Abstract
Purpose
To determine the correlations among apoA-1, apoB, and apoB/A-1, the ratio of the first two and their relation to the severity of diabetic retinopathy (DR).
Methods
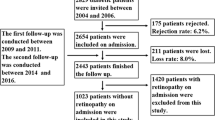
A total of 116 patients with type 2 diabetes, 34 with nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) and 82 with proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), were included. The serum levels of apoA-1, apoB, and the apoB/A-1 ratio were compared. We performed multiple regression analyses to determine whether age, diabetes duration, glycohemoglobin level, estimated glomerular filtration rate, body mass index, or hypertension contribute to PDR.
Results
The apoB levels were lower in the NPDR group than in the PDR group (90.8 ± 21.4 versus 102.5 ± 25.3 mg/dl) (P = 0.02). The apoA-1 levels did not differ between the groups. The apoA-1 was lower in the PDR group than in the NPDR group (136.9 ± 24.9 versus 145.6 ± 21.2 mg/dl) mg/dl (P = 0.08). The apoB/A-1 ratio differed significantly between groups (NPDR versus PDR, 0.64 ± 0.20 versus 0.77 ± 0.24) (P = 0.004). Age, apoB/A-1, and diabetes duration were independent risk factors for PDR (R = −3.49, 3.06, and 2.44; standard regression coefficient, −0.33, 0.28, and 0.23; P = 0.0007, P = 0.003, and P = 0.02, respectively). The PDR group had significantly higher serum levels of apoB and apoB/A-1 than the NPDR group.
Conclusions
The apoB/A-1 ratio may contribute to PDR progression in patients with DR. High apoB and apoB/A-1 values may be related to PDR development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McQueen MJ, Hawken S, Wang X, et al. Lipids, lipoproteins, and apolipoproteins as risk markers of myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART Study): a case-control study. Lancet 2008;372:224–233.
Sato H, Kawasaki R, Yamashita T, et al. Oxidative stress and cell damage in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Jpn J Clin Ophthalmol 2004;58:211–216.
Wilkinson CP, Ferris FL 3rd, Klein RE, et al. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology 2003;110:1677–1682.
Imai E, Horio M, Yamagata K, et al. Estimation of glomerular filtration rate by the MDRD study equation modified for Japanese patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 2007;11:41–50.
Nissen SE, Tsunoda T, Tuzcu EM, et al. Effect of recombinant apoA-I Milano on coronary atherosclerosis in patients with acute coronary syndromes: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2003; 290:2292–2300.
Sniderman AD, St-Pierre AC, Cantin B, et al. Concordance/discordance between plasma apolipoprotein b levels and the cholesterol indexes of atherosclerotic risk. Am J Cardiol 2003;91:1173–1177.
Ohkubo Y, Kishikawa H, Araki E, et al. Intensive insulin therapy prevents the progression of diabetic microvascular complications in Japanese patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: a randomized prospective 6-year study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1995;28:103–117.
Wu M, Chen Y, Wilson K, et al. Intraretinal leakage and oxidation of LDL in diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2008;49:2679–2685.
Simo R, Garcia-Ramirez M, Higuera M, et al. Apolipoprotein A1 is overexpressed in the retina of diabetic patients. Am J Ophthalmol 2009;147:319–325.
Lyons TJ, Jenkins AJ, Zheng D, et al. Diabetic retinopathy and serum lipoprotein subclasses in the DCCT/EDIC cohort. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2004;45:910–918.
Keech A, Simes RJ, Barter P, et al. FIELD study investigators. Lancet 2005;366:1849–1861.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Deguchi, Y., Maeno, T., Saishin, Y. et al. Relevance of the serum apolipoprotein ratio to diabetic retinopathy. Jpn J Ophthalmol 55, 128–131 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-010-0913-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-010-0913-y