Abstract
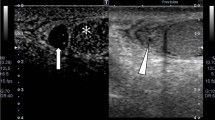
We report the sonographic findings in a case of torsed appendix epididymis that occurred in an adult, which was misdiagnosed as a tunica vaginalis tumor such as cystic mesothelioma. Scrotal gray-scale sonography revealed an ovoid-shaped, heterogeneously hypoechoic mass with multiple tiny cystic foci and thick septa in the sac of the right tunica vaginalis, which abuts to the right epididymal head. Color Doppler sonography showed no blood flow within the mass. Pathological examination revealed torsion of the appendix epididymis.


Similar content being viewed by others

References
Strauss S, Faingold R, Manor H. Torsion of the testicular appendages: sonographic appearance. J Ultrasound Med. 1997;16:189–92.
Hesser U, Rosenborg M, Gierup J, et al. Gray-scale sonography in torsion of the testicular appendages. Pediatr Radiol. 1993;23:529–32.
Park SJ, Kim HJ, Yi BH. Sonography of intrascrotal appendage torsion: varying echogenicity of the torsed appendage according to the time from onset. J Ultrasound Med. 2011;30:1391–6.
Lev M, Ramon J, Mor Y, et al. Sonographic appearances of torsion of the appendix testis and appendix epididymis in children. J Clin Ultrasound. 2015;43:485–9.
Yang DM, Lim JW, Kim JE, et al. Torsed appendix testis: gray scale and color Doppler sonographic findings compared with normal appendix testis. J Ultrasound Med. 2005;24:87–91.
Baldisserotto M, de Souza JC, Pertence AP, et al. Color Doppler sonography of normal and torsed testicular appendages in children. AJR. 2005;184:1287–92.
Rakha E, Puls F, Saidul I, et al. Torsion of the testicular appendix: importance of associated acute inflammation. J Clin Pathol. 2006;59:831–4.
Dogra VS, Gottlieb RH, Oka M, et al. Sonography of the scrotum. Radiology. 2003;227:18–36.
Chien AJ, Struse PJ, Koo HP. Cystic mesothelioma of the testis in an adolescent patient. J Ultrasound Med. 2000;19:423–5.
Lane TM, Schofield WJ, Trotter GA. Benign cystic mesothelioma of the tunica vaginalis. BJU Int. 1999;84:533–4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Ethical statements
All procedures followed were in accordance with ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, D.M., Kim, H.C., Kim, S.W. et al. Torsed appendix epididymis in an adult: misdiagnosis as tumor of tunica vaginalis on sonography. J Med Ultrasonics 45, 363–365 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-017-0828-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-017-0828-z