Summary
Therapy with electromagnetic fields has a very old tradition in medicine. The indications are widespread, whereas little is known about the effects. Controlled randomizied studies with positive results for pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF) are available for osteotomies, the healing of skin wounds, and osteoarthritis. Comparison of the studies is difficult because of the different doses applied and intervals of therapy. Therefore recommendations regarding an optimal dosis and interval are, depending on the disease, quite variable.
Zusammenfassung
Die Magnetfeldtherapie ist eine sehr alte physikalische Therapiemodalität, wobei die Wirkung der permanenten und niederfrequent pulsierenden elektromagnetischen Felder (PEMF) bereits seit 2000 Jahren Gegenstand der Heilkunde ist. Bei den unterschiedlichsten Erkrankungen wird die Magnetfeldtherapie empfohlen und teilweise ohne stichhaltige, in randomisierten Studien bestätigte Erfolge angewendet. Ein nachweislich positiver Effekt der Magnetfeldtherapie konnte bisher in mehreren randomisierten Studien bei der Knochenheilung, der Wundheilung und als Analgetikum bei degenerativen Gelenkserkrankungen gefunden werden. Eine exakte Empfehlung hinsichtlich der Therapiedauer und Intensität kann leider aufgrund der fehlenden Datenlage nicht gegeben werden.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Basset CA (1989) Veränderungen auf molekularem Gebiet. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 17: 451–529
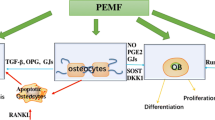
Cane V, Botti P, Soana S (1993) Pulsed magnetic fields improve osteoblast activity during the repair of an experimental osseous defect. J Orthop Res 11: 664–670
Gossling HR, Bernstein RA, Abbott J (1992) Treatment of ununited tibial fractures: a comparison of surgery and pulsed electromagnetic fields (PEMF). Orthopedics 15: 711–719
Mammi GI, Rocchi R, Cadossi R, Massari L, Traina GC (1993) The electrical stimulation of tibial osteotomies. Clin Orthop 246–253
Borsalino G, Bagnacani M, Bettati E et al (1988) Electrical stimulation of human femoral intertrochanteric osteotomies. Clin Orthop 237: 256–263
Hofmann S, Mazieres B (2000) Osteonekrose: Natürlicher Verlauf und konservative Therapie. Orthopäde 29: 403–410
Trock DH, Bollet AJ, Markoll R (1994) The effect of pulsed electromagnetic fields in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee and cervical spine. J Rheumatol 21: 1903–1911
Pages ICH, Hermann H, Conradi E (1985) Magnetfeldtherapie bei chronisch degenerativen Erkrankungen des Bewegungsapparates. Z Physiother 37: 21–24
Dal Conte G (1983) Studio controllato nella capacita die campi magnetici pulsati ad alleviare i sintomi della coxartrosi. Atti 13 Congresso. Naz Simfer Verona 11: 98–104
Sutbeyaz ST, Sezer N, Koseoglu BF (2006) The effect of pulsed electromagnetic fields in the treatment of cervical osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled trial. Rheumatol Int 26: 320–324
Hong CZ, Lin JC, Bender LF et al (1982) Magnetic necklace: Its therapeutic effectiveness on neck and shoulder pain. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 63: 462–466
Senn E, Baviera B, Felchlin E, Egli S (1985) Der Vergleich der Wirksamkeit einer magnetischen Halskette, einer Placebohalskette und einer individuellen physiotherapeutischen Behandlung bei Patienten mit einem chronischen zervikovertebralen Syndrom. Z Phys Med Baln Med Klim 14: 239–255
Singer F, Schieler K (1977) Erfahrungen mit pulsierender niederfrequenter elektromagnetischen Energie bei der Behandlung degenerativer Gelenkserkrankungen. Z Physiother 29: 339–341
Thamsborg G, Florescu A, Oturai P et al (2005) Treatment of knee osteoarthritis with pulsed electromagnetic fields: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 13: 575–581
Hulme JM, Robinson VA, De Bie R, Wells G, Judd M, Tugwell P (2006) Electromagnetic fields for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Conchrane Database Syst Rev 2006(4)
De Mattei M, Caruso A, Pezzetti F et al (2001) Effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields on human articular chondrocyte proliferation. Connect Tissue Res 42: 269–279
Fini M, Giavaresi G, Torricelli P et al (2005) Pulsed electromagnetic fields reduce knee osteoarthritis lesion progression in the aged Dunkin Hartley guinea pig. J Orthop Res 23: 899–908
Uzunca K, Birtane M, Tastekin N (2006) Effectiveness of pulsed electromagnetic field therapy in lateral epicondylitis. Clin Rheumatol Apr 22; [Epub ahead of print]
Todd DJ, Heylings DJ, Allen GE et al (1991) Treatment of chronic varicose ulcers with pulsed electromagnetic fields: a controlled pilot study. Ir Med J 84: 54–55
Stiller MJ, Pak GH, Shupack JL et al (1992) A portable pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF) device to enhance healing of recalcitrant venous ulcers: a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Br J Dermatol 127: 147–154
Weintraub MI, Cole SP (2004) Pulsed magnetic field therapy in refractory neuropathic pain secondary to peripheral neuropathy: electrodiagnostic parameters – pilot study. Neurorehabil Neural Repair 18: 42–46
Musaev AV, Guseinova SG, Imamverdieva SS (2003) The use of pulsed electromagnetic fields with complex modulation in the treatment of patients with diabetic polyneuropathy. Neurosci Behav Physiol 33: 745–752
Xu S, Okano H, Ohkubo C (2001) Acute effects of wholebody exposure to static magnetic fields and 50 Hz electromagnetic fields on muscle microcirculation in anesthetized mice. Bioelectrochemistry 53: 127–135
Smith TL, Wong-Gibbons D, Maultsby J (2004) Microcirculatory effects of pulsed electromagnetic fields. J Orthop Res 22: 80–84
Schuhfried O, Vacariu G, Rochowanski H et al (2005) The effect of low-dosed and high-dosed low-frequency electromagnetic fields on microcirculation and skin temperature in healthy subjects. Int J Sports Med 26: 886–890
McMeeken JM (1992) Effects on blood flow in human subjects. Physiother Ther Pract 8: 5–9
Gwechenberger M, Rauscha F, Stix G et al (2006) Interference of programmed electromagnetic stimulation with pacemakes and automatic implantable cardioverter defibrillitaors. Bioelectromagnetics
Fialka-Moser V (2005) Elektrotherapie. Pflaum, München, S195
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pieber, K., Schuhfried, O. & Fialka-Moser, V. Magnetfeldtherapie – Ergebnisse hinsichtlich evidence based medicine. Wien Med Wochenschr 157, 34–36 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10354-006-0369-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10354-006-0369-3