Abstract
Purpose
We compared the ability of four discriminant models to detect keratoconus (KC) using Zernike coefficients of corneal aberrations.
Methods
We studied 51 eyes with KC, 46 with KC suspect, 50 after laser in situ keratomileusis, and 65 normal eyes. Four statistical discriminant analyses—linear discriminant analysis, k-nearest neighbor algorithm, Mahalanobis distance method, and neural network method—were performed using Zernike coefficients of corneal aberrations obtained by a Placido-based topographer. The detection scheme was constructed using a training set of data from one half of the randomly selected study participants, and performance was evaluated by a validation set in the other half.
Results
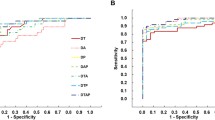
Performance of the four models was different when <12 explanatory variables were included. Performance using the 2nd- to 4th-order Zernike terms did not differ significantly among models; average accuracy was 79 %.
Conclusions
Determining explanatory variables of Zernike expansion coefficients of the corneal topography in discriminant models may contribute to improving accuracy of KC detection over the discriminant model, as appropriate selection of explanatory variables gave similar results despite different discriminant models.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krachmer JH, Feder RS, Belin MW. Keratoconus and related noninflammatory corneal thinning disorders. Surv Ophthalmol. 1984;28:293–322.
Rabinowitz YS. Keratoconus. Surv Ophthalmol. 1998;42:297–319.
Keates RH, Falkenstein S. Keratoplasty in keratoconus. Am J Ophthmol. 1972;74:442–4.
Kim KH, Choi SH, Ahn K, Chung ES, Chung TY. Comparison of refractive changes after deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty and penetrating keratoplasty for keratoconus. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2011;55:93–7.
Seiler T, Quurke AW. Iatrogenic keratectasia after LASIK in a case of forme fruste keratoconus. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1998;24:1007–9.
Randleman JB, Russell B, Ward MA, Thompson KP, Stulting RD. Risk factors and prognosis for corneal ectasia after LASIK. Ophthalmology. 2003;110:267–75.
Klyce SD. Chasing the suspect: keratoconus. Br J Ophthalmol. 2009;93:845–7.
Snibson GR. Collagen cross-linking: a new treatment paradigm in corneal disease—a review. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2010;38:141–53.
Rabinowitz YS, McDonnell PJ. Computer-assisted corneal topography in keratoconus. Refract Corneal Surg. 1989;5:400–8.
Wilson SE, Lin DT, Klyce SD. Corneal topography of keratoconus. Cornea. 1991;10:2–8.
Schwiegerling J, Greivenkamp JE, Miller JM. Representation of videokeratoscopic height data with Zernike polynomials. J Opt Soc Am A Opt Image Sci Vis. 1995;12:2105–13.
Auffarth GU, Wang L, Völcker HE. Keratoconus evaluation using the Orbscan Topography System. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26:222–8.
Bessho K, Maeda N, Kuroda T, Fujikado T, Tano Y, Oshika T. Automated keratoconus detection using height data of anterior and posterior corneal surfaces. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2006;50:409–16.
de Sanctis U, Loiacono C, Richiardi L, Turco D, Mutani B, Grignolo FM. Sensitivity and specificity of posterior corneal elevation measured by Pentacam in discriminating keratoconus/subclinical keratoconus. Ophthalmology. 2008;115:1534–9.
Li Y, Meisler DM, Tang M, Lu ATH, Thakrar V, Reiser BJ, et al. Keratoconus diagnosis with optical coherence tomography pachymetry mapping. Ophthalmology. 2008;115:2159–66.
Miháltz K, Kovács I, Kránitz K, Erdei G, Németh J, Nagy ZZ. Mechanism of aberration balance and the effect on retinal image quality in keratoconus: optical and visual characteristics of keratoconus. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2011;37:914–22.
Twa MD, Parthasarathy S, Roberts C, Mahmoud AM, Raasch TW, Bullimore MA. Automated decision tree classification of corneal shape. Optom Vis Sci. 2005;82:1038–46.
Chastang PJ, Borderie VM, Carvajal-Gonzalez S, Rostène W, Laroche L. Automated keratoconus detection using the EyeSys videokeratoscope. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2000;26:675–83.
Maeda N, Klyce SD, Smolek MK. Neural network classification of corneal topography. Preliminary demonstration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1995;36:1327–35.
Carvalho LA. Preliminary results of neural networks and Zernike polynomials for classification of videokeratography maps. Optom Vis Sci. 2005;82:151–8.
Rabinowitz YS, Rasheed K. KISA% index: a quantitative videokeratography algorithm embodying minimal topographic criteria for diagnosing keratoconus. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1999;25:1327–35.
Kosaki R, Maeda N, Bessho K, Hori Y, Nishida K, Suzaki A, et al. Magnitude and orientation of Zernike terms in patients with keratoconus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48:3062–8.
Alió JL, Shabayek MH. Corneal higher order aberrations: a method to grade keratoconus. J Refract Surg. 2006;22:539–45.
Rand RH, Howland HC, Applegate RA. Mathematical model of a Placido disk keratometer and its implications for recovery of corneal topography. Optom Vis Sci. 1997;74:926–30.
Thibos LN, Applegate RA, Schwiegerling JT, Webb R. Standards for reporting the optical aberrations of eyes. J Refract Surg. 2002;18:652–60.
Howland HC, Howland B. A subjective method for the measurement of monochromatic aberrations of the eye. J Opt Soc Am. 1977;67:1508–18.
Fisher RA. The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems. Ann Eugen. 1936;7:179–88.
Cover T, Hart P. Nearest neighbor pattern classification. IEEE Trans Inf Theory. 1967;13:21–7.
McCulloch WS, Pitts W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull Math Biophys. 1943;5:115–33.
Hopfield JJ. Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1982;79:2554–8.
R Development Core team (2007). R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, http://www.R-project.org.
Marcos S, Barbero S, Llorente L, Merayo-Lloves J. Optical response to LASIK surgery for myopia from total and corneal aberration measurements. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2001;42:3349–56.
Kamiya K, Hirohara Y, Mihashi T, Hiraoka T, Kaji Y, Oshika T. Progression of pellucid marginal degeneration and higher-order wavefront aberration of the cornea. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2003;47:523–5.
Oie Y, Maeda N, Kosaki R, Suzaki A, Hirohara Y, Mihashi T, et al. Characteristics of ocular higher-order aberrations in patients with pellucid marginal corneal degeneration. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008;34:1928–34.
Smolek MK, Klyce SD. Goodness-of-prediction of Zernike polynomial fitting to corneal surfaces. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005;31:2350–5.
Karnowski K, Kaluzny BJ, Szkulmowski M, Gora M, Wojtkowski M. Corneal topography with high-speed swept source OCT in clinical examination. Biomed Opt Express. 2011;2:2709–20.
Ortiz S, Pérez-Merino P, Alejandre N, Gambra E, Jimenez-Alfaro I, Marcos S. Quantitative OCT-based corneal topography in keratoconus with intracorneal ring segments. Biomed Opt Express. 2012;3:814–24.
Bühren J, Kook D, Yoon G, Kohnen T. Detection of subclinical keratoconus by using corneal anterior and posterior surface aberrations and thickness spatial profiles. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51:3424–32.
Saad A, Gatinel D. Evaluation of total and corneal wavefront high order aberrations for the detection of forme fruste keratoconus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53:2978–92.
Schweitzer C, Roberts CJ, Mahmoud AM, Colin J, Maurice-Tison S, Kerautret J. Screening of forme fruste keratoconus with the ocular response analyzer. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51:2403–10.
Wilson SE, Lin DTC, Klyce SD, Reidy JJ, Insler MS. Topographic changes in contact lens-induced corneal warpage. Ophthalmology. 1990;97:734–44.
Hawkins DM. The problem of overfitting. J Chem Inf Comput Sci. 2004;44:1–12.
Acknowledgments
Supported in part by the Japan Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture, Tokyo, Japan (No. 24592669).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Saika, M., Maeda, N., Hirohara, Y. et al. Four discriminant models for detecting keratoconus pattern using Zernike coefficients of corneal aberrations. Jpn J Ophthalmol 57, 503–509 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-013-0269-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-013-0269-1