Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the effect on intraocular pressure (IOP) of increased corneal thickness after Descemet’s stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty (DSAEK) and of non-Descemet’s stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty (nDSAEK) as measured by four different techniques.
Methods
Twenty-four eyes (22 patients; mean age, 74.0 years) with successful DSAEK (11 eyes) or nDSAEK (13 eyes) treatment at least 3 months prior to testing were enrolled. IOP was measured with Goldmann applanation tonometry (GAT), dynamic contour tonometry (DCT), pneumatonometry, and Tono-Pen XL (Tonopen). Central corneal thickness (CCT) was measured by ultrasonic pachymetry. These data were used for statistical analysis.
Results
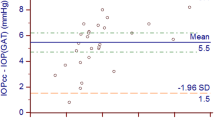
Mean IOP measured by GAT, DCT, pneumatonometry, and Tonopen was 14.4, 13.9, 11.2, and 13.2 mmHg, respectively, in the DSAEK group; and 15.0, 14.4, 12.5, and 14.4 mmHg, respectively, in the nDSAEK group. Correlations between IOP and CCT were not statistically significant in either group. Pressure measured by pneumatonometry was significantly and consistently lower than that obtained by the other three methods.
Conclusion
For both DSAEK and nDSAEK, IOP readings by the four tonometers seem to be unrelated to artificially thickened corneas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melles GR, Eggink FA, Lander F, et al. A surgical technique for posterior lamellar keratoplasty. Cornea 1998;17:618–626.
Terry MA, Ousley PJ. Small-incision deep lamellar endothelial keratoplasty (DLEK): six-month results in the first prospective clinical study. Cornea 2005;24:59–65.
Terry MA, Ousley PJ. Deep lamellar endothelial keratoplasty: visual acuity, astigmatism, and endothelial survival in a large prospective series. Ophthalmology 2005;112:1541–1548.
Price MO, Price FW Jr. Descemet’s stripping with endothelial keratoplasty: comparative outcomes with microkeratome-dissected and manually dissected donor tissue. Ophthalmology 2006;113: 1936–1942.
Price FW Jr, Price MO. Descemet’s stripping with endothelial keratoplasty in 200 eyes: early challenges and techniques to enhance donor adherence. J Cataract Refract Surg 2006;32:411–418.
Gorovoy MS. Descemet-stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty. Cornea 2006;25:886–889.
Kobayashi A, Yokogawa H, Sugiyama K. Non-Descemet stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty for endothelial dysfunction secondary to argon laser iridotomy. Am J Ophthalmol 2008;146: 543–549.
Kobayashi A, Yokogawa H, Sugiyama K. In vivo laser confocal microscopy findings after non-Descemet stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty. Ophthalmology 2009;116:1306–1313.
Miyake K, Matsuda M, Inaba M. Corneal endothelial changes in pseudoexfoliation syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol 1989;108:49–52.
Kobayashi A, Mawatari Y, Yokogawa H, Sugiyama K. In vivo laser confocal microscopy after Descemet’s stripping with automated endothelial keratoplasty. Am J Ophthalmol 2008;145:977–985.
Punjabi OS, Kniestedt C, Stamper RL, Lin SC. Dynamic contour tonometry: principle and use. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol 2006;34:837–840.
Herndon LW. Measuring intraocular pressure-adjustments for corneal thickness and new technologies. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 2006;17:115–119.
Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986;1: 307–310.
Vajaranant TS, Price MO, Price FW, et al. Intraocular pressure measurements following Descemet stripping endothelial keratoplasty. Am J Ophthalmol 2008;145:780–786.
Price MO, Price FW Jr, Trespalacios R. Endothelial keratoplasty technique for aniridic aphakic eyes. J Cataract Refract Surg 2007;33:376–379.
Price FW Jr, Price MO. Endothelial keratoplasty to restore clarity to a failed penetrating graft. Cornea 2006;25:895–899.
Schneider E, Grehn F. Intraocular pressure measurement—comparison of dynamic contour tonometry and Goldmann applanation tonometry. J Glaucoma 2006;15:2–6.
Herdener S, Pache M, Lautebach S, Funk J. Dynamic contour tonometry versus Goldmann applanation tonometry—a comparison of agreement and reproducibility. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2007;245:1027–1030.
Doyle A, Lachkar Y. Comparison of dynamic contour tonometry with Goldmann applanation tonometry over a wider range of central corneal thickness. J Glaucoma 2005;14:288–292.
Francis BA, Hsieh A, Lai M, et al. Effects of corneal thickness, corneal curvature, and intraocular pressure level on Goldmann applanation tonometry and dynamic contour tonometry. Ophthalmology 2007;114:20–26.
Martinez JM, Garcia-Feijoo J, Vico E, et al. Effect of corneal thickness on dynamic contour, rebound, and Goldmann tonometry. Ophthalmology 2006;113:2156–2162.
Barleon L, Hoffman EM, Berres M, et al. Comparison of dynamic contour tonometry and Goldmann applanation in glaucoma patients and healthy subjects. Am J Ophthalmol 2006;142: 583–590.
Kniestedt C, Lin S, Choe J, et al. Clinical comparison of contour and applanation tonometry and their relationship to pachymetry. Arch Ophthalmol 2005;123:1532–1537.
Medeiros FA, Sample PA, Weinreb RN. Comparison of dynamic contour tonometry and Goldmann applanation tonometry in African-American subjects. Ophthalmology 2007;114:658–665.
Salvetat ML, Zeppieri M, Tosoni C, Brusini P. Comparisons between PASCAL dynamic tonometry, the tonopen, and Goldmann applanation tonometry in patients with glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 2007;85:272–279.
Zadok D, Tran D, Twa M, et al. Pneumotonometric versus Goldmann tonometry after laser in situ keratomileusis for myopia. J Cataract Refract Surg 1999;25:1344–1348.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Mawatari, Y., Kobayashi, A., Yokogawa, H. et al. Intraocular pressure after Descemet’s stripping and non-Descemet’s stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty. Jpn J Ophthalmol 55, 98–102 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-010-0916-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-010-0916-8