Abstract
Purpose
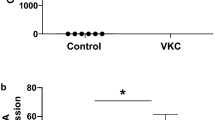
Galectin-3 is a damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMPs), released from damaged or dying cells. In this study, we investigated the concentration and source of galectin-3 in the tears of patients with vernal keratoconjunctivitis (VKC) and evaluated whether the concentration of galectin-3 in tears represents a biomarker of corneal epithelial damage.
Study design
Clinical and experimental.
Methods
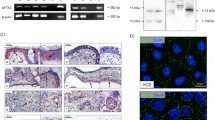
We measured the concentration of galectin-3 in tear samples from 26 patients with VKC and 6 healthy controls by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The expression of galectin-3 in cultured human corneal epithelial cells (HCEs) stimulated with or without tryptase or chymase was investigated by polymerase chain reaction (PCR), ELISA, and Western blotting. We also estimated the concentration of galectin-3 in the supernatants of cultured HCEs induced to necrosis. Finally, we investigated whether recombinant galectin-3 induced the expression of various genes related to cell migration or the cell cycle in HCEs by using microarray analysis.
Results
High concentrations of galectin-3 were detected in the tears of patients with VKC. The concentration showed significant correlation with the severity of corneal epithelial damage. Stimulation of cultured HCEs with various concentrations of tryptase or chymase had no effect on the expression of galectin-3. However, high concentrations of galectin-3 were detected in the supernatants of necrotic HCEs. Recombinant human galectin-3 induced various cell migration- and cell cycle-related genes.
Conclusion
The concentrations of galectin-3 in the tears of patients with VKC may represent a biomarker of the severity of corneal epithelial damage.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leffler H, Carlsson S, Hedlund M, Qian Y, Poirier F. Introduction to galectins. Glycoconj J. 2002;19:433–40.
Liu FT, Rabinovich GA. Galectins: regulators of acute and chronic inflammation. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1183:158–82.
Frigeri LG, Liu FT. Surface expression of functional IgE binding protein, an endogenous lectin, on mast cells and macrophages. J Immunol. 1992;148:861–7.
Liu FT, Frigeri LG, Gritzmacher CA, Hsu DK, Robertson MW, Zuberi RI. Expression and function of an IgE-binding animal lectin (epsilon BP) in mast cells. Immunopharmacology. 1993;26:187–95.
Frigeri LG, Zuberi RI, Liu FT. Epsilon BP, a beta-galactoside-binding animal lectin, recognizes IgE receptor (Fc epsilon RI) and activates mast cells. Biochemistry. 1993;32:7644–9.
Zuberi RI, Frigeri LG, Liu FT. Activation of rat basophilic leukemia cells by epsilon BP, an IgE-binding endogenous lectin. Cell Immunol. 1994;156:1–12.
Craig SS, Krishnaswamy P, Irani AM, Kepley CL, Liu FT, Schwartz LB. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of galectin-3, an IgE binding protein, in human mast cells and basophils. Anat Rec. 1995;242:211–9.
Brewer CF, Miceli MC, Baum LG. Clusters, bundles, arrays and lattices: novel mechanisms for lectin-saccharide-mediated cellular interactions. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2002;12:616–23.
Rabinovich GA, Toscano MA, Jackson SS, Vasta GR. Functions of cell surface galectin-glycoprotein lattices. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2007;17:513–20.
Dumic J, Dabelic S, Flögel M. Galectin-3: an open-ended story. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1760:616–35.
Ahmad N, Gabius HJ, André S, Kaltner H, Sabesan S, Roy R, et al. Galectin-3 precipitates as a pentamer with synthetic multivalent carbohydrates and forms heterogeneous cross-linked complexes. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:10841–7.
MacKinnon AC, Farnworth SL, Hodkinson PS, Henderson NC, Atkinson KM, Leffler H, et al. Regulation of alternative macrophage activation by galectin-3. J Immunol. 2008;180:2650–8.
Henderson NC, Mackinnon AC, Farnworth SL, Poirier F, Russo FP, Iredale JP, et al. Galectin-3 regulates myofibroblast activation and hepatic fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:5060–5.
Nishi Y, Sano H, Kawashima T, Okada T, Kuroda T, Kikkawa K, et al. Role of galectin-3 in human pulmonary fibrosis. Allergol Int. 2007;56:57–65.
Newlaczyl AU, Yu LG. Galectin-3–a jack-of-all-trades in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2011;313:123–8.
Ho JE, Liu C, Lyass A, Courchesne P, Pencina MJ, Vasan RS, et al. Galectin-3, a marker of cardiac fibrosis, predicts incident heart failure in the community. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60:1249–56.
Riccio AM, Mauri P, De Ferrari L, Rossi R, Di Silvestre D, Benazzi L, et al. Galectin-3: an early predictive biomarker of modulation of airway remodeling in patients with severe asthma treated with omalizumab for 36 months. Clin Transl Allergy. 2017;7:6.
Koufakis DI, Karabatsas CH, Sakkas LI, Alvanou A, Manthos AK, Chatzoulis DZ. Conjunctival surface changes in patients with Sjogren’s syndrome: a transmission electron microscopy study. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006;47:541–4.
Danjo Y, Watanabe H, Tisdale AS, George M, Tsumura T, Abelson MB, et al. Alteration of mucin in human conjunctival epithelia in dry eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998;39:2602–9.
Uchino Y, Mauris J, Woodward AM, Dieckow J, Amparo F, Dana R, et al. Alteration of galectin-3 in tears of patients with dry eye disease. Am J Ophthalmol. 2015;159:1027-35.e3.
Ge XN, Ha SG, Liu FT, Rao SP, Sriramarao P. Eosinophil-expressed galectin-3 regulates cell trafficking and migration. Front Pharmacol. 2013;4:37.
Rao SP, Wang Z, Zuberi RI, Sikora L, Bahaie NS, Zuraw BL, et al. Galectin-3 functions as an adhesion molecule to support eosinophil rolling and adhesion under conditions of flow. J Immunol. 2007;179:7800–7.
Han JL, Ding RY, Zhao L, Ren Z, Jiang XJ. Rosiglitazone attenuates allergic inflammation and inhibits expression of galectin-3 in a mouse model of allergic rhinitis. J Int Med Res. 2008;36:830–6.
Zuberi RI, Hsu DK, Kalayci O, Chen HY, Sheldon HK, Yu L, et al. Critical role for galectin-3 in airway inflammation and bronchial hyperresponsiveness in a murine model of asthma. Am J Pathol. 2004;165:2045–53.
Ge XN, Bahaie NS, Kang BN, Hosseinkhani MR, Ha SG, Frenzel EM, et al. Allergen-induced airway remodeling is impaired in galectin-3-deficient mice. J Immunol. 2010;185:1205–14.
del Pozo V, Rojo M, Rubio ML, Cortegano I, Cárdaba B, Gallardo S, et al. Gene therapy with galectin-3 inhibits bronchial obstruction and inflammation in antigen-challenged rats through interleukin-5 gene downregulation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166:732–7.
López E, Zafra MP, Sastre B, Gámez C, Lahoz C, del Pozo V. Gene expression profiling in lungs of chronic asthmatic mice treated with galectin-3: downregulation of inflammatory and regulatory genes. Mediators Inflamm. 2011;2011: 823279.
Saegusa J, Hsu DK, Chen HY, Yu L, Fermin A, Fung MA, et al. Galectin-3 is critical for the development of the allergic inflammatory response in a mouse model of atopic dermatitis. Am J Pathol. 2009;174:922–31.
Hrdlicková-Cela E, Plzák J, Smetana K Jr, Mĕlková Z, Kaltner H, Filipec M, et al. Detection of galectin-3 in tear fluid at disease states and immunohistochemical and lectin histochemical analysis in human corneal and conjunctival epithelium. Br J Ophthalmol. 2001;85:1336–40.
Andrade FEC, Covre JL, Ramos L, Hazarbassanov RM, Santos MSD, Campos M, et al. Evaluation of galectin-1 and galectin-3 as prospective biomarkers in keratoconus. Br J Ophthalmol. 2018;102:700–7.
Andrade FEC, Corrêa MP, Gimenes AD, Dos Santos MS, Campos M, Chammas R, et al. Galectin-3: role in ocular allergy and potential as a predictive biomarker. Br J Ophthalmol. 2018;102:1003–10.
Takamura E, Uchio E, Ebihara N, Ohno S, Ohashi Y, Okamoto S, et al. Japanese guidelines for allergic conjunctival diseases 2017. Allergol Int. 2017;66:220–9.
Ebihara N, Matsuda A, Nakamura S, Matsuda H, Murakami A. Role of the IL-6 classic- and trans-signaling pathways in corneal sterile inflammation and wound healing. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52:8549–57.
Ochieng J, Fridman R, Nangia-Makker P, Kleiner DE, Liotta LA, Stetler-Stevenson WG, et al. Galectin-3 is a novel substrate for human matrix metalloproteinases-2 and -9. Biochemistry. 1994;33:14109–14.
Nangia-Makker P, Raz T, Tait L, Hogan V, Fridman R, Raz A. Galectin-3 cleavage: a novel surrogate marker for matrix metalloproteinase activity in growing breast cancers. Cancer Res. 2007;67:11760–8.
Ebihara N, Funaki T, Takai S, Miyazaki M, Fujiki K, Murakami A. Tear chymase in vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Curr Eye Res. 2004;28:417–20.
Matzinger P. The danger model: a renewed sense of self. Science. 2002;296:301–5.
Oppenheim JJ, Yang D. Alarmins: chemotactic activators of immune responses. Curr Opin Immunol. 2005;17:359–65.
Bianchi ME. DAMPs, PAMPs and alarmins: all we need to know about danger. J Leukoc Biol. 2007;81:1–5.
Chen CJ, Kono H, Golenbock D, Reed G, Akira S, Rock KL. Identification of a key pathway required for the sterile inflammatory response triggered by dying cells. Nat Med. 2007;13:851–6.
Filley WV, Holley KE, Kephart GM, Gleich GJ. Identification by immunofluorescence of eosinophil granule major basic protein in lung tissues of patients with bronchial asthma. Lancet. 1982;2:11–6.
Pégorier S, Wagner LA, Gleich GJ, Pretolani M. Eosinophil-derived cationic proteins activate the synthesis of remodeling factors by airway epithelial cells. J Immunol. 2006;177:4861–9.
Leiferman KM, Ackerman SJ, Sampson HA, Haugen HS, Venencie PY, Gleich GJ. Dermal deposition of eosinophil-granule major basic protein in atopic dermatitis. Comparison with onchocerciasis. N Engl J Med. 1985; 313:282-5.
Omoto M, Gu LH, Sugiura H, Uehara M. Heterogeneity of dermal deposition of eosinophil granule major basic protein in acute lesions of atopic dermatitis. Arch Dermatol Res. 2000;292:51–4.
Secchi A, Leonardi A, Abelson M. The role of eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) and histamine in vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 1995;3:23–8.
Leonardi A, Borghesan F, Faggian D, Secchi A, Plebani M. Eosinophil cationic protein in tears of normal subjects and patients affected by vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Allergy. 1995;50:610–3.
Pucci N, Novembre E, Lombardi E, Cianferoni A, Bernardini R, Massai C, et al. Atopy and serum eosinophil cationic protein in 110 white children with vernal keratoconjunctivitis: differences between tarsal and limbal forms. Clin Exp Allergy. 2003;33:325–30.
Saravanan C, Liu FT, Gipson IK, Panjwani N. Galectin-3 promotes lamellipodia formation in epithelial cells by interacting with complex N-glycans on alpha3beta1 integrin. J Cell Sci. 2009;122:3684–93.
Yabuta C, Yano F, Fujii A, Shearer TR, Azuma M. Galectin-3 enhances epithelial cell adhesion and wound healing in rat cornea. Ophthalmic Res. 2014;51:96–103.
Cao Z, Said N, Amin S, Wu HK, Bruce A, Garate M, et al. Galectins-3 and -7, but not galectin-1, play a role in re-epithelialization of wounds. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:42299–305.
Saravanan C, Cao Z, Head SR, Panjwani N. Detection of differentially expressed wound-healing-related glycogenes in galectin-3-deficient mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009;50:5690–6.
Fujii A, Shearer TR, Azuma M. Galectin-3 enhances extracellular matrix associations and wound healing in monkey corneal epithelium. Exp Eye Res. 2015;137:71–8.
Mauris J, Woodward AM, Cao Z, Panjwani N, Argüeso P. Molecular basis for MMP9 induction and disruption of epithelial cell-cell contacts by galectin-3. J Cell Sci. 2014;127:3141–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Y. Ito, None; A. U-Ouchi, None; N. Ebihara, None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Corresponding Author: Nobuyuki Ebihara
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, Y., Usui-Ouchi, A. & Ebihara, N. Galectin-3, a damage-associated molecular pattern, in tears of patients with vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Jpn J Ophthalmol 67, 431–439 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-023-00994-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-023-00994-9