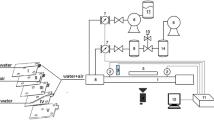
Abstract
In this experimental study, the effects on two-phase flow dynamics in a microfluidic snake channel due to periodic forcing were considered. Time series analysis was exploited to investigate on the obtained bubbles’ flow considering two aspects: the role of driven frequency through Fourier analysis and the nonlinear behavior through the evaluation of d-infinite and Largest Lyapunov exponent. Phase diagrams summarize the results: the two nonlinear parameters are plotted versus the air fraction and the frequency of the input flow rates. The identified relation maps allow the classification of the flow dynamics, opening the way for the control of bubble flow through signal analysis.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aurell E, Boffetta G, Crisanti A, Paladin G, Vulpiani A (1997) Predictability in the large: an extension of the concept of Lyapunov exponent. J Phys A 30:1–26
Barbier V, Willaime H, Tabeling P (2006) Producing droplets in parallel microfluidic systems. Phys Rev Lett E 74:046306-1–046306-4
Barry R, Ivanov D (2004) Microfluidics in biotechnology. J Nanobiotechnol 2:1–5
Bonasera A, Bucolo M, Fortuna L, Frasca M, Rizzo A (2003) The \(d_{\infty}\) parameter to characterise chaotic dynamics. Non linear Phenom Complex Syst 6:565–570
Bringer MR, Gerdts CJ, Song H, Tice JD, Ismagilov RF (2004) Microfluidic systems for chemical kinetics that rely on chaotic mixing in droplets. Philos Trans R Soc A 362:1087–1104
Cubaud T, Ho CM (2004) Transport of bubbles in square microchannels. Phys Fluids 16:4575-4585
Dreyfus R, Tabeling P, Willaime H (2003) Ordered and disordered patterns in two-phase flows in microchennels. Phys Rev Lett 90:144505-1–144505-4
Garstecki P, Fuerstman J, M Fischbach, Sia SK, Whitesides GM (2006) Mixing with bubbles: a practial technology for use with portable microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 6:207–212
Griffiths AD, Tawfik DS (2006) Miniaturising the laboratory in emulsion droplets. Trends Biotechnol 24:395–402
Jiao Z, Nguyen N-T, Huang X (2007) Chaotic motion of microplugs under high-frequency thermocapillary actuation. J Micromech Microeng 7:184–185
Joanicot M, Ajdari A (2005) Droplet control for microfluidics. Appl Phys 309:887-888
Kantz H, Schreiber T (2004) Nonlinear time series analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Mao X, Juluri BK, Lapsley MI, Stratton ZS, Huang, TJ (2010) Milliseconds microfluidic chaotic bubble mixer. Microfluid Nanofluid 8:139–144
Nguyen N-T, Wereley S (2002) Fundamentals and applications of microfluidics, 2nd edn. Integrated Microsystems Series. Artech House, London
Nguyen NT et al (2006) Optical detection for droplet size control in microfluidic droplet-based analysis systems. Sens Actuators B 117:431–436
Sapuppo F, Schembri F, Fortuna L, Bucolo M (2009) Microfluidic circuits and systems. Circuits Syst Mag IEEE 9:6–19
Sarrazin F, Prat L, Di Miceli N, Cristobal G, Link DR, Weitz DA (2007) Mixing characterization inside microdroplets engineered on a microcoalescer. Chem Eng Sci 62:1042–1048
Serizawa A, Feng Z, Kawara Z (2002) Two-phase flow in microchennels. Exp Thermal Fluid Sci 26:703–714
Sprott JC, Wereley S (2003) Chaos and time-series analysis. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Thompson JMT, Stewart HB (1989) Nonlinear dynamics and chaos. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Tice JD, Song H, Lyon AD, Ismagilov RF (2003) Formation of droplets and mixing in multiphase microfluidics at low values of the reynolds and capillary numbers. Langmuir 19:9127–9133
Whitesides GM (2006) The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 442:368–373
Willaime H, Barbier V, Kloul L, Tabeling P (2006) Arnold tongues in microfluidic drop emitter. Phys Rev Lett 96:054501-1–054501-4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schembri, F., Bucolo, M. Periodic input flows tuning nonlinear two-phase dynamics in a snake microchannel. Microfluid Nanofluid 11, 189–197 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-011-0786-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-011-0786-5