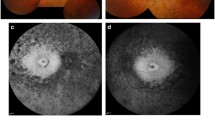
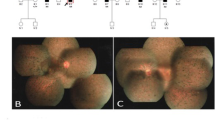
Abstract
Purpose
To screen for the 328 bp Alu insertion (c.4052_4053ins328, p.Tyr1352Alafs) in RP1 in a group of retinitis pigmentosa (RP) patients who had been previously identified with a heterozygous deleterious mutation in the gene.
Study design
Prospective, clinical and experimental study.
Methods
The Alu insertion in RP1 was screened with an optimized PCR-based method in 26 RP patients with a heterozygous deleterious mutation (nonsense or frameshift) in RP1 that had been identified in a preceding genetic study. The genetic location of the previously identified mutation and its inheritance pattern were assessed.
Results
Out of 26 RP patients with a heterozygous deleterious mutation in RP1, 5 (19.2%) were found to carry an additional heterozygous Alu insertion, presumably resulting in a compound heterozygous state. This included 3 patients who had been previously diagnosed as autosomal dominant RP based on genetic findings. They were re-diagnosed as having an autosomal recessive disease following our new findings. In all patients identified with the Alu insertion, the other mutations found in the preceding study were outside the defined region in exon 4 (encoding amino acids 677 to 917) in which truncation mutations have been suggested to exert a dominant negative effect.
Conclusion
The founder Alu insertion in RP1 is an important cause of autosomal recessive RP in Japanese patients and can be missed in standard targeted resequencing. Screening optimized for this mutation is warranted, particularly in patients with a heterozygous deleterious mutation outside the defined region in exon 4 of RP1.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Q, Zhou J, Daiger SP, Farber DB, Heckenlively JR, Smith JE, et al. Identification and subcellular localization of the RP1 protein in human and mouse photoreceptors. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002;43:22–32.
Liu Q, Zuo J, Pierce EA. The retinitis pigmentosa 1 protein is a photoreceptor microtubule-associated protein. J Neurosci. 2004;24:6427–36.
Pierce EA, Quinn T, Meehan T, McGee TL, Berson EL, Dryja TP. Mutations in a gene encoding a new oxygen-regulated photoreceptor protein cause dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Nat Genet. 1999;22:248.
Guillonneau X, Piriev NI, Danciger M, Kozak CA, Cideciyan AV, Jacobson SG, et al. A nonsense mutation in a novel gene is associated with retinitis pigmentosa in a family linked to the RP1 locus. Hum Mol Genet. 1999;8:1541–6.
Sullivan LS, Heckenlively JR, Bowne SJ, Zuo J, Hide WA, Gal A, et al. Mutations in a novel retina-specific gene cause autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Nat Genet. 1999;22:255.
Khaliq S, Abid A, Ismail M, Hameed A, Mohyuddin A, Lall P, et al. Novel association of RP1 gene mutations with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. J Med Genet. 2005;42:436–8.
Avila-Fernandez A, Corton M, Nishiguchi KM, Muñoz-Sanz N, Benavides-Mori B, Blanco-Kelly F, et al. Identification of an RP1 prevalent founder mutation and related phenotype in Spanish patients with early-onset autosomal recessive retinitis. Ophthalmology. 2012;119:2616–21.
Corton M, Nishiguchi KM, Avila-Fernández A, Nikopoulos K, Riveiro-Alvarez R, Tatu SD, et al. Exome sequencing of index patients with retinal dystrophies as a tool for molecular diagnosis. PLoS One. 2013;8:e65574.
Verbakel SK, van Huet RA, den Hollander AI, Geerlings MJ, Kersten E, Klevering BJ, et al. Macular dystrophy and cone-rod dystrophy caused by mutations in the RP1 gene: extending the RP1 disease spectrum. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019;60:1192–203.
Riera M, Abad-Morales V, Navarro R, Ruiz-Nogales S, Méndez-Vendrell P, Corcostegui B, et al. Expanding the retinal phenotype of RP1: from retinitis pigmentosa to a novel and singular macular dystrophy. Br J Ophthalmol. 2020;104:173–81.
Lykke-Andersen S, Jensen TH. Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay: an intricate machinery that shapes transcriptomes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015;16:665.
Koyanagi Y, Akiyama M, Nishiguchi KM, Momozawa Y, Kamatani Y, Takata S, et al. Genetic characteristics of retinitis pigmentosa in 1204 Japanese patients. J Med Genet. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2018-105691.
Nanda A, McClements ME, Clouston P, Shanks ME, MacLaren RE. The location of exon 4 mutations in RP1 raises challenges for genetic counseling and gene therapy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2019;202:23–9.
Oishi M, Oishi A, Gotoh N, Ogino K, Higasa K, Iida K, et al. Comprehensive molecular diagnosis of a large cohort of Japanese retinitis pigmentosa and Usher syndrome patients by next-generation sequencing. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55:7369–75.
Hosono K, Ishigami C, Takahashi M, Park DH, Hirami Y, Nakanishi H, et al. Two novel mutations in the EYS gene are possible major causes of autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa in the Japanese population. PLoS One. 2012;7:e31036.
Nishiguchi KM, Ikeda Y, Fujita K, Kunikata H, Akiho M, Hashimoto K, et al. Phenotypic features of Oguchi disease and retinitis pigmentosa in patients with S-antigen (SAG) mutations. Ophthalmology. 2019;126:1557–66.
Iwanami M, Oshikawa M, Nishida T, Nakadomari S, Kato S. High prevalence of mutations in the EYS gene in Japanese patients with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53:1033–40.
Taira K, Nakazawa M, Sato M. Mutation c. 1142 del G in the PRPF31 gene in a family with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa (RP11) and its implications. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2007;51:45–8.
Katagiri S, Akahori M, Sergeev Y, Yoshitake K, Ikeo K, Furuno M, et al. Whole exome analysis identifies frequent CNGA1 mutations in Japanese population with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. PLoS One. 2014;9:e108721.
Nikopoulos K, Cisarova K, Quinodoz M, Koskiniemi-Kuendig H, Miyake N, Farinelli P, et al. A frequent variant in the Japanese population determines quasi-Mendelian inheritance of rare retinal ciliopathy. Nat Commun. 2019;10:2884.
Maeda A, Yoshida A, Kawai K, Arai Y, Akiba R, Inaba A, et al. Development of a molecular diagnostic test for Retinitis Pigmentosa in the Japanese population. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2018;62:451–7.
Kawamura M, Wada Y, Noda Y, Itabashi T, Ogawa S-I, Sato H, et al. Novel 2336-2337delCT mutation in RP1 gene in a Japanese family with autosomal dominant retinitis pigmentosa. Am J Ophthalmol. 2004;137:1137–9.
Acknowledgements
The work was supported in part by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (#19ek0109213h0001, Nishiguchi). The manuscript was edited by a professional English editing service (Mr. Tim Hilts). The patients were recruited through the Japanese Retinitis Pigmentosa Registry Project (JRPRP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
K. M. Nishiguchi, None; K. Fujita, Grant (NIDEK, TOPCON); Y. Ikeda, Grant (HOYA, Bayer, Santen), Lecture fee (HOYA, Nidek, Bayer, Santen, Alcon), Consultant fee (HOYA, Santen); H. Kunikata, None; Y. Koyanagi, None; M. Akiyama, None; T. Abe, None; Y. Wada, None; K. Sonoda, None; T. Nakazawa, None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Corresponding Author: Koji M Nishiguchi
About this article
Cite this article
Nishiguchi, K.M., Fujita, K., Ikeda, Y. et al. A founder Alu insertion in RP1 gene in Japanese patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Jpn J Ophthalmol 64, 346–350 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-020-00732-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-020-00732-5