Abstract
Purpose
To determine whether optical coherence tomography (OCT) can detect early retinal changes after ischemia–reperfusion injury in rats.
Methods
The intraocular pressure (IOP) was elevated to induce retinal ischemia in brown Norway rats. After 90 min of ischemia, the IOP was reduced, and after reperfusion of 1, 2, 4, or 7 days, OCT was performed. After the OCT examination, the eyes were enucleated and histological sections were made.
Results
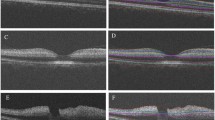
The OCT-determined mean retinal thickness was 168 ± 16.9 µm in the untreated control group, and 177 ± 2.16, 170 ± 7.55, 159 ± 5.34, and 140 ± 5.56 µm on days 1, 2, 4, and 7, respectively, in the ischemia–reperfusion group. The histologically determined retinal thicknesses correlated with those obtained by tomographic images, but the histologic thicknesses were 9.5% to 18.5% thinner than those obtained by OCT. Fixation and dehydration of the histological specimens most likely caused tissue shrinkage.
Conclusions
OCT can detect retinal changes quantitatively after ischemia–reperfusion injury, and the retinal thicknesses obtained from OCT images are probably a better measure of the true retinal thickness than those measured on histological sections.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sho, K., Takahashi, K., Fukuchi, T. et al. Quantitative evaluation of ischemia–Reperfusion injury by optical coherence tomography in the rat retina. Jpn J Ophthalmol 49, 109–113 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-004-0150-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-004-0150-3