Abstract
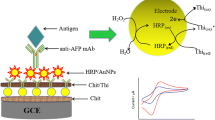
A mediator-free electrochemical immunoassay protocol based on a disposable immunosensor for the detection of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in human serum was developed. To fabricate such an immunosensor, a layer of sol–gel composite film containing room temperature ionic liquid and chitosan was initially formed on a glassy carbon electrode. Nanogold particles were then adsorbed onto the membrane via the amine groups of chitosan molecules, and then horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled hepatitis B surface antibodies (HRP-anti-HBs) were immobilized onto the nanogold surface. With a non-competitive immunoassay format, the antibody–antigen complex could be formed by a simple one-step immunoreaction between the immobilized HRP-anti-HBs and HBsAg in sample solution. The formed immunocomplex inhibited partly the active center of the HRP, which decreased the immobilized HRP toward the reduction of H2O2. The performance and factors influencing the performance of the immunosensor were evaluated. Under optimal conditions, the current change obtained from the carried HRP relative to H2O2 system was proportional to HBsAg concentration in the range of 1.5–400 ng/mL with a detection limit of 0.5 ng/mL (at 3δ). The reproducibility, selectivity, and stability of the proposed immunosensor were acceptable. Moreover, the proposed immunosensors were used to analyze HBsAg in human serum specimens. Analytical results of clinical samples suggested that the developed immunosensor has a promising alternative approach for detecting HBsAg in the clinical diagnosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhargava B, Balasubramanian S, Klein M (2008) Modelling room temperature ionic liquids. Chem Commun 29:3339–3351
Bilitewski U (2006) Protein-sensing assay formats and devices. Anal Chim Acta 568:232–247
Borisov S, Klimant I (2008) Optical nanosensor-Smart tools in bioanalytics. Analyst 133:1302–1307
Dittrich P, Tachikawa K, Manz A (2006) Micro total analysis systems: latest advancements and trends. Anal Chem 78:3887–3907
Frens G (1973) Controlled nucleation for the regulation of the particle size in mondisperse gold suspensions. Nat Phys Sci 241:20–22
Happiot P, Lagrost C (2008) Electrochemical room temperature ionic liquids. Chem Rev 108:2238–2264
Islam M, Ferdousi B, Okajima T, Ohsaka T (2005) A catalytic activity of a mercury electrode towards dioxygen reduction in room-temperature ionic liquids. Eletrochem Commun 7:789–795
Li J, Yu J, Zhao F, Zeng B (2007) Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase entrapped in nano gold particles-ionic liquid-N, N-dimethylformanmide composite film on glassy carbon electrode and glucose sensing. Anal Chim Acta 587:33–40
Liang R, Peng H, Qiu J (2008) Fabrication, characterization, and application of potentiometric immunosensor based on biocompatible and controllable three-dimensional porous chitosan membranes. J Colloid Interface 320:125–131
Liu G, Lin Y (2007) Nanomaterial labels in electrochemical immunosensors and immunoassays. Talanta 74:308–317
Lu X, Zhang Q, Zhang L, Li J (2006) Direct electron transfer of horseradish peroxidase and its biosensor based on chitosan and room temperature ionic liquid. Electrochem Commun 8:874–878
Maleki N, Safavi A, Tajabadi F (2006) High-performance carbon composite electrode based on an ionic liquid as binder. Anal Chem 78:3820–3826
Minerick A (2008) The rapidly growing field of micro and nanotechnology to measure living cells. AIChE J 54:2230–2237
Patra M, Manzoor K, Manoth M, Negi S, Vadera S, Kumar N (2008) Nanotechnology applications for chemical and biological sensors. Defence Sci J 58:636–649
Sperling R, Rivera Gil P, Zhang F, Zanella M, Parak W, Corma A, Garcia H (2008) Biological application of gold nanoparticles. Chem Soc Rev 37:1896–1908
Tang D, Yuan R, Chai Y, Zhong X, Liu Y, Dai J (2004) A novel immunosensor based on immobilization of hepatitis B surface antibody on platinum electrode modified colloidal gold and polyvinyl butyral as matrices via electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Bioelectrochemistry 65:15–22
Tang D, Yuan R, Chai Y (2008) Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for clinical immunoassay using thionine-doped magnetic gold nanospheres as labels and horseradish peroxidase as enhancer. Anal Chem 80:1582–1588
Wang Y, Yan Z, Chen F, Zhan X (2008) Nanotechnology in heterogeneous catalysis. Progress Chem 20:1263–1269
Wei D, Ivaska A (2008) Applications of ionic liquids in electrochemical sensors. Anal Chim Acta 607:126–135
Wilson R (2008) The use of gold nanoparticles in diagnostics and detection. Chem Soc Rev 37:2028–2045
Yuan R, Tang D, Chai Y, Zhong X, Liu Y, Dai J (2004) Ultrasensitive potentiometric immunosensor based on SA and OCA techniques for immobilization of HBsAb with colloidal Au and polyvinyl butyral as matrixes. Langmuir 20:7240–7245
Zhang L, Webster T (2009) Nanotechnology and nanomaterials: Promises for improved tissue regeneration. Nano Today 4:66–80
Zhuo Y, Yuan R, Chai Y, Li X, Zhang Y, Zhu Q, Wang N (2005) An amperometric immunosensor based on immobilization of hepatitis B surface antibody on gold electrode modified gold nanoparticles and horseradish peroxidase. Anal Chim Acta 548:205–210
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Alexander von Humboldt-Foundation, Germany, and the Postgraduate Science and Technology Innovation Program, and Foundation of Excellent PhD Dissertation of SWU, China (grant no. 200602) to Dr. Tang.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, D., Li, H. & Liao, J. Ionic liquid and nanogold-modified immunosensing interface for electrochemical immunoassay of hepatitis B surface antigen in human serum. Microfluid Nanofluid 6, 403–409 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-008-0385-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-008-0385-2