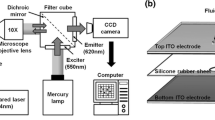
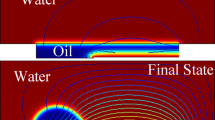
Abstract
Light is used to dynamically control the pattern of electroosmotic flow in a microfluidic channel. One wall of the channel is formed by a photoconductor film in a specific geometry. Illumination of this surface results in an increase of the conductivity that modifies the structure of the electric field inside the channel. A dramatic change of the electroosmotic flow pattern can be achieved. This approach provides useful capabilities for the manipulation of fluids in microfluidic systems like directing flow and mixing.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian RJ (1991) Particle-imaging techniques for experimental fluid mechanics. Ann Rev Fluid Mech 23:261–304
Chiou PY, Moon H, Toshiyoshi H, Kim CJ, Wu MC (2003) Light actuation of liquid by optoelectrowetting. Sens Actuators A 104:222–228
Chiou PY, Ohta AT, Wu MC (2005) Massively parallel manipulation of single cells and microparticles using optical images. Nature 436:370–372
Duffy DC, McDonald JC, Schueller OJA, Whitesides GM (1998) Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal Chem 70:4974–4984
Hayward RC, Saville DA, Aksay IA (2000) Electrophoretic assembly of colloidal crystals with optically tunable micropatterns. Nature 404:56–59
Herr AE, Molho JI, Santiago JG, Mungal MG, Kenny TW, Garguilo MG (2000) Electroosmotic capillary flow with nonuniform zeta potential. Anal Chem 72:1053–1057
Horiuchi K, Dutta P (2006) Electrokinetic flow control in microfluidic chip using field-effect transistor. Lab-on-a-Chip 6:714–723
Johnson TJ, Ross D, Locascio LE (2002) Rapid microfluidic mixing. Anal Chem 74:45–51
Kirby BJ, Hasselbrink EF (2004) Zeta-potential of microfluidic substrates: 2. Data for polymers. Electrophoresis 25:203–213
Lee CY, Lee GB, Fu LM, Lee KH, Yang RJ (2004) Electrokinetically driven active micro-mixers utilizing zeta potential variation induced by field effect. J Micromech Microeng 14:1390–1398
Moorthy J, Khoury C, Moore JS, Beebe DJ (2001) Active control of electroosmotic flow in microchannels using light. Sens Actuators B 75:223–229
Oroszi L, Der A, Kirei H, Rakovics V, Ormos P (2006) Control of electroosmostic flow by light. Appl Phys Lett 89:263508
Psaltis D, Quake SR, Yang C (2006) Developing optofluidic technology through the fusion of microfluidics and optics. Nature 442:381–386
Rakovics V (2006) Chemical bath deposition of CdS and CdPbS nanocrystalline thin films and investigation of their photoconductivity. Soc Symp Proc 900E:O03-30.1
Roy S, Kar S, Chaudhuri S, Dasgupta A (2006) Potential of cadmium sulphide nanorods as an optical microscopic probe to the folding state of cytochrome C. Biophys Chem 124:52–61
Stroock AD, Dertinger SKW, Ajdari A, Mezic I, Stone HA, Whitesides GM (2002) Chaotic mixer for microchannels. Science 295:647–654
Stroock AD, Weck M, Chiu DT, Huck WTS, Kenis PJA, Ismagilov RF, Whitesides GM (2000) Patterning electro-osmotic flow with patterned surface charge. Phys Rev Lett 84:3314–3317
Sze A, Erickson D, Ren L, Li D (2003) Zeta-potential measurement using the Smoluchowski equation and the slope of the current-time relationship in electroosmotic flow. J Colloid Interface Sci 261:402–410
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant Országos Tudományos Kutatási Alap NK72375.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oroszi, L., Dér, A., Kirei, H. et al. Manipulation of microfluidic flow pattern by optically controlled electroosmosis. Microfluid Nanofluid 6, 565–569 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-008-0346-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-008-0346-9