Abstract
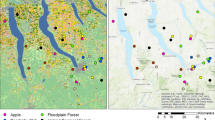
Anthropogenic food is often concentrated in cities where it can attract wildlife, promote conflict with people, and potentially spread disease. Although these associations are well-documented for conventional garbage, they are unexplored for many seemingly innocuous and even environmentally friendly attractants such as piles of compost. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that municipal piles of compost are underappreciated and potentially important contributors to a recent rise in encounters with urban-adapted wildlife by attracting wildlife and promoting the spread of wildlife disease. We used remote cameras to compare visitation rates to compost piles and urban natural areas by coyotes (Canis latrans). For each site type, we assessed photographs for evidence of ectoparasites, screened scats for endoparasites, and sampled compost for harmful mycotoxins. At compost piles, visitation rates were eight times more frequent, coyotes with visible parasitic infections were 4.5 times more common, scats were 10 times more likely to contain tapeworm eggs, and mycotoxins were detected in 86% of piles and often at concentrations higher than legal limits for animal feed. Greater securement of compost waste in cities may reduce encounters with animals, susceptibility to and spread of disease, and rates of human–wildlife conflict for coyotes and other urban-adapted species.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alzaga V, Vicente J, Villanua D, Acevedo P (2008) Body condition and parasite intensity correlates with escape capacity in Iberian hares (Lepus granatensis). Behav Ecol Sociobiol 62:769–775. doi:10.1007/s00265-007-0502-3.
Arjo WM, Pletscher DH, Ream RR (2002) Dietary overlap between wolves and coyotes in northwestern Montana. J Mammal 83:754–766. doi: 10.1644/1545-542(2002)083<0754:DOBWAC>2.0.CO;2.
Arlian LG, Runyan RA, Achar S, Estes SA (1984) Survival and infectivity of Sarcoptes scabiei var. canis and var. hominis. J Am Acad Dermatol 11: 210–215.
Arlian LG, Vyszenski-Moher DL, Pole MJ (1989) Survival of adults and development stages of Sarcoptes scabiei var. canis when off the host. Exp Appl Acarol 6:181–7.
Becker DJ, Streiker DG, Altizer S (2015) Linking anthropogenic resources to wildlife – pathogen dynamics: a review and meta-analysis. Ecol Lett 18:483-495. doi:10.1111/ele.12428.
Bekoff, M (Ed.) (1978) Coyotes: biology, behavior, and management. New York: Academic Press.
Bhat R V, Beedu SR, Ramakrishna Y, Munshi K (1989) Outbreak of trichotothecene mycotoxicosis associated with consumption of mould-damaged wheat products in Kashmir Valley, India. Lancet 3333(8628):35–37.
Bivand R, Piras G (2015) Comparing Implementations of estimation methods for spatial econometrics. Journal of Statistical Software 63:1–36. http://www.jstatsoft.org/v63/i18/.
Conover MR (2002a) Diversion. In: Resolving Human-Wildlife Conflicts. CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, pp 271–289.
Conover MR (2002b) Exclusion. In: Resolving Human-Wildlife Conflicts. CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, pp 291–319.
CONTAM (2011) Scientific Opinion on the risks for animal and public health related to the presence of T-2 and HT-2 toxin in food and feed. EFSA J 9:187. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2481.
Gabrey SW, Belant JL, Dolbeer RA, Bernhardt GE (1994) In my experience: Bird and rodent abundance at yard-waste compost facilities in Northern Ohio. Wild Soc Bull 22:288-295.
Gehrt SD, Riley SPD (2010) Coyotes (Canis latrans). In: Gehrt S, Riley S, Cypher B (eds) Urban carnivores: ecology, conflict, and conservation. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, ML, pp 79–95.
Gottdenker NL, Streicker DG, Faust CL, Carroll CR (2014) Anthropogenic land use change and infectious diseases: A review of the evidence. Ecohealth 11:619–632. doi:10.1007/s10393-014-0941-z.
Leung M, Smith T, Karrow N, Boermans H (2007) Effects of foodborne Fusarium mycotoxins with and without a polymeric glucomannan mycotoxin adsorbent on food intake and nutrient digestibility, body weight, and physical and clinicopathologic variables of mature dogs. Am J Vet Res 68:122–129.
Leung MC, Diaz-Llano G, Smith TK (2006) Mycotoxins in Pet Food: A review on worldwide prevalence and preventative strategies. J Agric Food Chem 54: 9623–9635.
Liccioli S, Kutz SJ, Ruckstuhl KE, Massolo A (2014) Spatial heterogeneity and temporal variations in Echinococcus multilocularis infections in wild hosts in a North American urban setting. Int J Parasitol 44:457–465. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2014.03.007.
Lukasik VM, Alexander SM (2012) Spatial and temporal variation of coyote (Canis latrans) diet in Calgary, Alberta. Cities Environ 4:1–25.
Morey PS, Gese EM, Gehrt S (2007) Spatial and temporal variation in the diet of coyotes in the Chicago Metropolitan Area. Am Midl Nat 158:147–161.
Murray M, Cembrowski A, Latham ADM, Lukasik VM, Pruss S, St Clair CC (2015a) Greater consumption of protein-poor anthropogenic food by urban relative to rural coyotes increases diet breadth and potential for human-wildlife conflict. Ecography 38:1 – 8. doi:10.1111/ecog.01128.
Murray M, Edwards MA, Abercrombie B, Cassady C, Clair S (2015b) Poor health is associated with use of anthropogenic resources in an urban carnivore. Proc R Soc B 282:20150009.
Mustapha I (2013) Composting by households in Canada. EnviroStats 7:1–6.
Oleaga A, Casais R, Balseiro A, Espí A, Llaneza L, Hartasánchez A, Gortázar C (2011) New techniques for an old disease: sarcoptic mange in the Iberian wolf. Vet Parasitol 181:255–66. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.04.036.
Oro D, Genovart M, Tavecchia G, Fowler MS, Martínez-Abraín A (2013) Ecological and evolutionary implications of food subsidies from humans. Ecol Lett 16:1501–1514. doi:10.1111/ele.12187.
Pinheiro J, Bates D, DebRoy S, Sarkar D, Team RDC (2012) nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. R Package Version 3. ftp://ftp.uni-bayreuth.de/pub/math/statlib/R/CRAN/doc/packages/nlme.pdf.
Rundberget T, Skaar I, Flåøyen A (2004) The presence of Penicillium and Penicillium mycotoxins in food wastes. Int J Food Microbiol 90:181–188. doi:10.1016/S0168-1605(03)00291-5.
Samuel W, Pybus MJ, Kocan AA (2001) Parasitic diseases of wild mammals, 2nd edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames.
Stock TM, Vasseur K, Anton C (2014) Parasites in parks: The zoonotic potential related to socioeconomic factors and types of pets. Cities and the Environment 7(2):3.
Taylor AK, Cao W, Vora KP, De La Cruz J, Shieh W-J, Zaki SR, Katz JM, Sambhara S, Gangappa S (2013) Protein energy malnutrition decreases immunity and increases susceptibility to influenza infection in mice. J Infect Dis 207:501–10. doi:10.1093/infdis/jis527.
Veit P, Bilger B, Schad V, Schäfer J, Frank W, Lucius R (1995) Influence of environmental factors on the infectivity of Echinococcus multilocularis eggs. Parasitology 110:79–86.
Yeakel JD, Patterson BD, Fox-Dobbs K, Okumura MM, Cerling TE, Moore JW, Koch PL, Dominy NJ (2009) Cooperation and individuality among man-eating lions. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106:19040–3. doi:10.1073/pnas.0905309106.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Mary Zhou for her conceptual contributions to mycotoxin screening and to several field assistants and volunteers for help with data collection. We appreciate funding from the Alberta Conservation Association, Alberta Innovates, the Alberta Sport, Recreation, Parks, and Wildlife Foundation, the Canadian Wildlife Foundation, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Royal Alberta Museum, and the Vanier Canada Graduate Scholarships Program. Camera monitoring was conducted with a City of Edmonton Partners in Parks Agreement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murray, M.H., Hill, J., Whyte, P. et al. Urban Compost Attracts Coyotes, Contains Toxins, and may Promote Disease in Urban-Adapted Wildlife. EcoHealth 13, 285–292 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10393-016-1105-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10393-016-1105-0