Abstract
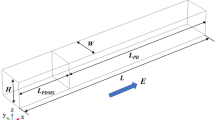
Poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) is usually considered as a dielectric material and the PDMS microchannel wall can be treated as an electrically insulated boundary in an applied electric field. However, in certain layouts of microfluidic networks, electrical leakage through the PDMS microfluidic channel walls may not be negligible, which must be carefully considered in the microfluidic circuit design. In this paper, we report on the experimental characterization of the electrical leakage current through PDMS microfluidic channel walls of different configurations. Our numerical and experimental studies indicate that for tens of microns thick PDMS channel walls, electrical leakage through the PDMS wall could significantly alter the electrical field in the main channel. We further show that we can use the electrical leakage through the PDMS microfluidic channel wall to control the electrolyte flow inside the microfluidic channel and manipulate the particle motion inside the microfluidic channel. More specifically, we can trap individual particles at different locations inside the microfluidic channel by balancing the electroosmotic flow and the electrophoretic migration of the particle.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajdari A (2000) Pumping liquids using asymmetric electrode arrays. Phys Rev E 61:R45
Asbury CL, Diercks AH, van den Engh G (2002) Trapping of DNA by dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 23:2658–2666
Beebe DJ, Mensing GA, Walker GM (2002) Physics and applications of microfluidics in biology. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 4:261–286
Bousse L, Cohen C, Nikiforov T, Chow A, Kopf-Sill AR, Dubrow R, Parce JW (2000) Electrokinetically controlled microfluidic analysis systems. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 29:155–181
Brown ABD, Smith CG, Rennie AR (2000) Pumping of water with ac electric fields applied to asymmetric pairs of microelectrodes. Phys Rev E 63:016305
Choi S, Park JK (2005) Microfluidic system for dielectrophoretic separation based on a trapezoidal electrode array. Lab Chip 5:1161–1167
Doherty EA, Meagher RJ, Albarghouthi MN, Barron AE (2003) Microchannel wall coatings for protein separations by capillary and chip electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 24:34–54
Duffy DC, McDonald JC, Schueller OJA, Whitesides GM (1998) Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Anal Chem 70:4974–4984
Fiedler S, Shirley SG, Schnelle T, Fuhr G (1998) Dielectrophoretic sorting of particles and cells in a microsystem. Anal Chem 70:1909–1915
Gao J, Xu J, Locascio LE, Lee CS (2001) Integrated microfluidic system enabling protein digestion, peptide separation, and protein identification. Anal Chem 73:2648–2655
Gascoyne PRC, Vykoukal J (2002) Particle separation by dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 23:1973–1983
Gonzalez A, Ramos A, Green NG, Castellanos A, Morgan H (2000) Fluid flow induced by nonuniform ac electric fields in electrolytes on microelectrodes.II. A linear double-layer analysis. Phys Rev E 61:4019–4028
Green NG, Morgan H, Milner JJ (1997) Manipulation and trapping of sub-micron bioparticles using dielectrophoresis. J Biochem Biophys Methods 35:89–102
Green NG, Ramos A, Gonzalez A, Morgan H, Castellanos A (2000) Fluid flow induced by nonuniform ac electric fields in electrolytes on microelectrodes.I. Experimental measurements. Phys Rev E 61:4011–4018
Green NG, Ramos A, Gonzalez A, Morgan H, Castellanos A (2002) Fluid flow induced by nonuniform ac electric fields in electrolytes on microelectrodes.III. Observation of streamlines and numerical simulation. Phys Rev E 66:026305
Heller C (2001) Principles of DNA separation with capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 22:629–643
Horiuchi K, Dutta P (2006) Electrokinetic flow control in microfluidic chips using a field-effect transistor. Lab Chip 6:714–723
Hsieh S, Lin H, Lin C (2006) Electroosmotic flow velocity measurements in a square microchannel. Colloid Polym Sci 284:1275–1286
Huang X, Gordon MJ, Zare RN (1988) Current-monitoring method for measuring the electroosmotic flow rate in capillary zone electrophoresis. Anal Chem 60:1837–1838
Li D (2004) Electrokinetics in microfluidics. Academic Press, London
Lichtenberg J, Verpoorte E, de Rooij NF (2001) Sample preconcentration by field amplification stacking for microchip-based capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 22:258–271
Liu Z, Guo C, Yang J, Yuan L (2006) Tapered fiber optical tweezers for microscopic particle trapping: fabrication and application. Opt Express 14:12510–12516
Mark JE (1999) Polymer data handbook. Oxford University Press, New York
McDonald JC, Whitesides GM (2002) Poly(dimethylsiloxane) as a material for fabricating microfluidic devices. Acc Chem Res 35:491–499
Mineta T, Kida N, Nomura S, Makino E, Sugawara T, Toh S, Shibata T (2008) Pulsation sensor integrated with microvascular holding actuator for thrombosis monitoring. Sensor Actuator Phys 143:14–19
Müller T, Gerardino A, Schnelle T, Shirley SG, Bordoni F, Gasperis GD, Leoni R, Fuhr G (1996) Trapping of micrometre and sub-micrometre particles by high-frequency electric fields and hydrodynamic forces. J Phys D Appl Phys 29:340–349
Polson NA, Hayes MA (2000) Electroosmotic flow control of fluids on a capillary electrophoresis microdevice using an applied external voltage. Anal Chem 72:1088–1092
Reyes DR, Iossifidis D, Auroux PA, Manz A (2002) Micro total analysis systems. 1. introduction, theory, and technology. Anal Chem 74:2623–2636
Schasfoort RBM, Schlautmann S, Hendrikse J, van den Berg A (1999) Field-effect flow control for microfabricated fluidic networks. Science 286:942–945
Sia KS, Whitesides GM (2003) Microfluidic devices fabricated in poly(dimethylsiloxane) for biological studies. Electrophoresis 24:3563–3576
Stroink T, Paarlberg E, Waterval JCM, Bult A, Underberg WJM (2001) On-line sample preconcentration in capillary electrophoresis, focused on the determination of proteins and peptides. Electrophoresis 22:2374–2383
Thorsen T, Maerkl SJ, Quake SR (2002) Microfluidic large-scale integration. Science 298:580–584
Xu F, Jabasini M, Baba Y (2002) DNA separation by microchip electrophoresis using low-viscosity hydroxypropylmethylcellulose-50 solutions enhanced by polyhydroxy compounds. Electrophoresis 23:3608–3614
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support from NSF (Award# CBET-0643583), and DoD (W81XWH07-1-0507).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Vajandar, S.K., Xu, D. et al. Experimental characterization of electrical current leakage in poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 6, 589–598 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-008-0331-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-008-0331-3