Abstract
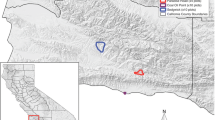
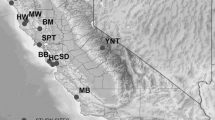
Ecologies of zoonotic vector-borne diseases may shift with climate and land use change. As many urban-adapted mammals can host ectoparasites and pathogens of human and animal health concern, our goal was to compare patterns of arthropod-borne disease among medium-sized mammals across gradients of rural to urban landscapes in multiple regions of California. DNA of Anaplasma phagocytophilum was found in 1–5% of raccoons, coyotes, and San Joaquin kit foxes; Borrelia burgdorferi in one coyote, rickettsiae in two desert kit foxes, and Yersinia pestis in two coyotes. There was serological evidence of rickettsiae in 14–37% of coyotes, Virginia opossums, and foxes; and A. phagocytophilum in 6–40% of coyotes, raccoons, Virginia opossums, and foxes. Of six flea species, one Ctenocephalides felis from a raccoon was positive for Y. pestis, and Ct. felis and Pulex simulans fleas tested positive for Rickettsia felis and R. senegalensis. A Dermacentor similis tick off a San Joaquin kit fox was PCR-positive for A. phagocytophilum. There were three statistically significant risk factors: risk of A. phagocytophilum PCR-positivity was threefold greater in fall vs the other three seasons; hosts adjacent to urban areas had sevenfold increased A. phagocytophilum seropositivity compared with urban and rural areas; and there was a significant spatial cluster of rickettsiae within greater Los Angeles. Animals in areas where urban and rural habitats interconnect can serve as sentinels during times of change in disease risk.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adjemian JZ, Adjemian MK, Foley P, Chomel BB, Kasten RW, Foley JE (2008) Evidence of multiple zoonotic agents in a wild rodent community in the eastern Sierra Nevada. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 44:737–742
Barbour AG, Bunikis J, Travinsky B, Hoen AG, Diuk-Wasser MA, Fish D, Tsao JI (2009) Niche partitioning of Borrelia burgdorferi and Borrelia miyamotoi in the same tick vector and mammalian reservoir species. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 81:1120–1131
Blanton LS, Idowu BM, Tatsch TN, Henderson JM, Bouyer DH, Walker DH (2016) Opossums and cat fleas: new insights in the ecology of murine typhus in Galveston, Texas. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 95:457
Bown KJ, Lambin X, Ogden NH, Begon M, Telford G, Woldehiwet Z, Birtles RJ (2009) Delineating Anaplasma phagocytophilum ecotypes in coexisting, discrete enzootic cycles. Emerging Infectious Disease 15:1948–1954
Brown HE, Levy CE, Enscore RE, Schriefer ME, DeLiberto TJ, Gage KL, Eisen RJ (2011) Annual seroprevalence of Yersinia pestis in coyotes as predictors of interannual variation in reports of human plague cases in Arizona, United States. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases 11:1439–1446
Carrade D, Foley J, Sullivan M, Foley CW, Sykes JE (2011) Spatial distribution of seroprevalence for Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Borrelia burgdorferi, Ehrlichia canis, and Dirofilaria immitis in dogs in Washington, Oregon, and California. Veterinary Clinical Pathology 40:293–302
Centers for Disease Control (2020) Common fleas of the United States. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/fleas/fleas_of_the_us.html
Chan YG, Cardwell MM, Hermanas TM, Uchiyama T, Martinez JJ (2009) Rickettsial outer-membrane protein B (rOmpB) mediates bacterial invasion through Ku70 in an actin, c-Cbl, clathrin and caveolin 2-dependent manner. Cellular Microbiology 11:629–644
Crooks KR (2002) Relative sensitivities of mammalian carnivores to habitat fragmentation. Conservation Biology 16:488–502
Cuarón AD, Reid F (2016) Spilogale gracilis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T136797A45221721. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T136797A45221721.en. Accessed on 21 May 2023.
Cypher BL, Rudd J, Westall T, Woods L, Stephenson N, Foley J, Richardson D, Clifford D (2016) Sarcoptic mange in endangered kit foxes (Vulpes macrotis mutica): case histories, diagnoses, and implications for conservation. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 53:46–53
Cypher BL, List R (2014) Vulpes macrotis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2014: e.T41587A62259374. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2014-3.RLTS.T41587A62259374.en. Accessed on 21 May 2023.
Cypher B (2010) Kit Foxes. In: Urban Carnivores: Ecology, Conflict, and Conservation S. Gehrt, S. Riley, and B. Cypher (editors), Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press, pp 49–60
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2012) jModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nature Methods 9:772–772
De Sousa R, Barata C, Vitorino L, Santos-Silva M, Carrapato C, Torgal J, Walker D, Bacellar F (2006) Rickettsia sibirica isolation from a patient and detection in ticks. Portugal. Emerging Infectious Diseases 12:1103
Delisle J, Mendell NL, Stull-Lane A, Bloch KC, Bouyer DH, Moncayo AC (2016) Human infections by multiple spotted fever group rickettsiae in Tennessee. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 94:1212
Drazenovich NL, Brown RN, Foley JE (2006) Use of real-time quantitative PCR targeting the msp2 protein gene to identify cryptic Anaplasma phagocytophilum infections in wildlife and domestic animals. Vector Borne and Zoonotic Diseases 6:83–90
Eisen RJ, Gage KL (2012) Transmission of flea-borne zoonotic agents. Annual Review of Entomology 57:61–82
Eremeeva ME, Dasch GA (2015) Challenges posed by tick-borne rickettsiae: eco-epidemiology and public health implications. Frontiers in Public Health 3:55
Foley J (2000) Human ehrlichiosis: a review of clinical disease and epidemiology for the physician. Infectious Disease in Clinical Practice 9:93–98
Foley JE, Foley P, Madigan JE (2001) Spatial distribution of seropositivity to the causative agent of granulocytic ehrlichiosis in dogs in California. American Journal of Veterinary Research 62:1599–1605
Foley JE, Foley P, Brown RN, Lane RS, Dumlers JS, Madigan JE (2004) Ecology of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Borrelia burgdorferi in the western United States. Journal of Vector Ecology 29:41–50
Furman DP, Loomis EC (1984) The Ticks of California (Acari: Ixodida). Berkeley, CA: University of California Press
Gage KL, Kosoy MY (2005) Natural history of plague: perspectives from more than a century of research. Annual Review of Entomology 50:505–528
Gage KL, Burkot TR, Eisen RJ, Hayes EB (2008) Climate and vectorborne diseases. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 35:436–450
Gehrt SD, Anchor C, White LA (2009) Home range and landscape use of coyotes in a metropolitan landscape: conflict or coexistence? Journal of Mammalogy 90:1045–1057
Heath DG, Anderson GW Jr, Mauro JM, Welkos SL, Andrews GP, Adamovicz J, Friedlander AM (1998) Protection against experimental bubonic and pneumonic plague by a recombinant capsular F1-V antigen fusion protein vaccine. Vaccine 16:1131–1137
Hechemy K, Raoult D, Fox J, Han Y, Elliott L, Rawlings J (1989) Cross-reaction of immune sera from patients with rickettsial diseases. Journal of Medical Microbiology 29:199–202
Helgen K, Reid F (2016) Mephitis mephitis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T41635A45211301. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T41635A45211301.en. Accessed on 21 May 2023.
Holden K, Boothby JT, Anand S, Massung RF (2003) Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi, Ehrlichia chaffeensis, and Anaplasma phagocytophilum in ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) from a coastal region of California. Journal of Medical Entomology 40:534–539
Jaarsma RI, Sprong H, Takumi K, Kazimirova M, Silaghi C, Mysterud A, Rudolf I, Beck R, Földvári G, Tomassone L (2019) Anaplasma phagocytophilum evolves in geographical and biotic niches of vertebrates and ticks. Parasites & Vectors 12:1–17
Jado I, Oteo JA, Aldámiz M, Gil H, Escudero R, Ibarra V, Portu J, Portillo A, Lezaun MJ, García-Amil C (2007) Rickettsia monacensis and human disease. Spain. Emerging Infectious Diseases 13:1405
Johnson CK, Hitchens PL, Pandit PS, Rushmore J, Evans TS, Young CC, Doyle MM (2020) Global shifts in mammalian population trends reveal key predictors of virus spillover risk. Proceedings of the Royal Society B 287:20192736
Jones KE, Patel NG, Levy MA, Storeygard A, Balk D, Gittleman JL, Daszak P (2008) Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature 451:990–993
Karpathy SE, Slater KS, Goldsmith CS, Nicholson WL, Paddock CD (2016) Rickettsia amblyommatis sp. nov., a spotted fever group Rickettsia associated with multiple species of Amblyomma ticks in North, Central and South America. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 66:5236
Kays R (2018) Canis latrans (errata version published in 2020). The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2018: e.T3745A163508579, https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T3745A163508579.en. Accessed on 21 May 2023.
Kim YS, Choi YJ, Lee KM, Ahn KJ, Kim HC, Klein T, Jiang J, Richards A, Park KH, Jang WJ (2017) First isolation of Rickettsia monacensis from a patient in South Korea. Microbiology and Immunology 61:258–263
Koopman ME, Scrivner JH, Kato T (1998) Patterns of den use by San Joaquin kit foxes. Journal of Wildlife Management 62:373–379
Krasnov BR (2008) Functional and Evolutionary Ecology of Fleas: a model for ecological parasitology. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Kulldorff M, Heffernan R, Hartman J, Assuncao R, Mostashari F (2005) A space-time permutation scan statistic for disease outbreak detection. PLoS Medicine 2:216–224
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Molecular Biology and Evolution 35:1547–1549
Lado P, Glon M, Klompen H (2021) Integrative taxonomy of Dermacentor variabilis (Ixodida: Ixodidae) with description of a new species, Dermacentor similis n. sp. Journal of Medical Entomology 58:2216–2227
Levin ML, Nicholson WL, Massung RF, Sumner JW, Fish D (2002) Comparison of the reservoir competence of medium-sized mammals and Peromyscus leucopus for Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Connecticut. Vector Borne and Zoonotic Diseases 2:125–136
López-Pérez A, Sánchez-Montes S, Foley J, Guzmán-Cornejo C, Colunga-Salas P, Pascoe E, Becker I, Delgado-de la Morae J, Licona-Enriquez J, Suzan G (2019) Molecular evidence of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto and Rickettsia massiliae in ticks collected from a domestic-wild carnivore interface in Chihuahua, Mexico. Ticks and Tick-Borne Disease 10:1118–1123
Los Angeles County Department of Public Health (2022) Facts about plague in Los Angelos County, http://publichealth.lacounty.gov/acd/docs/Facts%20Plague.pdf, accessed 23 March 2022.
Macaluso KR, Sonenshine DE, Ceraul SM, Azad AF (2002) Rickettsial infection in Dermacentor variabilis (Acari: Ixodidae) inhibits transovarial transmission of a second Rickettsia. Journal of Medical Entomology 39:809–813
Madeddu G, Mancini F, Caddeo A, Ciervo A, Babudieri S, Maida I, Fiori ML, Rezza G, Mura MS (2012) Rickettsia monacensis as cause of Mediterranean spotted fever–like illness. Italy. Emerging Infectious Diseases 18:702
McGee BK, Butler MJ, Pence DB, Alexander JL, Nissen JB, Ballard WB, Nicholson KL (2006) Possible vector dissemination by swift foxes following a plague epizootic in black-tailed prairie dogs in northwestern Texas. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 42:415–420
Moncayo AC, Cohen SB, Fritzen CM, Huang E, Yabsley MJ, Freye JD, Dunlap BG, Huang J, Mead DG, Jones TF (2010) Absence of Rickettsia rickettsii and occurrence of other spotted fever group rickettsiae in ticks from Tennessee. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 83:653
Nelson K, Maina AN, Brisco A, Foo C, Croker C, Ngo V, Civen R, Richards AL, Fujioka K, Wekesa JW (2018) A 2015 outbreak of flea-borne rickettsiosis in San Gabriel Valley, Los Angeles County. California. Plos Neglected Tropical Diseases 12:e0006385
Novakova M, Literak I, Chevez L, Martins TF, Ogrzewalska M, Labruna MB (2015) Rickettsial infections in ticks from reptiles, birds and humans in Honduras. Ticks and Tick-Borne Diseases 6:737–742
Olson PE, Kallen AJ, Bjorneby JM, Creek JG (2000) Canines as sentinels for Lyme disease in San Diego County, California. Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation 12:126–129
Paddock CD, Allerdice ME, Karpathy SE, Nicholson WL, Levin ML, Smith TC, Becker T, Delph RJ, Knight RN, Ritter JM (2017) Unique strain of Rickettsia parkeri associated with the hard tick Dermacentor parumapertus Neumann in the western United States. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 83:e03463-e3416
Patz J, Githeko A, McCarty J, Hussein S, Confalonieri U, De Wet N (2003) Climate change and infectious diseases. In: Climate change and human health: risks and responses Geneva: World Health Organization, pp 103–137
Plourde BT, Burgess TL, Eskew EA, Roth TM, Stephenson N, Foley JE (2017) Are disease reservoirs special? Taxonomic and life history characteristics. PLoS One 12:e0180716
Poessel SA, Breck SW, Gese EM (2016) Spatial ecology of coyotes in the Denver metropolitan area: influence of the urban matrix. Journal of Mammalogy 97:1414–1427
Randa LA, Yunger JA (2004) The influence of prey availability and vegetation characteristics on scent station visitation rates of coyotes, Canis latrans, in a heterogeneous environment. The Canadian Field-Naturalist 118:341–353
Riley SP, Sauvajot RM, Fuller TK, York EC, Kamradt DA, Bromley C, Wayne RK (2003) Effects of urbanization and habitat fragmentation on bobcats and coyotes in southern California. Conservation Biology 17:566–576
Riley SP, Cypher BL, Gehrt SD (2010) Urban Carnivores. Baltimore: JHU Press
Rochlin I, Toledo A (2020) Emerging tick-borne pathogens of public health importance: a mini-review. Journal of Medical Microbiology 69:781
Roemer GW, Cypher BL (2016) Urocyon cinereoargenteus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T22780A46178068. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T22780A46178068.en. Accessed on 21 May 2023.
Roux V, Raoult D (2000) Phylogenetic analysis of members of the genus Rickettsia using the gene encoding the outer-membrane protein rOmpB (ompB). International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology 50:1449–1455
Rudenko N, Golovchenko M, Grubhoffer L, Oliver JH Jr (2009) Borrelia carolinensis sp. nov., a new (14th) member of the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex from the southeastern region of the United States. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 47:134–141
Rust JH Jr, Cavanaugh DC, O’Shita R, Marshall JD Jr (1971) The role of domestic animals in the epidemiology of plague. I. Experimental infection of dogs and cats. Journal of Infectious Diseases 124:522–526
Sacks BN (2005) Reproduction and body condition of California coyotes (Canis latrans). Journal of Mammalogy 86:1036–1041
Salkeld DJ, Eisen RJ, Stapp P, Wilder AP, Lowell J, Tripp DW, Albertson D, Antolin MF (2007) The potential role of swift foxes (Vuples velox) and their fleas in the plague outbreaks in prairie dogs. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 43
Sarwar M (2016) Diseases transmitted by blood sucking mites and integrated mite management for their prevention. American Journal of Food Science and Health 2:169–175
Simes MT, Longshore KM, Nussear KE, Beatty GL, Brown DE, Esque TC (2015) Black-tailed and white-tailed jackrabbits in the American West: History, ecology, ecological significance, and survey methods. Western North American Naturalist 75:491–519
Sonenshine DE (2018) Range expansion of tick disease vectors in North America: implications for spread of tick-borne disease. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 15:478
Stark H (1958) The Siphonoptera of Utah: Their taxonomy, distribution, host relations, and medical importance. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, Public Health Service, Bureauof State Services Communicable Disease Center
Stenos J, Graves SR, Unsworth NB (2005) A highly sensitive and specific real-time PCR assay for the detection of spotted fever and typhus group rickettsiae. American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene 73:1083–1085
Stuen S, Granquist EG, Silaghi C (2013) Anaplasma phagocytophilum—a widespread multi-host pathogen with highly adaptive strategies. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 3:31
Thomas CU, Hughes PE (1992) Plague surveillance by serological testing of coyotes (Canis latrans) in Los Angeles County, California. Journal of Wildlife Diseases 28:610–613
US Census Bureau (2020) Urban and rural. https://www.census.gov/programs-surveys/geography/guidance/geo-areas/urban-rural.html, Retrieved September 16, 2020.
Versage J, Severin D, Chu M, Petersen J (2003) Development of a multitarget real-time TaqMan PCR assay for enhanced detection of Francisella tularensis in complex specimens. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 41:5492–5499
Villarreal Z, Stephenson N, Foley J (2018) Possible northward introgression of a tropical lineage of Rhipicephalus sanguineus ticks at a site of emerging Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Journal of Parasitology 104:240–245
Walker JB, Keirans JE, Horak IG (2000) The genus Rhipicephalus (Acari, Ixodidae): a guide to the brown ticks of the world. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press
Webb L, Carl M, Malloy DC, Dasch GA, Azad AF (1990) Detection of murine typhus infection in fleas by using the polymerase chain reaction. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 28:530–534
Westrom D, Lane R, Anderson J (1985) Ixodes pacificus (Acari: Ixodidae): population dynamics and distribution on Columbian Black-tailed deer (Odocoileus hemionus columbianus). Journal of Medical Entomology 22:507–511
Whitaker J (1996) National Audubon Society Field Guide to North American Mammals. New York: Knopf
Yabsley MJ, Murphy SM, Luttrell MP, Little SE, Massung RF, Stallknecht DE, Conti LA, Blackmore CG, Durden LA (2008) Experimental and field studies on the suitability of raccoons (Procyon lotor) as hosts for tick-borne pathogens. Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases 8:491–504
Acknowledgements
We thank fellow laboratory members in the Foley Laboratory of Infectious Disease Ecology, especially Laura Backus, Alejandra Castillo Valenzuela, Kim Conway, and Nadia Javeed; Kelsey Clark at CDFW; and Patrick Foley. JEF acknowledges funding support from the Pacific Southwest Regional Center of Excellence for Vector-borne Diseases funded by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (Cooperative Agreement 1U01CK000516); and LCS was supported by the Preventive Veterinary Medicine Graduate Group.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Figure 1
. Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree generated with the General Time Reversible Model with Gamma distribution (GTR + G) of the gltA gene of Rickettsia species in medium sized mammals and their ectoparasites from the greater LA region of southern California. Each sequence is indicated by its GenBank accession number, sample type (ectoparasite species/tissue), and host species (VM = Vulpes macrotis; CL = Canis latrans; PL = Procyon lotor; DV = Didelphis virginiana). Bold font indicates samples from this study. Numbers in parentheses are the number of sequences obtained from tissue and ectoparasite.
Supplementary file1 (TIF 776 KB)
Supplementary Figure 2
. Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree generated with the General Time Reversible Model with Gamma distribution (GTR + G) of the ompB gene of Rickettsia species in medium sized mammals and their ectoparasites from the greater LA region of southern California. Each sequence is indicated by its GenBank accession number, sample type (ectoparasite species/tissue), and host species (VM = Vulpes macrotis; CL = Canis latrans; PL = Procyon lotor; DV = Didelphis virginianawalker). Bold font indicates samples from this study. Numbers in parentheses are the number of sequences obtained from tissue and ectoparasite.
Supplementary file2 (TIF 709 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shultz, L., López-Pérez, A.M., Jasuja, R. et al. Vector-Borne Disease in Wild Mammals Impacted by Urban Expansion and Climate Change. EcoHealth 20, 286–299 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10393-023-01650-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10393-023-01650-x