Summary
Background
The current study is the first to evaluate the protective effect of everolimus on biochemical and histopathological features with an experimental hepatic ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injury model.
Methods
Twenty-four Wistar Albino rats were randomized into four groups: Group 1 (sham group) was subjected to laparotomy. Group 2 (I/R group) was subjected to ischemia for 1 hour and reperfusion for 24 hours without treatment. Group 3 was treated with 1.5 mg/kg/day everolimus perorally for 7 days without performing I/R. Group 4 was treated with 1.5 mg/kg/day everolimus perorally for 7 days followed with performing I/R. Blood samples and liver tissues were obtained to assess serum aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanin aminotransferase (ALT), albumin, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tissue malonyl dialdehyde (MDA), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels and histopathologic examination.
Results
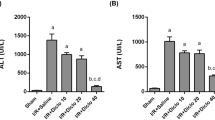
Serum AST and ALT levels of I/R group were significantly higher than sham group. Serum transaminase levels were significantly decreased after treatment with everolimus (group 4) when compared with I/R group (group 2). TNFα and MDA levels were decreased; however, SOD levels were increased in group 4. The sham group and group 3 showed normal histological findings. Morphologic analysis showed reduced degrees of injury in group 4 than group 2 with regards to cholestasis, sinusoidal dilatation, congestion, hydropic degeneration, and subcapsular necrosis.
Conclusions
This is the first report as regards everolimus attenuates biochemical and histopathological alterations of hepatic I/R injury. Everolimus can be a choice for preventing I/R injury during liver transplantation surgery in the future besides its well-known immunosuppressive property.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blankenstejin JD, Terpstra OT. Liver preservation: the past and the future. Hepatology. 1990;13(6):1235–50.
Clavien PA, Harvey PRC, Strasberg SM. Preservation and reperfusion injuries in liver allografts. Transplantation. 1992;53(5):957–8.
Rosser BG, Gores GJ. Liver cell necrosis: cellular mechanisms and clinical implications. Gastroenterology. 1995;108(1):252–75.
Kim SJ, Moon YJ, Lee SM. Protective effects of baicalin against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat liver. J Nat Prod. 2010;73(12):2003–8.
Jin LM, Liu YX, Zhou L, Feng XW, Li H, Zheng SS. Ischemic preconditioning attenuates morphological and biochemical changes in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Pathobiology. 2010;77(3):136–46.
Marinov M, Ziogas A, Pardo OE, et al. AKT/mTOR pathway activation and BCL-2 family proteins modulate the sensitivity of human small cell lung cancer cells to RAD001. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(4):1277–87.
Wolpin BM, Hezel AF, Abrams T, et al. Oral mTOR inhibitor everolimus in patients with gemcitabine-refractory metastatic pancreatic cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(2):193–8.
Oliveira CP, Lopasso FP, Laurindo FR, Leitão RM, Laudanna AA. Protection against liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by Silymarin or Verapamil. Transplant Proc. 2001;33(6):3010–4.
Dunn C, Croom KF. Everolimus: a rewiev of its use in renal and cardiac transplantation. Drugs. 2006;66(4):547–70.
Iwasaki Y, Togaya N, Hattori Y, Yamaguchi K, Kubota K. Protective effect of ischemic preconditioning against intermittent warm-ischemia-induced liver injury. J Surg Res. 2002;107(1):82–92.
Colletti LM, Cortis A, Lukacs N, Kunkel SL, Green M, Strieter RM. Tumor necrosis factor up-regulates intercellular adhesion molecule 1, which is important in the neutrophil-dependent lung and liver injury associated with ischemia and reperfusion in the rat. Shock. 1998;10(3):182–91.
Donato M, D’Annunzio V, Berg G, et al. Ischemic postconditioning reduces infarct size by activation of A1 receptors and K (ATP) channels in both normal and hypercholesterolemic rabbits. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007;49(5):287–92.
Chattopadhayay P, Wahi AK. Inhibition by folic acid of tumor necrosis factor alpha and apoptosis following normothermic ischemia-reperfusion. Arzneimittelforschung. 2010;60(10):621–6.
Kotsch K, Ulrich F, Reutzel-Selke A, et al. Methylprednisolone therapy in decreased donors reduces inflammation in the donor liver and improves outcome after liver transplantation: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg. 2008:248(6):1042–9.
Caraceni P, Pertosa AM, Giannone F, et al. Antagonism of the cannabinoid CB-1 receptor protects rat liver against ischaemia-reperfusion injury complicated by endotoxaemia. Gut. 2009;58(8):1135–43.
Zhang F, Mao Y, Qiao H, et al. Protective effects of taurine against endotoxin-induced acute liver injury after hepatic ischemia reperfusion. Amino Acids. 2010;38(1):237–45.
Yilmaz S, Ates E, Tokyol C, Pehlivan T, Erkasap S, Koken T. The protective effect of erythropoietin on ischaemia/reperfusion injury of liver. HPB(Oxford). 2004;6(3):169–73.
Fondevila C, Shen XD, Tsuchiyashi S, Yamashita K, Csizmadia E, Lassman C. Biliverdin therapy protects rat livers from ischemia and reperfusion injury. Hepatology. 2004;40(6):1333–41.
Kim SJ, Moon YJ, Lee SM. Protective effects of baicalin against ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat liver. J Nat Prod. 2010;73(12):2003–8.
Bockhorn M, Fingas CD, Rauen U, et al. Erythropoietin treatment improves liver regeneration and survival in rat models of extended liver resection and living donor liver transplantation. Transplantation. 2008;86(11):1578–85.
Kannerup AS, Gronbaek H, Fuch-Jensen P, Tønnesen E, Jørgensen RL, Mortensen FV. Cytokine changes during warm ischemia and reperfusion of the pig liver with or without preconditioning. Eur Surg Res. 2009;42(4):216–22.
Schrelm S, Lehle K, Birnbaum DE, Preuner JG. mTOR-inhibitors simultaneously inhibit proliferation and basal IL-6 synthesis of human coronary artery endothelial cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2007;7(6):781–90.
Ninomiya M, Shimada M, Harada N, et al. Beneficial effect of MCI-186 on hepatic warm ischemia-reperfusion in the rat. Transplantation. 2002;74(10):1470–2.
Zhao T, Xi L, Chelliah J, Levasseur JE, Kukreja RC. Inducible nitric oxide synthase mediates delayed myocardial protection induced by activation of adenosine A(1) receptors: evidence from gene-knockout mice. Circulation. 2000;102(8):902–7.
Ozturk H, Gezici A, Ozturk H. The effect of celecoxib, a selective COX-2 inhibitor, on liver ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress in rats. Hepatol Res. 2006;342(2):76.
Arrigo AP, Firdaus WJ, Mellier G, et al. Cytotoxic effects induced by oxidative stress in cultured mammalian cells and protection provided by Hsp27 expression. Methods. 2005;35(2):126–38.
Hassan L, Bueno P, Ferron-Celma I, et al. Time course of antioxidant enzyme activities in liver transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 2005;37(9):3932–5.
Chen CF, Hsueh CW, Tang TS, Wang D, Shen CY, Pei JS. Reperfusion liver injury-induced superoxide dismutase and catalase expressions and the protective effects of N-Acetyl-Cysteine. Transplan Proc. 2007;39(4):858–60.
Song SW, Tolba RH, Yonezawa K, Manekeller S, Minor T. Exogenous superoxide dismutase prevents peroxynitrite-induced apoptosis in non-heart-beating donor livers. Eur Surg Res. 2008;41(4):353–61.
Freudenthaler SM, Schreeb KH, Wiese A, Pilz J, Gleiter CH. Influence of controlled hypoxia and radical scavenging agents on erythropoetin and malondialdehyde concentrations in humans. Acta Physion Scand. 2002;174(3):231–5.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the present study was funded by IMSED (Education Society of Internal Medicine After Graduation).
Bahar Gurlek Demirci, Mehmet Cindoruk, and Aydin Dalgic designed the research/study; Bahar Gurlek Demirci, Utku Tonguc Yilmaz, Ipek Isik Gonul, Ozlem Gulbahar, and Umut Demirci performed the research/study; Yilmaz performed the surgical procedures; Demirci and Yilmaz contributed important reagents; Demirci collected the data; Mehmet Derya Demirag analyzed the data; and Demirci wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demirci, B., Cindoruk, M., Yilmaz, U. et al. Effects of everolimus on hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in an experimental rat model. Eur Surg 44, 325–330 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10353-012-0152-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10353-012-0152-1