 140:75–89
Mishchuk NA (1998b) Perspectives of electrodialysis intensification. Desalination 117:283–296
Mishchuk NA (1999) Water dissociation at strong concentration polarisation of disperse particles. Colloids Surf A 159:467–475
Mishchuk NA (2006) Electrokinetic phenomena of the second kind. In: Mishchuk NA (ed) Encyclopedia of surface and colloid science, vol 3. Taylor & Francis, New York, p 2180
Mishchuk NA (2010) Concentration polarization of interface and non-linear electrokinetic phenomena. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 2010(160):16–39
Mishchuk NA, Barinova NO (2005) Peculiarities of electroosmosis of the second kind at the surfaces of one and two ionite granules. Colloid J 67:164–171
Mishchuk NA, Dukhin SS (1989) Electrophoresis of spherical non-conductive particle at strong concentration polarization of double layer. Colloid J (USSR) 50:952–958
Mishchuk NA, Dukhin SS (2002a) Electrophoresis of solid particles at large Peclet number. Electrophoresis 13:2012–2022
Mishchuk NA, Dukhin SS (2002b) Electrokinetic phenomena of the second kind. In: Delgado A (ed) Interfacial electrokinetics and electrophoresis. Marcel Dekker, New York, p 241
Mishchuk NA, Gonzalez-Caballero F (2006a) Nonstationary electroosmotic flow in open cylindrical capillaries. Electrophoresis 27:650–660
Mishchuk NA, Gonzalez-Caballero F (2006b) Nonstationary electroosmotic flow in closed cylindrical capillaries. Electrophoresis 27:661–671
Mishchuk NA, Takhistov PV (1995) Electroosmosis of the second kind. Colloids Surf A 95:119–131
Mishchuk NA, Barany S, Tarovsky AA, Madai F (1998) Superfast electrophoresis of electron-type conducting particles. Colloids Surf A 140:43–51
Mishchuk NA, Koopal LK, Gonzalez-Caballero F (2001) Intensification of electrodialysis by a non-stationary electric field. Colloids Surf A 176:195–212
Mishchuk NA, Delgado AV, Ahualli S, González-Caballero F (2007) Non-stationary electro-osmotic flow in closed cylindrical capillaries. Theory and experiment. J Colloid Interface Sci 309:308–314
Mishchuk NA, Heldal T, Volden T, Auerswald J, Knapp H (2009) Micropump based on electroosmosis of the second kind. Electrophoresis 30:3499–3506
Mpholo M, Smith CG, Brown ABD (2003) Low voltage plug flow pumping using anisotropic electrode arrays. Sens Actuators B 92:262–268
Nischang I, Chen G, Tallarek U (2006) Electrohydrodynamics in hierarchically structured monolithic and particulate fixed beds. J Chromatogr A 1109:32–50
Nischang I, Reichl U, Seidel-Morgenstern A, Tallarek U (2007) Concentration polarization and nonequilibrium electroosmotic slip in dense multiparticle systems. Langmuir 23:9271–9281
Nischang I, Höltzel A, Seidel-Morgenstern A, Tallarek U (2008) Concentration polarization and nonequilibrium electroosmotic slip in hierarchical monolithic structures. Electrophoresis 29:1140–1151
Oddy MH, Santiago JG (2004) A method for determining electrophoretic and electroosmotic mobilities using AC and DC electric field particle displacements. J Colloid Interface Sci 269:192–204
Ramos A, Morgan H, Green NG, González A, Castellanos A (2005) Pumping of liquids with travelling-wave electroosmosis. J Appl Phys 97:084906-1-8
Rathore AS, Horvath C (1997) Capillary electrochromatography: theories on electroosmotic flow in porous media. J Chromatogr A 781:185–195
Reichmuth DS, Chirica GS, Kirby BJ (2003) Increasing the performance of high-pressure, high-efficiency electrokinetic micropumps using zwitterionic solute additives. Sens Actuators B 79:37–43
Roberts RM, Chang H-C (2000) Wave-enhanced interfacial transfer. Chem Eng Sci 55:1127–1141
Rubinstein I, Maletzki F (1991) Electroconvection at an electrically inhomogeneous permselective membrane surface. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 87:2079–2087
Rubinstein I, Shtilman L (1979) Voltage against current curves of cation exchange membranes. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 2(75):231–246
Rubinstein I, Zaltzman B, Kedem O (1997) Electric fields in and around ion-exchange membranes. J Membr Sci 125:17–21
Stol R, Kok WTh, Poppe H (2001) Size-exclusion electrochromatography with controlled pore flow. J Chromatogr A 914:201–209
Strickland DG, Suss ME, Zangle TA, Santiago JG (2010) Evidence shows concentration polarization and its propagation can be key factors determining electroosmotic pump performance. Sens Actuators B 143:795–798
Studer V, Pepin A, Chen Y, Ajdari A (2004) An integrated AC electrokinetic pump in a microfluidic loop for fast and tunable flow control. Analyst 129:944–949
Suss ME, Mani A, Zangle TA, Santiago JQ (2011) Electroosmotic pump performance is affected by concentration polarizations of both electrodes and pump. Sens Actuators A 165:310–315
Takhistov P, Duginova K, Chang H-C (2003) Electrokinetic mixing vortices due to electrolyte depletion at microchannel junctions. J Colloid Interface Sci 263:133–143
Tallarek U, Leinweber FC, Nischang I (2005) Perspective on concentration polarization effects in electrochromatographic separations. Electrophoresis 26:391
Tikhomolova KP (1993) Electroosmosis. Ellis Horwood, Chichester
Wang P, Chen Z, Chang H-C (2006) A new electro-osmotic pump based on silica monoliths. Sens Actuators B 113:500–509
Yang J, Bhattacharyya A, Masliyah JH, Kwok DY (2003) Oscillating laminar electrokinetic flow in infinitely extended rectangular microchannels. J Colloid Interface Sci 261:21–31
Yao Sh, Hertzog DE, Zeng Sh, Mikkelsen JC, Santiago JG (2003) Porous glass electroosmotic pumps: design and experiments. J Colloid Interface Sci 268:143–153
Zabolotskii VI, Nikonenko VV (1996a) Electrodialysis of diluted electrolyte solutions: some theoretical and applied aspects. Russ J Electrochem 32:223–230
Zabolotskii VI, Nikonenko VV (1996b) The ion transport in membranes. Nauka, Moscow (in Russian)
Zaltzman B, Rubinstein I (2007) Electro-osmotic slip and electroconvective instability. J Fluid Mech 579:173–226
Zeng Sh, Chen Ch-H, Mikkelsen JC, Santiago JG (2001) Fabrication and characterization of electroosmotic micropumps. Sens Actuators B 79:107–114
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishchuk, N.A., Heldal, T., Volden, T. et al. Microfluidic pump based on the phenomenon of electroosmosis of the second kind. Microfluid Nanofluid 11, 675–684 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-011-0833-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-011-0833-2