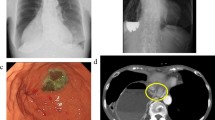
Abstract
Esophageal self-expandable metal stent placement is an effective treatment for palliation of malignant dysphagia, which has a low insertion-related complication rate. However, stent-related perforation can be a life-threatening event. We experienced a patient with advanced esophageal cancer who developed an iatrogenic esophageal perforation resulting from incorrect stent insertion. After removal of the original stent, we attempted to perform antegrade insertion of a second covered stent, but failed because we were not able to find the true lumen to the stomach. Due to his poor general condition and the high risk of surgical esophageal repair, we attempted esophageal stent placement using the combined antegrade–retrograde rendezvous technique using the gastrostomy route. By the performance of esophageal stenting using the rendezvous technique, we were able to avoid risky surgical esophageal repair. We expect that the rendezvous technique may be feasible therapy for patients with iatrogenic esophageal perforation when conventional antegrade endoscopic treatment fails.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA, Luketich JD. Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 2013;381:400–12.
Grilo A, Santos CA, Fonseca J. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy for nutritional palliation of upper esophageal cancer unsuitable for esophageal stenting. Arq Gastroenterol. 2012;49:227–31.
Sharma P, Kozarek R. Practice parameters committee of American college of gastroenterology. Role of esophageal stents in benign and malignant diseases. Am J Gastroenterol. 2010;105:258–73.
Jung GS, Park SD, Cho YD. Stent-induced esophageal perforation: treatment by means of placing a second stent after removal of the original stent. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2008;31:663–8.
Freeman RK, Van Woerkom JM, Ascioti AJ. Esophageal stent placement for the treatment of iatrogenic intrathoracic esophageal perforation. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;83:2003–7.
Vlavianos P, Zabron A. Clinical outcomes, quality of life, advantages and disadvantages of metal stent placement in the upper gastrointestinal tract. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 2012;6:27–32.
Baron TH. Minimizing endoscopic complications: endoluminal stents. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2007;17:83–104.
van Twisk JJ, Brummer RJ, Manni JJ. Retrograde approach to pharyngo-esophageal obstruction. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998;48:296–9.
Laurell G, Kraepelien T, Mavroidis P, Lind BK, Fernberg JO, Beckman M, et al. Stricture of the proximal esophagus in head and neck carcinoma patients after radiotherapy. Cancer. 2003;97:1693–700.
Maple JT, Petersen BT, Baron TH, Kasperbauer JL, Wong Kee Song LM, Larson MV. Endoscopic management of radiation-induced complete upper esophageal obstruction with an antegrade–retrograde rendezvous technique. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006;64:822–8.
Prachayakul V, Aswakul P, Kachintorn U. Complete obstructive esophageal cancer with esophagopleural fistula successfully treated by combined antegrade and retrograde rendezvous technique. Endoscopy. 2011;43(Suppl 2 UCTN):E354–5.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by an Inha University Research Grant.
Ethical Statement
This case report does not involve any studies performed with human or animal subjects by any authors.
Conflict of interest
There are no financial or other relations that could lead to a conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, JS., Bang, B.W., Kim, H.K. et al. A case of an iatrogenic esophageal perforation salvaged by anterograde–retrograde rendezvous approach and stenting. Esophagus 12, 86–90 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-013-0410-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-013-0410-8