Summary
Background
The aim of this study was to investigate the outcome of patients suffering from benign or malignant superior vena cava (SVC), brachiocephalic (BCV), and subclavian (SV) vein lesions treated with nitinol stents.
Methods
Retrospective analysis of consecutive patients in a university-based tertiary care center.
Results
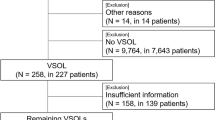
Twenty-two patients suffering from central venous occlusive disease (CVD) (9 malignant, mean age 58 years; 13 benign, mean age 66 years) were treated 2/2003–1/2012. In total, 89 % of malignant central venous occlusive disease (mCVD) patients underwent successful primary stenting (one reintervention 6 months after primary stenting). Two stent occlusions (22 %) were seen at last follow-up. All mCVD patients died within a median follow-up of 2 months (range: 0.8–54 months). In all, 92 % of benign central venous occlusive disease (bCVD) patients underwent primary stenting of SV (n = 8), BCV (n = 5), and SVC (n = 1). Six repeat interventions were performed in 42 % of patients. There was one stent occlusion (8 %) at last follow-up. Of all, 69 % of bCVD patients died within a median follow-up of 12.7 months (range: 1.3–82 months); 22 % of mCVD and 8 % of bCVD patients underwent bypass surgery as bail out procedure due to primary (n = 2) or secondary (n = 1) endovascular failure. All CVD patients experienced immediate post-interventional relief of symptoms.
Conclusion
Technical success of CVD stenting is high and leads to immediate relief of symptoms in patients with short life expectancy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parish JM, Marschke RF, Dines DE, Lee RE. Etiologic considerations in superior vena cava syndrome. Mayo Clin Proc. 1981;56:407–13.
Ostler PJ, Clarke DP, Watkinson AF, Gaze MN. Superior vena cava obstruction: a modern management strategy. Clin Oncol. 1997;9:83–9.
Charnsangavej C, Carrasco CH, Wallace S, Gianturco C, et al. Stenosis of the vena cava: preliminary assessment of treatment with expandable metallic stents. Radiology. 1986;161:295–8.
Urruticoechea A, Mesia R, Dominguez J, et al. Treatment of malignant superior vena cava syndrome by endovascular stent insertion. Experience on 52 patients with lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2004;43:209–14.
Agarwal AK, Patel BM, Farhan NJ. Central venous stenosis in hemodialysis patients is a common complication of ipsilateral central vein catheterization. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:368–9A.
Topf G, Jenkins P, Guttmann FD, Rieselbach RE, Saltzstein EC. Unilateral breast enlargement: a complication of an arterio-venous fistula and coincidental subclavian vein occlusion. JAMA. 1977;237:571–2.
Dethlefsen S, Shepro D, D’Amore PA. Comparison of the effects of mechanical stimulation on venous and arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro. J Vasc Res. 1996;33:405–13.
NKF-K/DOQUI clinical practice guidelines for vascular access. update 2000. Am J Kidney Dis. 2001;37:S137–81.
Aruny JE, Lewis CA, Cardella JF, Cole PE, Davis A, Drooz AT. Quality improvement guidelines for percutaneous management of the thrombosed or dysfunctional dialysis access. Standards of Practise Committee of the Society of Cardiovascular & Interventional Radiology. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003;14:S247–53.
Haage P, Vorwerk D, Piroth W, Schuemann K, Guenther RW. Treatment of hemodialysis-related central stenosis or occlusion: results of primary Wallstent placement and follow-up in 50 patients. Radiology. 1999;121:175–80.
Mickley V, Gorich J, Rilinger N, Storck M, Abendroth D. Stenting of central venous stenoses in hemodialysis patients: long-term results. Kidney Int. 1997;51:277–80.
Quinn SF, Schuman ES, Demlow TA, et al. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty versus endovascular stent placement in the treatment of venous stenoses in patients undergoing hemodialysis: intermediate results. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 1995;6:851–5.
Shoenfeld R, Hermans H, Novick A, et al. Stenting of proximal venous obstructions to maintain hemodialysis access. J Vasc Surg. 1994;9:532–9.
Vogel PM, Parise CP. SMART stent for salvage of hemodialysis access grafts. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2004;15(10):1051–60.
Fagedet D, Thony F, Timsit JF, et al. Endovascular treatment of malignant superior vena cava syndrome: results and predictive factors of clinical efficacy. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2013;36(1):140–9.
Canales JF, Cardenas JC, Dougherty K, Krajcer Z. Single center experience with percutaneous endovascular repair of superior vena cava syndrome. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;77(5):733–9.
Stanford W, Jolles H, Ell S, Chiu LC. Superior vena cava obstruction: venographic classification. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987;148:259–62.
Dondelinger R. Chronic upper extremity/superior vena cava venous occlusive disease. In: Mauro M, Murphy K, Thomson K, Venbrux A, Zollikofer C, editors. Image guided interventions. Philadelphia: Saunders Elsevier; 2008. pp. 1055–65.
Günther RW, Vorwerk D, Bohndorf K, et al. Venous stenoses in dialysis shunts: treatment with self-expanding metallic stents. Radiology. 1989;170(2):401–5.
Gloviczki P, Kalra M. Surgical treatment of superior vena cava obstruction. In: Cronenwett JL, editor. Rutherford’s vascular surgery. 7th ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders; 2010. pp. 963–75.
Kishi K, Sonomura T, Mitsuzane K, et al. Self-expandable stent therapy for superior vena cava syndrome: clinical observations. Radiology. 1993;189:531–5.
Hill T, Lewicki P. STATISTICS methods and applications. Tulsa: StatSoft; 2007.
Wolfram Research, Inc. Mathematica, Version 7.0, Champaign: Wolfram Research, Inc.; 2008.
Goeckenjan G, Sitter H, Thomas M, et al. Prevention, diagnosis, therapy, and follow-up of lung cancer. Interdisciplinary guideline of the German Respiratory Society and the German Cancer Society-abridged version. Pneumologie. 2011;65(8):e51–75.
Nagata T, Makutani S, Uchida H, et al. Follow-up results of 71 patients undergoing metallic stent placement for the treatment of a malignant obstruction of the superior vena cava. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2007;30(5):959–67.
Lanciego C, Pangua C, Chacon JI, et al. Endovascular stenting as the first step in the overall management of malignant superior vena cava syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009;193(2):549–58.
Ganeshan A, Hon LQ, Warakaulle DR, Morgan R, Uberoi R. Superior vena caval stenting for SVC obstruction: current status. Eur J Radiol. 2009;71:343–9.
de Gregorio AMA, Gamboa P, Gimeno MJ, et al. Percutaneous treatment of superior vena cava syndrome using metallic stents. Eur Radiol. 2003;13:853–62.
Matsushita J, Morita S, Suzuki K, et al. Pull-through technique with pincer tactics for stent placement in severe superior vena cava syndrome. Ann Vasc Surg. 2012;26(3):421.e11–5.
Ingram TL, Reid SH, Tisnado J, Cho SR, Posner MP. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty of brachiocephalic vein stenoses in patients with dialysis shunts. Radiology. 1988;166:45–7.
Kovalik EC, Newman GE, Suhocki P, Knelson M, Schwab SJ. Correction of central venous stenoses: use of angioplasty and vascular Wallstents. Kidney Int. 1994;45(4):1177–81.
Kundu S. Central venous obstruction management. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2009;26(2):115–21.
Dammers R, de Haan MW, Planken NR, van der Sande FM, Tordoir JH. Central vein obstruction in hemodialysis patients: results of radiological and surgical intervention. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2003;26(3):317–21.
Lumsden AB, MacDonald MJ, Isiklar H, et al. Central venous stenosis in the hemodialysis patient: incidence and efficacy of endovascular treatment. Cardiovasc Surg. 1997;5(5):504–9.
Oderich GS, Treiman GS, Schneider P, Bhirangi K. Stent placement for treatment of central and peripheral venous obstruction: a long-term multi-institutional experience. J Vasc Surg. 2000;32:760–9.
Bakken AM, Protack CD, Saad WE, Lee DE, Waldman DL, Davies MG. Long-term outcomes of primary angioplasty and primary stenting of central venous stenosis in hemodialysis patients. J Vasc Surg. 2007;45:776–83.
Glanz S, Gordon D, Butt KMH, Hong J, Adamson R, Sclafani SJ. Dialysis access fistulas: treatment of stenoses by transluminal angioplasty. Radiology. 1984;152(3):637–42.
Beathard GA. Percutaneous transvenous angioplasty in the treatment of vascular access stenosis. Kidney Int. 1992;42:1390–7.
Surowiec SM, Fegley AJ, Tanski WJ, et al. Endovascular management of central venous stenoses in the hemodialysis patient: results of percutaneous therapy. Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2004;38(4):349–54.
Himmelfarb J, Ikizler TA. Hemodialysis. N Eng J Med. 2010;363:1833–45
Gradman WS, Bressman P, Sernaque JD. Subclavian vein repair in patients with an ipsilateral arteriovenous fistula. Ann Vasc Surg. 1994;8:549–56.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Linni, K., Ugurluoglu, A., Aspalter, M. et al. Stent-supported percutaneous transluminal angioplasty in patients suffering from symptomatic benign or malignant central venous occlusive disease. Eur Surg 47, 166–174 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10353-015-0325-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10353-015-0325-9