Summary
Background
Retroperitoneal abscess is a rare condition and is usually secondary to underlying morbidity such as diabetes, previous surgery, cirrhosis, open or closed trauma, diverticulitis, appendicitis, renal tumour and immunosuppression.
Methods
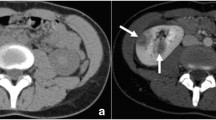
A 44 year old man without previous pathology presented with a retroperitoneal abscess. The C-reactive protein and leukocyte levels were elevated. The diagnosis was made by abdominal tomography.
Results
The patient was treated with imipenem and surgical drainage. Twelve months later the patient was asymptomatic.
Conclusions
Retroperitoneal abscess in healthy patient is a very uncommon condition. The pathology should be considered in a patient who presents with abdominal pain, fever and raised analytics. The treatment should be by drainage and antibiotic therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brook I, Frazier EH. Aerobic and anaerobic microbiology of retroperitoneal abscesses. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;26:938–41.
Tejido Sánchez A, Jiménez de la Peña MM, Duarte Ojeda JM, Villacampa Aubá F, Martín Muñoz MP, Lozano Ojeda F, et al. Percutaneous treatment of retroperitoneal abscesses. Actas Urol Esp. 2000;24:131–7.
Bahamondes L, Lopez de Maturana JC. Absceso retroperitoneal. Comunicación de dos casos y revisión de la literatura. Rev Chil Infect. 2001;18:147–52.
Capitán Manjón C, Tejido Sánchez A, Piedra Lara JD, Martínez Silva V, Cruceyra Betriu G, Rosino Sánchez A, et al. Retroperitoneal abscesses—analysis of a series of 66 cases. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2003;37:139–44.
Esposito S, Leone S, Carosi G. Analysis of current guidelines for intra-abdominal infections. J Chemother. 2009;21(Suppl 1):30–5.
Krid M, Atallah R, Tlili K, Mosbach A. Treatment of kidney and retroperitoneal abscesses using percutaneous drainage. Apropos of 17 cases. Prog Urol. 1994;4:378–83.
Gordon DH, Macchia RJ, Glanz S, Koser MW, Laungani GB. Percutaneous management of retroperitoneal abscesses. Urology. 1987;30:299–306.
Brook I. Intra-abdominal, retroperitoneal, and visceral abscesses in children. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2004;14:265–73.
Castillo O, Vitagliano G, Díaz M, Hoyos J, Pinto I, Cortés O, Estrada JC. Lumboscopic drainage of retroperitoneal abscess. Case report. Actas Urol Esp. 2006;30:711–3.
Arrabal-Polo MA, Arrabal-Martin M, Lopez-Leon VM, et al. Spontaneous retroperitoneal abscess as the first clinical manifestation of a non-functioning retroperitoneal paraganglioma. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2010;92:W17–9.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest and no funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arrabal-Polo, M., Arrabal-Martin, M. Retroperitoneal abscess in the anterior para-renal space in a healthy patient. Eur Surg 44, 349–350 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10353-012-0150-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10353-012-0150-3