Purpose
Despite technically successful surgery for diverticular disease, a significant group of patients who experience persistent or recurrent symptoms remains. This study was designed to determine the incidence and pattern of persistent symptoms and their association with peroperative parameters.
Methods
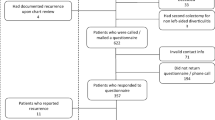
Follow-up (33 (range, 4–72) months) through structured interviews with patients who had surgery for diverticulitis in our department from December 1999 to November 2004 was conducted. Of 162 patients, 124 (76.5 percent) were available for follow-up. Nonparametric tests were used for comparison of patients who had undergone elective (n = 68) or emergency (n = 56) procedures.
Results
Of patients who had elective surgery, 25 percent suffered persistent symptoms, including painful constipation, painful abdominal distension, abdominal cramps, and frequent painful diarrhea. Neither the stage of disease (complicated or uncomplicated) nor the surgical technique (laparotomy or laparoscopy) were significantly related to the occurrence of symptoms. Recurrent diverticulitis was not observed. Similar results were obtained from comparisons with emergency patients.
Conclusions
The prevalence of persistent symptoms after successful surgery for diverticular disease may be an additional reason to carefully discuss the indication for prophylactic surgery. In any case, preoperative counseling and informed consent regarding the possibility of persistent symptoms after prophylactic elective surgery is essential.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parks TG. Natural history of diverticular disease of the colon. Clin Gastroenterol 1975;4:53–69.
Blake MF, Dwivedi A, Tootla A, Tootla F, Silva YJ. Laparoscopic sigmoid colectomy for chronic diverticular disease. JSLS 2005;9:382–5.
Horgan AF, McConnell EJ, Wolff BG, The S, Paterson C. Atypical diverticular disease: surgical results. Dis Colon Rectum 2001;44:1315–8.
Bassotti G, Battaglia E, de Roberto G, Morelli A, Tonini M, Villanacci V. Alterations in colonic motility and relationship to pain in colonic diverticulosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2005;3:248–53.
Floch MH, Bina I. The natural history of diverticulitis: fact and theory. J Clin Gastroenterol 2004;38:S2–7.
Moreaux J, Vons C. Elective resection for diverticular disease of the sigmoid colon. Br J Surg 1990;77:1036–8.
Bacon HE, Berkley JL. The surgical management of diverticulitis of the colon with particular reference to rehabilitation. Arch Surg 1960;80:646–9.
Benn PL, Wolff BG, Ilstrup DM. Level of anastomosis and recurrent colonic diverticulitis. Am J Surg 1986;151:269–71.
Farmakis N, Tudor RG, Keighley MR. The 5-year natural history of complicated diverticular disease. Br J Surg 1994;81:733–5.
Leigh JE, Judd ES, Waugh JM. Diverticulitis of the colon. Recurrence after apparently adequate segmental resection. Am J Surg 1962;103:51–4.
Marsh J, Liem RK, Byrd BF Jr, Daniel RA. One hundred consecutive operations for diverticulitis of the colon. South Med J 1975;68:133–7.
Janes S, Meagher A, Frizelle FA. Elective surgery after acute diverticulitis. Br J Surg 2005;92:133–42.
Parks TG, Connell AM. The outcome in 455 patients admitted for treatment of diverticular disease of the colon. Br J Surg 1970;57:775–8.
Breen RE, Corman ML, Robertson WG, Prager ED. Are we really operating on diverticulitis? Dis Colon Rectum 1986;29:174–6.
Munson KD, Hensien MA, Jacob LN, Robinson AM, Liston WA. Diverticulitis: a comprehensive follow-up. Dis Colon Rectum 1996;39:318–22.
Thorn M, Graf W, Stefansson T, Pahlman L. Clinical and functional results after elective colonic resection in 75 consecutive patients with diverticular disease. Am J Surg 2002;183:7–11.
Simpson J, Neal KR, Scholefield JH, Spiller RC. Patterns of pain in diverticular disease and the influence of acute diverticulitis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2003;15:1005–10.
Wong WD, Wexner SD, Lowry A, et al. Practice parameters for the treatment of sigmoid diverticulitis—supporting documentation. The Standards Task Force. The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons. Dis Colon Rectum 2000;43:290–7.
Kohler L, Sauerland S, Neugebauer E. Diagnosis and treatment of diverticular disease: results of a consensus development conference. The Scientific Committee of the European Association for Endoscopic Surgery. Surg Endosc 1999;13:430–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Egger, B., Peter, M.K. & Candinas, D. Persistent Symptoms After Elective Sigmoid Resection for Diverticulitis. Dis Colon Rectum 51, 1044–1048 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-008-9234-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-008-9234-3