Abstract
Aim
The study sought to determine the multidrug resistance (MDR) of Salmonella enterica typhi and paratyphi A isolates in correlation with the presence of virulent markers detected by a PCR-based approach.
Methods
Blood and stool samples were collected from suspected cases and further confirmation was done serologically and bacteriologically. The isolated strains were clustered using RAPD analysis. The multidrug resistance pattern of the isolates was checked against a panel of antibiotics and screened for the presence of biochemical and molecular virulent markers including fimA and stn by PCR methods.
Results
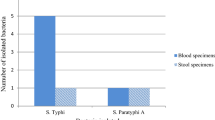
In total 368 suspected cases were identified. The geographical distribution showed 84 cases from the north zone (Lalgudi), 110 from the south zone (Palakarai), 91 from the east zone (Mattur and Tiruverambur) and 83 from the west zone (Petavaithalai). Among the 368 suspected cases, 349 (94.8%) and 177 (48.13%) cases were confirmed as typhoid fever serologically and bacteriologically, respectively. The clinical sample culturing yielded 144 isolates, of which 117 were S. typhi and 27 were S. paratyphi A. Both S. typhi and S. paratyphi A showed an absolute resistance pattern (100%) against chloramphenicol, erythromycin and tetracycline with next higher incidence of resistance against nalidixic acid and streptomycin. Irrespective of the presence of biochemical markers, all MDR strains showed the presence of fimA and stn.
Conclusion
No resistance pattern was observed for ceftriaxone, cephotaxime and co-trimoxazole. Thus, in this regard, the above-mentioned antibiotics can be used for the effective treatment of typhoid fever in this study locality. Molecular fingerprinting led to the hypothesis of diverse routes of Salmonella transmission and a putative high virulence potential for the isolates characterized.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arya SC, Sharma KB (1995) Urgent need for effective vaccine against Salmonella paratyphi A, B and C. Vaccine 13:1727–1728
Asten AJAM, Dijk JE (2005) Distribution of classic virulence factors among Salmonella sp. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 44:251–259
Baumler A, Gilde J, Tsolis RM, van der Velden AWM, Ahmer BMM, Heffron F (1997) Contribution of horizontal gene transfer and deletion events to development of distinctive patterns of fimbrial operons during evolution of Salmonella serotypes. J Bacteriol 179:317–322
Cappuccino JG, Sherman N (2004) Microbiology: a laboratory manual. Pearson Education, Singapore
Chopra AK, Peterson JW, Chary P, Prasad R (1994) Molecular characterization of an enterotoxin from Salmonella typhimurium. Microb Pathog 16:85–98
Clegg S, Gerlach GF (1987) Enterobacterial fimbriae. J Bacteriol 169:934–938
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Quality Manual; Third Edition. CLSI, 940 West Valley Road, Suite 1400, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087–1898 USA, 2003
Cohen HJ, Mechanda SM, Lin W (1996) PCR Amplification of the fimA gene sequence of Salmonella typhimurium, a specific method for detection of Salmonella sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:4303–4308
Cruickshank R, Duguid JP, Marmion BP, Swain RHA (1975) Medical microbiology. Volume II 12th edition. Edinburg. Churchill Livingstone, 403–404
Dombek PE, Johnson LK, Zimmerley ST, Sadowsky MJ (2000) Use of repetitive DNA sequences and the PCR to differentiate Escherichia coli isolates from human and animal sources. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2572–2577
Ekdahl K, de Jong B, Wollin R, Andersson Y (2005) Travel associated non-typhoidal salmonellosis—geographical and seasonal differences and serotype distribution. Clin Microbiol Infect 11:138–144
Gaind R, Paglietti B, Murgia M, Dawar R, Uzzau S, Cappuccinelli P, Deb M, Aggarwal P, Rubino S (2006) Molecular characterization of ciprofloxacin resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi and Paratyphi A causing enteric fever in India. J Antimicrob Chemother 58:1139–1144
Grewal HMS, Jureen R, Steinsland H, Digranes A (2002) Molecular epidemiological study of Salmonella enterica serovar paratyphi B infections imported from Turkey to Western Norway. Scand J Infect Dis 34:5–10
Helms M, Vastrup P, Gerner Smith P, Molbak K (2002) Excess mortality associated with antimicrobial drug resistant Salmonella typhimurium. Emerg Infect Dis 5:490–495
Hitchcock PJ, Leive L, Lakela PH, Riestschel ET, Strittmatter W, Morrison DC (1986) Lipopolysaccharide nomenclature—past, present and future. J Bacteriol 184:2857–2862
Ivanoff B, Levine MM, Lambert PH (1994) Vaccination against typhoid fever, present status. Bull WHO 72:957–971
Ivanoff B (1995) Typhoid fever, global situation and WHO recommendations. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 26:1–6
Kulkarni ML, Rego SJ (1994) Value of single widal test in the diagnosis of typhoid fever. Indian Pediatr 31:1373–1377
Libby SJ, Adams LJ, Ficht TA, Allen C, Whitford HA, Buchmeir AA (1997) The spv genes on the Salmonella Dublin virulence plasmid are required for severe enteritis and systemic infection in the natural host. Infect Immun 65:1786–1792
Lin FC, Ho VA, Bay PV (2000) The epidemiology of typhoid fever in the Dong Thap province, Mekong delta region of Vietnam. Am J Trop Med Hyg 62:644–648
Mazel D, Davies J (1998) Antibiotic resistance. The big picture. Adv Exp Med Biol 456:1–6
Porter SB, Curtiss R (1997) Effect of inv mutations on Salmonella virulence and colonization in 1-day-old white Leghorn chicks. Avian Dis 41:45–57
Rathish KC, Chandrashekar MR, Nagesha CN (1995) An outbreak of multi-drug resistant typhoid fever in Bangalore. Indian J Pediatr 62:445–448
Salisbury JG, Nicholls TJ, Lammerding AM, Turnidge J, Nunn MJ (2002) A risk analysis framework for the long-term management of antibiotic resistance in food-producing animals. Int J Antimicrob Agents 20:153–164
Schito GC (2002) Is antimicrobial resistance also subject to globalization? Clin Microbiol Infect 8:1–8
Selenska Pobell S, Evguenieva-Hackenberg E, Schwick erath O (1995) Random and repetitive primer amplified polymorphic DNA analysis of five soil and two clinical isolates of Rahnella aquatitis. Syst Appl Microbiol 18:425–438
Sinha A, Sazawal S, Kumar R (1999) Typhoid fever in children aged less than 5 years. Lancet 354:734–737
Slinger R, Desjardins M, McCarthy AE, Ramotar K, Jessamine P, Guibord C, Toye B (2004) Suboptimal clinical response to ciprofloxacin in patients with enteric fever due to Salmonella spp. with reduced fluoroquinolone susceptibility: a case series. BMC Inf Dis 4:36
Sood S, Kapil A, Dash N (1999) Paratyphoid fever in India: an emerging problem. Emerg Infect Dis 5:483–484
Sorum H, Sunde M (2001) Resistance to antibiotics in the normal flora of animals. Vet Res 32:227–241
Sur D, Ali M, von Seidlein L, Manna B, Deen JL, Acosta CJ, Clemens JD, Bhattacharya SK (2007) Comparisons of predictors for typhoid and paratyphoid fever in Kolkata, India. BMC Public Health 7:289
Thiagarajan D, Saeed M, Turek J, Asem E (1996) In vitro attachment and invasion of chicken ovarian granulosa cells by Salmonella enteritidis phage type 8. Infect Immun 64:5015–5021
Threlfall EJ (2000) Epidemic Salmonella typhimurium DT 104—a truly international multiresistant clone. J Antimicrob Chemother 46:7–10
Vollaard AM, Ali S, van Asten HA, Widjaja S, Visser LG, Surjadi C, Van Dissel JT (2004) Risk factors for typhoid and paratyphoid fever in Jakarta, Indonesia. JAMA 291:2607–2615
Acknowledgement
KNS and KVG are thankful to the University Grand Commission, New Delhi, India, for providing funds to carry out this research. TS is thankful to the University Grand Commission for the Rajiv Gandhi Fellowship.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sathiamoorthi, T., Dhanapaul, S., Vedhagiri, K. et al. Prevalence of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enteric serotype typhi and paratyphi A of human cases from the Tiruchirappalli district, India, and their associated virulent markers. J Public Health 19, 517–525 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-011-0414-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-011-0414-6