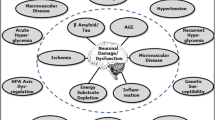
Summary
From large epidemiological studies, it has been demonstrated that diabetes mellitus is a risk factor for cognitive decline: Compared to healthy controls, patients with diabetes perform worse on cognitive tests, they experience a pronounced cognitive decline over time and have a higher incidence of dementia. Mechanisms contributing to cognitive decline include vascular damage, negative consequences of hypo- and hyperglycemia, and various dysfunctions in insulin action, summarized as insulin resistance. Possible targets for prevention and treatment of cognitive decline have attracted scientific attention.
Zusammenfassung
Epidemiologische Langzeituntersuchungen zeigen, dass Diabetes mellitus ein Risikofaktor für das Auftreten kognitiver Einbussen ist: Im Vergleich zu Stoffwechselgesunden zeigen sich schlechtere kognitive Leistungen, eine raschere Progredienz kognitiver Defizite, aber auch eine höhere Inzidenz von Demenzerkrankungen. Als Ursachen werden vaskulär-ischämische Schäden, negative Einflüsse von Hyper- und Hypoglykämie sowie Störungen im Gefolge der Insulinresistenz diskutiert. Mögliche Ansatzpunkte in Prävention und Therapie des kognitiven Abbaus sind ins Interesse der Forschung gerückt.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Resl M, Clodi M. Diabetes and cardiovascular complications. Wien Med Wochenschr, 160: 3–7, 2010
Wancata J, Musalek M, Alexandrowicz R, Krautgartner M. Number of dementia sufferers in Europe between the years 2000 and 2050. Eur Psychiatry, 18: 306–313, 2003
Fratiglioni L, Launer LJ, Andersen K, Breteler MM, Copeland JR, Dartigues JF, Lobo A, Martinez-Lage J, Soininen H, Hofman A. Incidence of dementia and major subtypes in Europe: a collaborative study of population-based cohorts. Neurologic Diseases in the Elderly Research Group. Neurology, 54: S10–S15, 2000
Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM. Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med, 362: 329–344, 2010
Biessels GJ, Kappelle LJ. Increased risk of Alzheimer's disease in Type II diabetes: insulin resistance of the brain or insulin-induced amyloid pathology? Biochem Soc Trans, 33: 1041–1044, 2005
Cukierman T, Gerstein HC, Williamson JD. Cognitive decline and dementia in diabetes – systematic overview of prospective observational studies. Diabetologia, 48: 2460–2469, 2005
van den BE, Reijmer YD, de Bresser J, Kessels RP, Kappelle LJ, Biessels GJ. A 4 year follow-up study of cognitive functioning in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia, 53: 58–65, 2010
Ott A, Stolk RP, Hofman A, van Harskamp F, Grobbee DE, Breteler MM. Association of diabetes mellitus and dementia: the Rotterdam Study. Diabetologia, 39: 1392–1397, 1996
Lu FP, Lin KP, Kuo HK. Diabetes and the risk of multi-system aging phenotypes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One, 4: e4144, 2009
Biessels GJ, Staekenborg S, Brunner E, Brayne C, Scheltens P. Risk of dementia in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Lancet Neurol, 5: 64–74, 2006
Roberts RO, Geda YE, Knopman DS, Christianson TJ, Pankratz VS, Boeve BF, Vella A, Rocca WA, Petersen RC. Association of duration and severity of diabetes mellitus with mild cognitive impairment. Arch Neurol, 65: 1066–1073, 2008
Kloppenborg RP, van den BE, Kappelle LJ, Biessels GJ. Diabetes and other vascular risk factors for dementia: which factor matters most? A systematic review. Eur J Pharmacol, 585: 97–108, 2008
Middleton LE, Yaffe K. Targets for the prevention of dementia. J Alzheimers Dis, 20: 915–924, 2010
Allen KV, Frier BM, Strachan MW. The relationship between type 2 diabetes and cognitive dysfunction: longitudinal studies and their methodological limitations. Eur J Pharmacol, 490: 169–175, 2004
Xu W, Qiu C, Winblad B, Fratiglioni L. The effect of borderline diabetes on the risk of dementia and Alzheimer's disease. Diabetes, 56: 211–216, 2007
Xu WL, Qiu CX, Wahlin A, Winblad B, Fratiglioni L. Diabetes mellitus and risk of dementia in the Kungsholmen project: a 6-year follow-up study. Neurology, 63: 1181–1186, 2004
Sanz C, Andrieu S, Sinclair A, Hanaire H, Vellas B. Diabetes is associated with a slower rate of cognitive decline in Alzheimer disease. Neurology, 73: 1359–1366, 2009
Middleton LE, Yaffe K. Promising strategies for the prevention of dementia. Arch Neurol, 66: 1210–1215, 2009
Middleton LE, Barnes DE, Lui LY, Yaffe K. Physical activity over the life course and its association with cognitive performance and impairment in old age. J Am Geriatr Soc, 58: 1322–1326, 2010
Craft S. Insulin resistance syndrome and Alzheimer's disease: age- and obesity-related effects on memory, amyloid, and inflammation. Neurobiol Aging, 26(Suppl 1): 65–69, 2005
de la Monte SM, Wands JR. Review of insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression, signaling, and malfunction in the central nervous system: relevance to Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis, 7: 45–61, 2005
Zhu X, Perry G, Smith MA. Insulin signaling, diabetes mellitus and risk of Alzheimer disease. J Alzheimers Dis, 7: 81–84, 2005
Umegaki H. Pathophysiology of cognitive dysfunction in older people with type 2 diabetes: vascular changes or neurodegeneration? Age Ageing, 39: 8–10, 2010
Fishel MA, Watson GS, Montine TJ, Wang Q, Green PS, Kulstad JJ, Cook DG, Peskind ER, Baker LD, Goldgaber D, Nie W, Asthana S, Plymate SR, Schwartz MW, Craft S. Hyperinsulinemia provokes synchronous increases in central inflammation and beta-amyloid in normal adults. Arch Neurol, 62: 1539–1544, 2005
Qiu WQ, Folstein MF. Insulin, insulin-degrading enzyme and amyloid-beta peptide in Alzheimer's disease: review and hypothesis. Neurobiol Aging, 27: 190–198, 2006
Matsuzaki T, Sasaki K, Tanizaki Y, Hata J, Fujimi K, Matsui Y, Sekita A, Suzuki SO, Kanba S, Kiyohara Y, Iwaki T. Insulin resistance is associated with the pathology of Alzheimer disease: the Hisayama study. Neurology 75: 764–770, 2010
Rasgon NL, Kenna HA, Wroolie TE, Kelley R, Silverman D, Brooks J, Williams KE, Powers BN, Hallmayer J, Reiss A. Insulin resistance and hippocampal volume in women at risk for Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging, in press; doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2009.12.005
Jolivalt CG, Lee CA, Beiswenger KK, Smith JL, Orlov M, Torrance MA, Masliah E. Defective insulin signaling pathway and increased glycogen synthase kinase-3 activity in the brain of diabetic mice: parallels with Alzheimer's disease and correction by insulin. J Neurosci Res, 86: 3265–3274, 2008
Kalaria RN, Harik SI. Abnormalities of the glucose transporter at the blood-brain barrier and in brain in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Clin Biol Res, 317: 415–421, 1989
de la Monte SM, Wands JR. Alzheimer's disease is type 3 diabetes-evidence reviewed. J Diabetes Sci Technol, 2: 1101–1113, 2008
Watson GS, Craft S. The role of insulin resistance in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease: implications for treatment. CNS Drugs, 17: 27–45, 2003
Heo JH, Lee ST, Kon C, Park HJ, Shim JY, Kim M. White matter hyperintensities and cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer disease. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol, 22: 207–212, 2009
Ahtiluoto S, Polvikoski T, Peltonen M, Solomon A, Tuomilehto J, Winblad B, Sulkava R, Kivipelto M: Diabetes, Alzheimer disease, and vascular dementia: a population-based neuropathologic study. Neurology, 75: 1195–1202, 2010
Musen G, Lyoo IK, Sparks CR, Weinger K, Hwang J, Ryan CM, Jimerson DC, Hennen J, Renshaw PF, Jacobson AM. Effects of type 1 diabetes on gray matter density as measured by voxel-based morphometry. Diabetes, 55: 326–333, 2006
Lobnig BM, Kromeke O, Optenhostert-Porst C, Wolf OT. Hippocampal volume and cognitive performance in long-standing Type 1 diabetic patients without macrovascular complications. Diabet Med, 23: 32–39, 2006
Hershey T, Perantie DC, Wu J, Weaver PM, Black KJ, White NH. Hippocampal volumes in youth with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes, 59: 236–241, 2010
Seaquist ER. The final frontier: how does diabetes affect the brain? Diabetes, 59: 4–5, 2010
Zhu X, Perry G, Smith MA. Insulin signaling, diabetes mellitus and risk of Alzheimer disease. J Alzheimers Dis, 7: 81–84, 2005
Valente T, Gella A, Fernandez-Busquets X, Unzeta M, Durany N. Immunohistochemical analysis of human brain suggests pathological synergism of Alzheimer's disease and diabetes mellitus. Neurobiol Dis, 37: 67–76, 2010
Guglielmotto M, Aragno M, Tamagno E, Vercellinatto I, Visentin S, Medana C, Catalano MG, Smith MA, Perry G, Danni O, Boccuzzi G, Tabaton M. AGEs/RAGE complex upregulates BACE1 via NF-kappaB pathway activation. Neurobiol Aging, in press; doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.05.026
McCall AL. Cerebral glucose metabolism in diabetes mellitus. Eur J Pharmacol, 490: 147–158, 2004
Northam EA, Rankins D, Lin A, Wellard RM, Pell GS, Finch SJ, Werther GA, Cameron FJ. Central nervous system function in youth with type 1 diabetes 12 years after disease onset. Diabetes Care, 32: 445–450, 2009
Whitmer RA, Karter AJ, Yaffe K, Quesenberry CP Jr, Selby JV. Hypoglycemic episodes and risk of dementia in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA, 301: 1565–1572, 2009
Kempermann G, Van Praag H, Gage FH. Activity-dependent regulation of neuronal plasticity and self repair. Prog Brain Res, 127: 35–48, 2000
Van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage FH. Running increases cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Nat Neurosci, 2: 266–270, 1999
Abbas T, Faivre E, Holscher C. Impairment of synaptic plasticity and memory formation in GLP-1 receptor KO mice: Interaction between type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer's disease. Behav Brain Res, 205: 265–271, 2009
Watson GS, Cholerton BA, Reger MA, Baker LD, Plymate SR, Asthana S, Fishel MA, Kulstad JJ, Green PS, Cook DG, Kahn SE, Keeling ML, Craft S. Preserved cognition in patients with early Alzheimer disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment during treatment with rosiglitazone: a preliminary study. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry, 13: 950–958, 2005
Landreth G, Jiang Q, Mandrekar S, Heneka M. PPARgamma agonists as therapeutics for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Neurotherapeutics, 5: 481–489, 2008
Reger MA, Watson GS, Green PS, Baker LD, Cholerton B, Fishel MA, Plymate SR, Cherrier MM, Schellenberg GD, Frey WH, Craft S. Intranasal insulin administration dose-dependently modulates verbal memory and plasma amyloid-beta in memory-impaired older adults. J Alzheimers Dis, 13: 323–331, 2008
Hsu CC, Wahlqvist ML, Lee MS, Tsai HN. Incidence of Dementia is Increased in Type 2 Diabetes and Reduced by the Use of Sulfonylureas and Metformin. J Alzheimers Dis, 24: 485–493, 2011
Chen Y, Zhou K, Wang R, Liu Y, Kwak YD, Ma T, Thompson RC, Zhao Y, Smith L, Gasparini L, Luo Z, Xu H, Liao FF. Antidiabetic drug metformin (GlucophageR) increases biogenesis of Alzheimer's amyloid peptides via up-regulating BACE1 transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 106: 3907–3912, 2009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iglseder, B. Diabetes mellitus und kognitive Störungen. Wien Med Wochenschr 161, 524–530 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10354-011-0003-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10354-011-0003-x