Abstract
Aim
To explore the influencing factors of Chinese elderly health literacy (HL) by using meta-analysis method and to provide reference for the development of elderly HL intervention strategies.
Methods
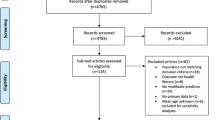
CNKI, CBMdisc, WanFang, VIP, PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Springer Link, Cochrane Library, Wiley Online Library, Elsevier Science Direct, and EBSCO databases were used to search for published HL research. The search time limit was from the establishment of the database to the end of February 2021.
Results
A total of 31 studies were included. The HL level of the elderly was 12.28% (95% CI, 10.70%–13.95%), with three dimensions: knowledge (20.35%, 95% CI, 17.91–22.90%), behavior (14.69%, 95% CI, 12.37–17.18%) and skills (17.82%, 95% CI, 16.29–19.41%). Regression analysis found that general physical condition (OR 1.38, 95% CI, 1.11–1.71), with or without spouse (OR 1.38, 95% CI, 1.13–1.70), population distribution (OR 1.72, 95% CI, 1.49–1.99), and place of residence (OR 2.51, 95% CI, 2.14–2.94) were the main influencing factors of low HL levels in the elderly in China.
Conclusion
Chinese elderly people who generally have low HL levels tend to live in rural areas, non-eastern regions, have poor general health, and no spouse, and targeted measures will help to improve HL levels in Chinese elderly people.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
This meta-analysis study was based on secondary data sources (published studies).
Code availability
revman 5.4
References
Baker DW et al (1996) The health care experience of patients with low literacy. Arch Fam Med 5(6):329–334. https://doi.org/10.1001/archfami.5.6.329
Chen YF et al (2018) Analysis of the health literacy of the elderly and its influencing factors. Prev Med 30(09):964–966 (in Chinese)
Department of Health and Human Services, US (2008) Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The six domains of health care quality. https://cahps.ahrq.gov/consumer-reporting/talkingquality/create/sixdomains.html
Walt D et al (2004) Literacy and health outcomes: a systematic review of the literature. J Gen Intern Med 19(12):1228–1239. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1497.2004.40153.x
Ding XM (2020) Study on the supply and demand of long-term care services for the elderly in China. Dissertation, University of International Business and Economics (in Chinese)
Du WJ et al (2015) Analysis of status and influence factors of health literacy of Chinese residents aged 60-69 years. Chin Health Edu 31:129–133 (in Chinese)
Elliott JO et al (2007) A health literacy assessment of the National Epilepsy Foundation web site. Epilepsy Behav 11(4):525–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2007.08.021
Fabbri M et al (2020) Health literacy and outcomes among patients with heart failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JACC Heart Fail 8(6):451–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchf.2019.11.007
General Office of the State Council, PRC (2016a) Outline of Healthy China 2030 Plan http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2016-10/25/content_5124174.htm Accessed 25 October 2016
General Office of the State Council, PRC (2017) China’s Medium- and Long-Term Plan for Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Diseases (2017–2025).http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2017-02/14/content_5167886.htm. Accessed 14 February 2021
General Office of the State Council, PRC (2017b) The 13th Five-Year Plan on Hygiene and Health http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2017-01/10/content_5158488.htm. Accessed 10 January 2017
General Office of the State Council, PRC (2017c) “13th Five-Year” Plan for the Development of the National Aging and the Construction of the Aging System http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2017-03/06/content_5173930.htm. Accessed 06 March 2017
General Office of the State Council, PRC (2016b) General Office of the State Council on printing and distributing the development plan for elderly education (2016–2020). http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/content/2016-10/19/content_5121344.htm?isappinstalled=0. Accessed 19 October 2016
Guo HJ et al (2020a) Difference analysis on health management status and health literacy of elderly people in urban and rural areas in Zunyi City. Chin J Pub Health Manage 36(05):718–722 (in Chinese)
Guo XR (2013) Study on multimorbidity and it’s main influence factors among elderly in China. Dissertation, Xiamen University (in Chinese)
Guo Y et al (2020b) The health literacy level and influencing factors of the elderly 60-69 years old in Xiangtan City. Health Voc Edu 38(02):122–125 (in Chinese)
He ZF (2013) Current status, influence and measures of health literacy of the elderly in rural areas of China. Shanxi Agr Econ 10:30–31 (in Chinese)
Hu J et al (2016) Health literacy and its influencing factors among residents aged 60-69 years in Jiangsu province. Chin Pub Health 32(09):1156–1158 (in Chinese)
Huang TN et al (2019) Investigation and analysis of the health literacy level of the elderly in the community. Chin Health Indus 16(28):160–162 (in Chinese)
Hochhauser M et al (2019) Health literacy in an Israeli elderly population. Isr J Health Policy Res 8(1):61. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13584-019-0328-2
Huang XY et al (2020) Chronic disease prevention and control literacy and influencing factors of residents of different age groups in Pudong new area, Shanghai in 2018. Chin J Prevent Control Dis 28(09):702–705 (in Chinese)
Jia X (2020) Current situation of health literacy and related research progress of elderly in China. Chin J Pub Health Manage 36(06):790–793 (in Chinese)
Kobayashi L et al (2016) Aging and functional health literacy: a systematic review and Meta-Analysis.Psychol. Sci Soc Sci 71(3):445–457. https://doi.org/10.1093/geronb/gbu161
Lee SY et al (2004) Health literacy, social support, and health: a research agenda. Soc Sci Med 58(7):1309–1321. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0277-9536(03)00329-0
Li HD et al (2021) Regional differences and trends of aging in China. Statistics Decision 37(03):71–75 (in Chinese)
Li L et al (2014) Research on the status and influencing factors of health literacy among urban community elderly residents. Mod Prev Med 41(21):3931–3935 (in Chinese)
Li XX et al (2019) The health literacy level and its influencing factors of the elderly aged 60-69 in Jilin Province. Chin J Gerontol 39(02):458–461 (in Chinese)
Li YF (2016) Evaluation of the intervention effect of the Teach-back method on the health literacy of the elderly in Urumqi nursing homes. Dissertation, Xinjiang medical university (in Chinese)
Liang XQ et al (2013) Investigation of elderly health literacy and influencing factors in Erdos city. Chin J Nurs Edu 10(02):90–93 (in Chinese)
Liu JL et al (2018) Influencing factors of healthy lifestyle and behavioral literacy in Gaomi City, Shandong Province. Chin J Health Edu 34(08):750–752 (in Chinese)
Liu WD et al (2016) Health literacy levels and influencing factors of the elderly aged 45 to 69 years in Huai 'an, Jiangsu Province. Chin J Prevent Control Chronic Dis 24(12):908–910 (in Chinese)
Liu YB (2013) Study on the influence of health literacy on the self-care ability and social status of the elderly in nursing institutions. Dissertation, Xinjiang medical university (in Chinese)
Luo Y et al (2018) Nalysis on the status and the trend of health literacy among residents aged 60–69 years in Hubei Province. Chin Health Edu (10): 943–946 (in Chinese)
Mao K et al (2020) Analysis on the current situation and influencing factors of clinical health literacy of rural elderly aged 60–75 in Hunan Province. Occup Health 2020, 36(05): 626–629+633 (in Chinese)
Meng LJ et al (2017) The analysis of health literacy status of 60–69 year old elderly in Shibei district of Qingdao city in 2017. Chin Commun Physician 34(32):164–166 (in Chinese)
Ministry of Health, PRC (2018) Health literacy of Chinese citizens-basic knowledge and skills (Trial Implementation). Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House (PMPH). http://www.gov.cn/gzdt/2008-02/05/content_884068.htm. Accessed 05 February 2021
National Bureau of Statistics of the People's Republic of China (2011) Main data bulletin of the sixth national population census in 2010. http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/tjgb/rkpcgb/qgrkpcgb/201104/t20110428_30327.htm. Accessed 28 April 2020
National Health and Family Planning Commission (2017) Notice on issuing the “13th Five-Year” Healthy Aging Plan. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/rkjcyjtfzs/zcwj2/201703/53164cb31b494359a21c607713451342.shtml.Accessed 17 March 2017
National Library of Medicine (2019) Health Literacy: MedlinePlus. https://medlineplus.gov/healthliteracy.html Accessed 05 November 2020
Paasche-Orlow MK et al (2007) The causal pathways linking health literacy to health outcomes. Am J Health Behav 31(Suppl 1):S19–S26. https://doi.org/10.1001/archfami.5.6.329
Pang YH et al (2019) Status of health literacy and its influencing factors among the middle aged and elderly in poor areas of Liaoning. Mod Prev Med 46(07):1207–1210+1275 (in Chinese)
Peng F et al (2019) Analysis on the status of health literacy and influencing factors of 65-69-year-olds in poverty-stricken areas of Chongqing. Chin J Prevent Control Chronic Dis 27(12):912–916 (in Chinese)
Pobhirun T et al (2019) The association between health literacy and pesticide use behaviors among sweet corn farmers in the Pak Chong district of Thailand: a cross-sectional study. F1000Research. 8:448. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.18398.2
Qian Y et al (2015) Survey on the health literacy of people in the retirement year. Zhejiang J Prev Med 27(05):527–528+534 (in Chinese)
Qin L et al (2016) A cross-sectional study of the effect of health literacy on diabetes prevention and control among elderly individuals with prediabetes in rural China. BMJ Open 6(5):e011077. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011077
Sharp LK et al (2018) Community health workers supporting clinical pharmacists in diabetes management: a randomized controlled trial. Pharmacotherapy 38(1):58–68. https://doi.org/10.1002/phar.2058
Shen Y (2020) Health literacy status and comparative study of elderly people living at home in community and nursing home in Chongqing. Dissertation, Chongqing Medical University (in Chinese)
Shi MF et al (2019) Study on the health literacy level and its influencing factors of the elderly 60–69 years old from 2012 to 2017. Chin J Health Edu 35(11): 963–966+988 (in Chinese)
Society for Public Heath Information (SOPHE) (2011) Seniors: heath literacy and healthy aging. http://www.sophe.org/Sophe/PDF/NHEWThurs_Seniors
Su N et al (2020) Survey on health literacy of farmers in Gansu province. Chin Pub Health 36(07):1075–1079 (in Chinese)
Sun X et al (2013) Determinants of health literacy and health behavior regarding infectious respiratory diseases: a pathway model. BMC Public Health 13:261. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-13-261
Sun XD et al (2021) Mental health in urban and rural widowed older adults: a socially-supported study. Ningxia Sco Sci 01:163–171 (in Chinese)
Sun Y et al (2020) Analyzing the health literacy of chronic diseases among the elderly in Weifang City and its influencing factors. Chin Health Serv Manage 37(11):848–852 (in Chinese)
Tian X et al (2015) Effect of oral motor intervention on oral feeding in premature infant: a meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis. Chin J Nurs 50(07):804–811 (in Chinese)
van der Heide I et al (2013) The relationship between health, education, and health literacy: results from the Dutch adult literacy and life skills survey. J Health Commun 18 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):172–184. https://doi.org/10.1080/10810730.2013.825668
Wang G et al (2018) Analysis on the status and its influencing factors among health literacy of elderly patients with coronary heart disease. Chin J Health Edu 34(09):859–861 (in Chinese)
Wang K et al (2019c) Investigation and analysis on the status of health literacy of the elderly in Xuzhou area and its influencing factors. J Community Med 17(09):498–501 (in Chinese)
Wang L (2020) Investigation on health literacy of the elderly in Hohhot. Dissertation, Inner Mongolia Normal University (in Chinese)
Wang LM et al (2019a) Study of the prevalence and disease burden of chronic disease in the elderly in China. Chin J Epidemiol 3:277–283 (in Chinese)
Wang Y et al (2019b) Survey on health literacy of senile tuberculosis patients in Xinjiang. Occup Health 35(07):929–932 (in Chinese)
Wang YY et al (2019d) Investigation on the status of health literacy of the elderly in Mudanjiang. Res Trace Elements Health 2019 36(05):45–47 (in Chinese)
Williams K et al (2004) Marital status, marital transitions, and health: a gendered life course perspective. J Health Soc Behav 45(1):81–98
Xie Y et al (2019) Analysis on health literacy of 60-69 years old residents in Fengxian District, Shanghai. Health Edu Health Promot 14(02):133–135 (in Chinese)
Xu WL et al (2019) The health literacy level of the elderly in Kaifeng in 2018. Jiangsu J Prev Med 30(05):587–588 (in Chinese)
Yan YP et al (2013) The east-west comparison of economic security sources of China's elderly population is based on the analysis of data from the sixth national census. Soc Sec Res 05:36–45 (in Chinese)
Yuan T et al (2019) Investigation on health literacy and influencing factors of elderly patients with chronic diseases in Anhui Province. Acta Acad Med Changzhi 33(04):263–267 (in Chinese)
Zhang JF (2017) Investigation and analysis of the current health needs and health literacy of residents over 60 years old in Luohu District, Shenzhen. Acta Acad Med Qiqihar 38(14):1703–1705 (in Chinese)
Zhang LX et al (2019a) Analysis of health literacy level and influencing factors of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Western Henan. J Commun Med 17(8):441–443 (in Chinese)
Zhang ZM et al (2019b) Study on health literacy status and its influencing factors among residents of middle-aged and elderly people in Shandong Province. J Shandong Agric Eng Univ 36(07):88–93 (in Chinese)
Zhao QK et al (2020) Analysis on health literacy level and its influencing factors of college students in Hainan Province. China Market 27:27–28 (in Chinese)
Zhong C et al (2015) Survey of health literacy and research of health promotion strategy among middle-aged and elderly population in Hengli town of Dongguan City. Chin Med 12(09):55–59 (in Chinese)
Zhou LH (2016) Survey on health literacy of old persons in the Community of Yancheng City. Chin Health Indus 13(06):102–105 (in Chinese)
Zhou QZ et al (2020) Research progress on health literacy of maintenance hemodialysis patients. Med Diet Health 18(11):203–205 (in Chinese)
Zhou SY (2013) Study of the influencing factors of the elderly health literacy in Zhouzhuang Town, Kunshan. Dissertation, Jiangsu University (in Chinese)
Funding
This study was funded by the Anhui Healthy Development Strategy Research Center Project (2021szk020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Xu LM & Xie LF; Literature review and selection of studies: Xu LM & Li X; Statistical analysis: Xu LM, Wang L and Gao YM; Writing original draft: Xu LM; Revising the manuscript critically: Xie LF. All authors (Liang-mei Xu, Lun-fang Xie, Xing Li, Lei Wang Yu-meng Gao) have read and approved the final version of the manuscript to be published.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
This study is based on secondary data; therefore, no ethical approval was required.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOC 72 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Lm., Xie, Lf., Li, X. et al. A meta-analysis of factors influencing health literacy among Chinese older adults. J Public Health (Berl.) 30, 1889–1900 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-021-01638-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-021-01638-3