Abstract
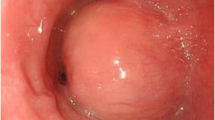
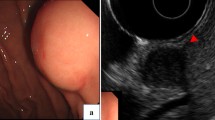
We report two cases of rare benign esophageal schwannoma showing high uptake of radiotracer on [18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET). Case 1 was a 78-year-old woman with a tumor (50 × 30 × 30 mm) located on the right side of the upper thoracic esophagus. Case 2 was a 70-year-old woman with a tumor (40 × 35 × 27 mm) located in the left anterior wall of the thoracic-to-cervical esophagus. Both tumors were enucleated and histologically diagnosed as benign esophageal schwannoma with nuclear palisading and lymphoid cuffing (Antoni A type). Immunohistochemical staining showed positivity for S-100 protein. There have been five reported cases of esophageal schwannoma with FDG-PET findings, including the present two cases. All five tumors were FDG-PET positive and presented histologically as benign esophageal schwannoma. There was no association between histological malignancy and FDG uptake. We therefore propose that the malignant potential of esophageal schwannomas cannot be evaluated using FDG-PET.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar R, Nadig MR, Chauhan A. Positron emission tomography: clinical applications in oncology. Part 1. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2005;5:1079–94.
Lodge MA, Lucas JD, Marsden PK, Cronin BF, O’Doherty MJ, Smith MA. A PET study of 18FDG uptake in soft tissue masses. Eur J Nucl Med. 1999;26:22–30.
Chatelin CL, Fissore A. Shwanome degenere de l’esophage. Confront Radio Anat Clin. 1967;7:114.
Esteves FP, Schuster DM, Halkar RK. Gastrointestinal tract malignancies and positron emission tomography: an overview. Semin Nucl Med. 2006;36:169–81.
Toyama E, Nagai Y, Baba Y, Yoshida N, Hayashi N, Miyanari N, et al. A case of thoracoscopically resected benign esophageal schwannoma with high uptake on FDG-PET. Esophagus. 2008;5:167–70.
Matsuki A, Kosugai S, Kanda T, Komukai S, Ohashi M, Umezu H, et al. Schwannoma of the esophagus: a case exhibiting high 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in positron emission tomography imaging. Dis Esophagus. 2009;22:E6–10.
Ota M, Nakamura T, Oguma H, Narumiya K, Kudo K, Yamamoto M. A case of a schwannoma of the esophagus showing high radiotracer concentration in FDG-PET. J Jpn Surg Assoc. 2007;68:49–53.
Benz MR, Czernin J, Dry SM, Tap WD, Allen-Auerbach MS, Elashoff D, et al. Quantitative F18-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography accurately characterizes peripheral nerve sheath tumors as malignant or benign. Cancer. 2010;116:451–8.
Ahmed AR, Watanabe H, Aoki J, Shinozaki T, Takagishi K. Schwannoma of the extremities: the role of PET in preoperative planning. Eur J Nucl Med. 2001;28:1541–51.
Beaulieu S, Rubin B, Djang D, Conrad E, Turcotte E, Eary JF. Positron emission tomography of schwannomas: emphasizing its potential in preoperative planning. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;182:971–4.
Demetri GD, Von Mehren M, Blanke CD, Van den Abbeele AD, Elsenberg B, Roberts PJ, et al. Efficacy and safety of imatinib mesylate in advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:472–80.
Van den Abbeele AD, Badawi RD. Use of positron emission tomography in oncology and its potential role to assess response to imatinib mesylate therapy in gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs). Eur J Cancer. 2002;38(Suppl 5):S60–5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakatsu, T., Motoyama, S., Maruyama, K. et al. Two cases of benign esophageal schwannoma with positive FDG-PET findings. Esophagus 8, 289–293 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-011-0290-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10388-011-0290-8