Abstract
Purpose
To compare the clinical outcomes of 3 marking methods for toric intraocular lens (IOL) implantation in cataract patients.
Methods
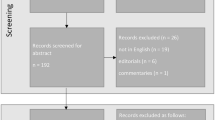
This study included 48 eyes of 48 cataract patients who underwent cataract surgery with toric IOL implantation. The rotational errors of 3 marking methods—the iris pattern marking method (iris pattern group), the pendulum marking method (pendulum group), and the 3-point marking method (3-point group)—were assessed.
Results
The respective rotational errors were 4.0° ± 3.1° (mean ± SD), 5.3° ± 4.1°, and 7.3° ± 6.0°. The iris pattern group had significantly (P = 0.048) smaller rotational errors than did the 3-point group; no significant difference was found between the iris pattern and pendulum groups. However, the differences in postoperative uncorrected distance visual acuity and astigmatism did not reach significance among the 3 groups.
Conclusion
The refractive and visual results of toric IOL implantation using the 3-point marking method were comparable to the other methods evaluated in this study, although the accuracy of the axis alignment of the toric IOLs was significantly lower than that obtained with the iris pattern method.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Viestenz A, Seitz B, Langenbucher A. Evaluating the eye’s rotational stability during standard photography: effect on determining the axial orientation of toric intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005;31:557–61.
Langenbucher A, Viestenz A, Szentmary N, Behrens-Baumann W, Viestenz A. Toric intraocular lenses: theory, matrix calculations, and clinical practice. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009;25:611–22.
Carey PJ, Leccisotti A, McGilligan VE, Goodall EA, Moore CB. Assessment of toric intraocular lens alignment by a refractive power/corneal analyzer system and slit lamp observation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010;36:222–9.
Hirnschall N, Maedel S, Weber M, Findl O. Rotational stability of a single-piece toric acrylic intraocular lens: a pilot study. Am J Ophthalmol. 2014;157:405–11.
Buckhurst PJ, Wolffsohn JS, Davies LN, Naroo SA. Surgical correction of astigmatism during cataract surgery. Clin Exp Optom. 2010;93:409–18.
Ben Simon GJ, Desatnik H. Correction of pre-existing astigmatism during cataract surgery: comparison between the effects of opposite clear corneal incisions and a single clear corneal incision. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2005;243:321–6.
Entabi M, Harman F, Lee N, Bloom PA. Injectable 1-piece hydrophilic acrylic toric intraocular lens for cataract surgery: efficacy and stability. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011;37:235–40.
Kersey JP, O’Donnell A, Illingworth CD. Cataract surgery with toric intraocular lenses can optimize uncorrected postoperative visual acuity in patients with marked corneal astigmatism. Cornea. 2007;26:133–5.
Shimizu K, Misawa A, Suzuki Y. Toric intraocular lenses: correcting astigmatism while controlling axis shift. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1994;20:523–6.
Watanabe K, Negishi K, Torii H, Saiki M, Dogru M, Tsubota K. Simple and accurate alignment of toric intraocular lenses and evaluation of their rotation errors using anterior segment optical coherence tomography. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2012;56:31–7.
Popp N, Hirnschall N, Maedel S, Findl O. Evaluation of 4 corneal astigmatic marking methods. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012;38:2094–9.
Kruger RR, Shea W, Zhou Y, Osher R, Slade SG, Chang DF. Intraoperative, real-time aberrometry during refractive cataract surgery with a sequentially shifting wavefront device. J Refract Surg. 2013;29:630–5.
Stewart CM, McAlister JC. Comparison of grafted and nongrafted patients with corneal astigmatism undergoing cataract extraction with a toric intraocular lens implant. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010;38:747–57.
Kim MH, Chung TY, Chung ES. Long-term efficacy and rotational stability of AcrySof toric intraocular lens implantation in cataract surgery. Korean J Ophthalmol. 2010;24:207–12.
Koshy JJ, Nishi Y, Hirnschall N, Crnej A, Gangwani V, Marurino V, et al. Rotational stability of a single-piece toric acrylic intraocular lens. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2010;36:1655–70.
Mendicute J, Irigoyen C, Aramberri J, Ondarrra A, Montes-Mico R. Foldable toric intraocular lens for astigmatism correction in cataract patients. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008;34:601–7.
Kwartz J, Edwards K. Evaluation of the long-term rotational stability of single-piece acrylic intraocular lenses. Br J Ophthalmol. 2010;94:1003–6.
Swiatek B, Malecka MK, Dorecka M, Romaniuk D, Romaniuk W. Results of the AcrySof toric intraocular lenses implantation. Med Sci Monit. 2012;18:11–4.
Holland E, Lane S, Horn JD, Ernest P, Arleo R, Miller KM. The AcrySof toric intraocular lens in subjects with cataracts and corneal astigmatism; a randomized, subject-masked, parallel group, 1-year study. Ophthalmology. 2010;117:2104–11.
Visser N, Berendschot TTJM, Bauer JC, Jurich J, Kersting O, Nuijts RMMA. Accuracy of toric intraocular lens implantation in cataract and refractive surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011;37:1394–402.
Miyata K, Miyai T, Minami K, Bissen-Miyajima H, Maeda N, Amano S. Limbal relaxing incisions using a reference point and corneal topography for intraoperative identification of the steepest meridian. J Refract Surg. 2011;27:339–44.
Cha D, Kang SY, Kim SH, Song JS, Kim HM. New axis-marking method for a toric intraocular lens: mapping method. J Refract Surg. 2011;27:375–9.
Igarashi A, Kamiya K, Shimizu K. Clinical evaluation of accuracy of horizontal meridian limbal marking. Optom Vis Sci. 2013;90:540–5.
Ueno Y, Hiraoka T, Beheregaray S, Miyazaki M, Ito M, Oshika T. Age-related changes in anterior, posterior, and total corneal astigmatism. J Refract Surg. 2014;30(3):192–7.
Ho JD, Liou SW, Tsai RJ, Tsai CY. Effects of aging on anterior and posterior corneal astigmatism. Cornea. 2010;29:632–7.
Koch DD, Ali SF, Weikert MP, Shirayama M, Jenkins R, Wang L. Contribution of posterior corneal astigmatism to total corneal astigmatism. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2012;38:2080–7.
Saunders H. Changes in the axis of astigmatism: a longitudinal study. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 1988;8:37–42.
Acknowledgments
We thank Sachiko Maui, Department of Ophthalmology, Keio University School of Medicine, for support with the data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
H. Onishi, None; H. Torii, None; K. Watanabe, None; K. Tsubota, None; K. Negishi, grant (Alcon Laboratories, Inc.), lecture fees (Alcon Japan Ltd.).
About this article
Cite this article
Onishi, H., Torii, H., Watanabe, K. et al. Comparison of clinical outcomes among 3 marking methods for toric intraocular lens implantation. Jpn J Ophthalmol 60, 142–149 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-016-0432-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-016-0432-6