Abstract
Purpose
To apply the acceleration time (AcT) ratio as an additional marker for diagnosing internal carotid artery (ICA) stenosis.
Methods
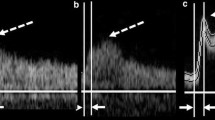
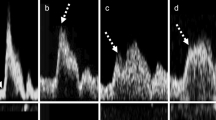
Carotid artery sonography was performed in 140 patients, and the AcT ratio was calculated as the AcT of the ICA divided by the AcT of the ipsilateral common carotid artery, and compared with diameter stenosis.
Results
There was a significant correlation between diameter stenosis and the AcT ratio. The receiver operating characteristic curve revealed a cutoff level of 1.5, with 90.0 % sensitivity and 93.5 % specificity for stenosis >65 %.
Conclusion
Our results indicate that applying the AcT ratio can help in the diagnosis of ICA stenosis.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Koga M, Kimura K, Minematsu K, et al. Diagnosis of internal carotid artery stenosis greater than 70% with power Doppler duplex sonography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001;22:413–7.
Handa N, Fukunaga R, Etani H, et al. Efficacy of echo-Doppler examination for the evaluation of renovascular disease. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1988;14:1–5.
European Carotid Surgery Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Randomised trial of endarterectomy for recently symptomatic carotid stenosis: final results of the MRC European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST). Lancet. 1998;351:1379–87.
The Joint Committee of the Japan Academy of Neurosonology and the Japan Society of Embolus Detection and Treatment on Guideline for Neurosonology. Carotid Ultrasound Examination. Neurosonology. 2006;19:49–67.
Schäberle W. Ultrasonography in vascular diagnosis. Berlin: Springer; 2011.
Tamura H, Akaiwa Y, Onda K. Usefulness of acceleration time for internal carotid artery origin stenosis. J Jpn Coll Angiol. 2011;51:365–71.
Takekawa H, Asakawa Y, Lee T, et al. Usefulness of acceleration time for assessment of stenosis in the extracranial internal carotid artery. Neurosonology. 2009;22:79–82.
Barnett HJ, Taylor DW, Eliasziw M, et al. Benefit of carotid endarterectomy in patients with symptomatic moderate or severe stenosis. North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1415–25.
Cremonesi A, Setacci C, Bignamini A, et al. Carotid artery stenting: first consensus document of the ICCS-SPREAD Joint Committee. Stroke. 2006;37:2400–9.
Naylor AR, Lin PH, Chaikof EL. Carotid artery disease. In: Davies AH, Brophy CM, editors. Vascular surgery. London: Springer; 2010. p. 155–80.
Oates CP, Naylor AR, Hartshorne T, et al. Joint recommendations for reporting carotid ultrasound investigations in the United Kingdom. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2009;37:251–61.
Zümre O, Salbacak A, Cicekcibasi AE, et al. Investigation of the bifurcation level of the common carotid artery and variations of the branches of the external carotid artery in human fetuses. Ann Anat. 2005;187:361–9.
O’Boyle MK, Vibhakar NI, Chung J, et al. Duplex sonography of the carotid arteries in patients with isolated aortic stenosis: imaging findings and relation to severity of stenosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1996;166:197–202.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Takekawa, H., Suzuki, K., Takada, E. et al. Acceleration time ratio for the assessment of extracranial internal carotid artery stenosis. J Med Ultrasonics 41, 63–67 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-013-0471-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-013-0471-2