Summary
Background
Pulmonary metastasectomy with curative intent is nowadays a common practice in thoracic surgery. The impact of metastasectomy on respiratory function has become a relevant factor in the treatment algorithm of these patients. However, no sufficient data on the loss of lung function following pulmonary metastasectomy is available to date.
Methods
A prospective single center study was designed to determine changes in lung function parameters in patients undergoing metastasectomy. Forty-five consecutive patients were included in the study. In 19 patients, metastases were removed by enucleation (laser = 10; electrocautery = 9), in 19 patients by wedge resection, and 7 patients received a lobectomy in order to achieve clear resection margins. Lung function testing was obtained from all patients preoperatively and 3 months after hospital discharge.
Results
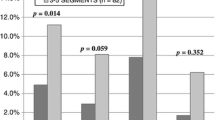
A significant decrease in FEV1 and VC was found when comparing enucleation/wedge/lobectomy patients (FEV1: 3.4 ± 0.7, 7.6 ± 1.5, 14.2 ± 3.0; VC: 2.4 ± 1.6, 4.7 ± 1.6, 16.9 ± 2.9; respectively). However, no differences were found regarding the loss of FEV1 per resected nodule between laser and electrocautery enucleations. These findings were confirmed by a volumetric analysis of the resected tissue and did not correlate with size of metastases as determined by preoperative CT evaluations.
Conclusions
The surgical resection of pulmonary metastases is associated with a detectable but mild loss of lung function. Lung parenchyma sparing resection methods—e.g. electrocautery or laser enucleations—should be preferred over less tissue-sparing techniques.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoetzenecker K, Lang G, Ankersmit HJ, Klepetko W. Pulmonary metastasectomy. Eur Surg. 2010;43:262–9.
Petrella F, Chieco P, Solli P, Veronesi G, Borri A, Galetta D, et al. Which factors affect pulmonary function after lung metastasectomy? Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009;35:792–6.
Welter S, Cheufou D, Sommerwerck U, Maletzki F, Stamatis G. Changes in lung function parameters after wedge resections: a prospective evaluation of patients undergoing metastasectomy. Chest. 2012;141:1482–9.
Internullo E, Cassivi SD, Van Raemdonck D, Friedel G, Treasure T. Pulmonary metastasectomy: a survey of current practice amongst members of the European Society of Thoracic Surgeons. J Thorac Oncol. 2008;3:1257–66.
Quanjer PH, Tammeling GJ, Cotes JE, Pedersen OF, Peslin R, Yernault JC. Lung volumes and forced ventilatory flows. Report Working Party Standardization of Lung Function Tests, European Community for Steel and Coal. Official Statement of the European Respiratory Society. Eur Respir J Suppl. 1993;16:5–40.
Venuta F, Rolle A, Anile M, Martucci N, Bis B, Rocco G. Techniques used in lung metastasectomy. J Thorac Oncol. 2010;5:S145–50.
Rolle A, Pereszlenyi A, Koch R, Richard M, Baier B. Is surgery for multiple lung metastases reasonable? A total of 328 consecutive patients with multiple-laser metastasectomies with a new 1318-nm Nd:YAG laser. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006;131:1236–42.
Mineo TC, Ambrogi V, Tonini G, Nofroni I. Pulmonary metastasectomy: might the type of resection affect survival? J Surg Oncol. 2001;76:47–52.
Bolliger CT, Jordan P, Soler M, Stulz P, Tamm M, Wyser C, et al. Pulmonary function and exercise capacity after lung resection. Eur Respir J. 1996;9:415–21.
Park JS, Kim HK, Choi YS, Kim K, Shim YM, Jo J, et al. Outcomes after repeated resection for recurrent pulmonary metastases from colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 2010;21:1285–9.
Wang J, Talmon GA, Feloney M, Morris MC. Twelve-year survival after multiple recurrences and repeated metastasectomies for renal cell carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 2011;9:155.
van Geel AN, Hoekstra HJ, van Coevorden F, Meyer S, Bruggink ED, Blankensteijn JD. Repeated resection of recurrent pulmonary metastatic soft tissue sarcoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 1994;20:436–40.
Kandioler D, Kromer E, Tuchler H, End A, Muller MR, Wolner E, et al. Long-term results after repeated surgical removal of pulmonary metastases. Ann Thorac Surg. 1998;65:909–12.
Jaklitsch MT, Mery CM, Lukanich JM, Richards WG, Bueno R, Swanson SJ, et al. Sequential thoracic metastasectomy prolongs survival by re-establishing local control within the chest. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2001;121:657–67.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoetzenecker, K., Schweiger, T., Nikolowsky, C. et al. Impact of resection techniques on postoperative lung function parameters in pulmonary metastasectomy. Eur Surg 45, 93–97 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10353-013-0202-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10353-013-0202-3