Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to assess prognostic factors in patients with congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH).
Methods
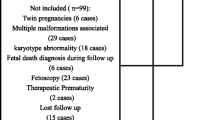
Thirteen patients with CDH diagnosed antenatally and delivered in our hospital between 1995 and 2006 were retrospectively studied. Assessments of sonographic examinations included gestational age at time of diagnosis; the ultrasonographic parameters [amniotic fluid index, cardiothoracic area ratio, and the lung-thoracic transverse area ratio (LTR)]; and the incidence of polyhydramnios, intrauterine growth retardation, and hydrops. Doppler velocimetry measurements comprised the resistance index of the umbilical artery, the resistance index of the midcerebral artery, the maximal velocity of the descending aorta, and the preload index of the inferior vena cava (IVCPLI). Results were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation. The features of survivors and nonsurvivors were compared.
Results
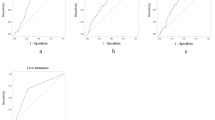
Six fetuses were survivors and seven were nonsurvivors. The mean LTR value tended to be markedly low in both groups (23.8 ± 16.4 vs 12.1 ± 1.1). In Doppler analysis, the mean IVCPLI value in survivors was significantly lower than that in nonsurvivors (0.34 ± 0.08 vs 0.52 ± 0.14, P = 0.01).
Conclusion
We concluded that fetal IVCPLI might be a good predictor of the outcome in patients with CDH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adzick NS, Harrison MR, Glick PL, et al. Diaphragmatic hernia in the fetus: prenatal diagnosis and outcome in 94 cases. J Pediatr Surg 1985;20:357–361.
Sharland GK, Lockhart SM, Heward AJ, et al. Prognosis in fetal diaphragmatic hernia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1992;166:9–13.
Harrison MR, Adzick NS, Estes JM, et al. A prospective study of the outcome for fetuses with diaphragmatic hernia. JAMA 1994;271:382–384.
Levin D. Morphologic analysis of the pulmonary vascular bed in congenital left-sided diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr 1978;92:805–809.
Pringle KC, Turner JW, Schofield JC, et al. Creation and repair of diaphragmatic hernia in the fetal lamb: lung development and morphology. J Pediatr Surg 1984;19:131–140.
George DK, Cooney TP, Chiu BK, et al. Hypoplasia and immaturity of the terminal lung unit in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1987;136:947–950.
O’Rourke PP, Vacanti JP, Crone RK, et al. Use of the postductal PaO2 as a predictor of pulmonary vascular hypoplasia in infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 1988;23:904–907.
Shochat S. Pulmonary vascular abnormalities in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Mod Probl Paediatr 1989;24:54–61.
Wilson JM, Lund DP, Lillehei CW, et al. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Predictors of severity in the ECMO era. J Pediatr Surg 1991;26:1028–1034.
Glick PL, Stannard VA, Leach CL, et al. Pathophysiology of congenital diaphragmatic hernia 2: the fetal lamb CDH model is surfactant deficient. J Pediatr Surg 1992;27:382–388.
Karamanoukian HL, Glick PL. Fetal upper respiratory tract function in antenatally diagnosed congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1994;14:254–255.
Chinn DH, Filly RA, Callen PW, et al. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia diagnosed prenatally by ultrasound. Radiology 1983;148:119–123.
Adzick NS, Vacanti JP, Lillehei CW, et al. Fetal diaphragmatic hernia: ultrasound diagnosis and clinical outcome in 38 cases. J Pediatr Surg 1989;24:654–658.
Harrison MR, Langer JC, Adzick NS, et al. Correction of congenital diaphragmatic hernia in utero, V. Initial clinical experience. J Pediatr Surg 1990;25:47–57.
Manni M, Heydanus R, Den Hollander NS, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a retrospective analysis of cases. Prenat Diagn 1994;14:187–190.
Burge DM, Atwell JD, Freeman NV. Could the stomach site help predict outcome in babies with left-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia diagnosed antenatally? J Pediatr Surg 1989;24:567–569.
Crawford DC, Wright VM, Drake DP, et al. Fetal diaphragmatic hernia: the value of fetal echocardiography in the prediction of postnatal outcome. Br J Obstet Gynecol 1989;96:705–710.
Kamata S, Hasegawa T, Ishikawa S, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of congenital diaphragmatic hernia and perinatal care: assessment of lung hypoplasia. Early Hum Dev 1992;29:375–379.
Metkus AP, Filly RA, Stringer MD, et al. Sonographic predictors of survival in fetal diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 1996;31:148–151.
Fox HE, Ba dalian SS, Fifer WP. Patterns of fetal perinasal fluid flow in cases of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1997;176:807–813.
Kalache KD, Hartung CJ, Wernecke KD, et al. Doppler assessment of tracheal fluid flow during fetal breathing movements in cases of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998;12:27–32.
Rabih C, Karim K, Cornelia T, et al. Pulmonary arterial Doppler velocimetry in fetuses with lung hypoplasia. Eur J Obstet Gynecol 1999;84:179–185.
Detti L, Mari G, Ferguson JE. Color Doppler ultrasonography of the superior mesenteric artery for prenatal ultrasonographic diagnosis of a left-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Ultrasound Med 2001;20:689–692.
Phelan JP, Ahn MO, Smith CV, et al. Amniotic fluid index measurements during pregnancy. J Reprod Med 1987;32:601–604.
Hasegawa T, Kamata S, Imura K, et al. Use of lung-thorax transverse area ratio in the antenatal evaluation of lung hypoplasia in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Clin Ultrasound 1990;18:705–709.
Kanzaki T, Chiba Y. Evaluation of preload condition of the fetus by inferior vena caval blood flow pattern. Fetal Diagn Ther 1990;5:168–174.
Goodfellow T, Hyde I, Burge DM, et al. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: the prognostic significance of the site of the stomach. Br J Radiol 1987;60:993–995.
Hatch EI, Kendall J, Blumhagen J. Stomach position as an in utero predictor of neonatal outcome in left-sided diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 1992;27:778–779.
Stringer M, Goldstein R, Filly R, et al. Fetal diaphragmatic hernia without visceral herniation. J Pediatr Surg 1995;30:1264–1266.
Albanese CT, Lopoo J, Goldstein RB, et al. Fetal liver position and perinatal outcome for congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Prenat Diagn 1998;18:1138–1142.
Lipshutz G, Albanese C, Feldstein V, et al. Lung-to-head ratio predicts survival in prenatally diagnosed congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 1997;32:1634–1646.
Kamata S, Hasegawa T, Matsuo Y. Fetal diaphragmatic hernia: prenatal evaluation of lung hypoplasia and effects of immediate operation. Pediatr Surg Int 1992;7:109–112.
Badalian SS, Fox HE, Chao CR, et al. Fetal breathing characteristics and postnatal outcome in cases of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1994;171:970–976.
Fuke S, Kanzaki T, Mu J, et al. Antenatal prediction of pulmonary hypoplasia by acceleration time/ejection time ratio of fetal pulmonary arteries by Doppler blood flow velocimetry. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2003;188:228–233.
Sherer DM, Eglinton GS, Goncalves LF, et al. Prenatal color and pulsed Doppler sonographic documentation of intrathoracic umbilical vein and ductus venosus, confirming extensive hepatic herniation in left congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Am J Perinatol 1996;13:159–162.
Capponi A, Rizzo G, De Angelis C, et al. Atrial natriuretic peptide levels in fetal blood in relation to inferior vena cava velocity waveforms. Obstet Gynecol 1997;89:242–247.
Chiba Y, Utsu M, Kanzaki T, et al. Changes in venous flow and intratracheal flow in fetal breathing movements. Ultrasound Med Biol 1985;11:43–49.
Rasanen J, Wood DC, Weiner S, et al. Role of the pulmonary circulation in the distribution of human fetal cardiac output during the second half of pregnancy. Circulation 1996;94:1068–1073.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Miura, H., Ogawa, M., Sato, A. et al. Fetal preload index of the inferior vena cava and neonatal outcome of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Med Ultrasonics 36, 77–81 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-008-0209-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10396-008-0209-8