Purpose
This study was designed to evaluate the accuracy of the Physiologic and Operative Severity Score for the enUmeration of Mortality and morbidity, Portsmouth–Physiologic and Operative Severity Score for the enUmeration of Mortality and morbidity, colorectal–Physiologic and Operative Severity Score for the enUmeration of Mortality and morbidity, and the Surgical Risk Scale for the treatment of patients with complicated diverticular disease.
Methods
Physiologic and Operative Severity Score for the enUmeration of Mortality and morbidity variables were prospectively recorded for 324 patients undergoing colorectal resections in 42 hospitals in the United Kingdom from January to December 2003. The accuracy of each model was evaluated by measures of discrimination, calibration, and subgroup analysis.
Results
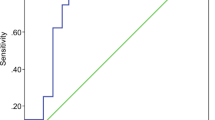
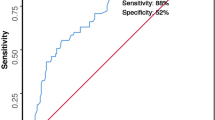
The overall operative mortality was 10.8 percent (Physiologic and Operative Severity Score for the enUmeration of Mortality and morbidity-estimated mortality rate, 21.9 percent; Portsmouth-Physiologic and Operative Severity Score for the enUmeration of Mortality and morbidity-estimated mortality rate, 10.5 percent; colorectal–Physiologic and Operative Severity Score for the enUmeration of Mortality and morbidity-estimated mortality rate, 10 percent; Surgical Risk Scale-estimated mortality rate, 38.2 percent). Physiologic and Operative Severity Score for the enUmeration of Mortality and morbidity and the Surgical Risk Scale over-predicted mortality in young patients (P < 0.001) and Portsmouth–Physiologic and Operative Severity Score for the enUmeration of Mortality and morbidity underpredicted mortality in elderly patients (P < 0.001). Physiologic and Operative Severity Score for the enUmeration of Mortality and morbidity and the Surgical Risk Scale overpredicted mortality in patients with generalized peritonitis (Hinchey III and IV). There was no significant difference between the observed and colorectal-Physiologic and Operative Severity Score for the enUmeration of Mortality and morbidity predicted mortality across patient subgroups and when the overall sample was considered.
Conclusions
The study suggested a lack of calibration of Physiologic and Operative Severity Score for the enUmeration of Mortality and morbidity, Portsmouth–Physiologic and Operative Severity Score for the enUmeration of Mortality and morbidity, and the Surgical Risk Scale at the extreme of age and for patients with severe peritoneal contamination. Colorectal–Physiologic and Operative Severity Score for the enUmeration of Mortality and morbidity was found to accurately evaluate mortality arising from complicated diverticular disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
WD Wong SD Wexner A Lowry et al. (2000) ArticleTitlePractice parameters for the treatment of sigmoid diverticulitis–supporting documentation. The Standards Task Force. The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons Dis Colon Rectum 43 290–297 Occurrence Handle10733108 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c7psFantA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02258291
P Ryan (1991) ArticleTitleTwo kinds of diverticular disease Ann R Coll Surg Engl 73 73–79 Occurrence Handle1741807 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6B3cnos1c%3D
M Bezzi R Lorusso A Forte et al. (2002) ArticleTitleEmergency surgical treatment of complicated acute diverticulitis [in Italian] Chir Ital 54 203–208 Occurrence Handle12038111
GP Copeland D Jones M Walters (1991) ArticleTitlePOSSUM: a scoring system for surgical audit Br J Surg 78 355–360 Occurrence Handle2021856 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6B3MrksV0%3D
DR Prytherch MS Whiteley B Higgins et al. (1998) ArticleTitlePOSSUM and Portsmouth POSSUM for predicting mortality. Physiological and operative severity score for the enUmeration of mortality and morbidity Br J Surg 85 1217–1220 Occurrence Handle9752863 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1cvitlOrtw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2168.1998.00840.x
PP Tekkis DR Prytherch HM Kocher et al. (2004) ArticleTitleDevelopment of a dedicated risk-adjustment scoring system for colorectal surgery (colorectal POSSUM) Br J Surg 91 1174–1182 Occurrence Handle15449270 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD2cvnvFSltQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1002/bjs.4430
P Sagar M Hartley B Mancey-Jones et al. (1994) ArticleTitleCompararative audit of colorectal resection with the POSSUM scoring system Br J Surg 81 1492–1494 Occurrence Handle7820482 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqC38%2FjvFM%3D
PM Sagar MN Hartley J MacFie et al. (1996) ArticleTitleComparison of individual surgeon's performance. Risk-adjusted analysis with POSSUM scoring system Dis Colon Rectum 39 654–658 Occurrence Handle8646952 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BymB2cbgslw%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02056945
PP Tekkis HM Kocher AJ Bentley et al. (2000) ArticleTitleOperative mortality rates among surgeons: comparison of POSSUM and P-POSSUM scoring systems in gastrointestinal surgery Dis Colon Rectum 43 1528–1532 Occurrence Handle11089587 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2Fkt1Gjuw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02236732
MJ Midwinter M Tytherleigh S Ashley (1999) ArticleTitleEstimation of mortality and morbidity risk in vascular surgery using POSSUM and the Portsmouth predictor equation Br J Surg 86 471–474 Occurrence Handle10215816 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3jtlOlsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2168.1999.01112.x
PP Tekkis N Kessaris HM Kocher et al. (2003) ArticleTitleEvaluation of POSSUM and P-POSSUM scoring systems in patients undergoing colorectal surgery Br J Surg 90 340–345 Occurrence Handle12594670 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3s%2Fot1Oitw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1002/bjs.4037
R Sutton S Bann M Brooks S Sarin (2002) ArticleTitleThe Surgical RiskScale as an improved tool for risk-adjusted analysis incomparative surgical audit Br J Surg 89 763–768 Occurrence Handle12027988 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD383ovVWjsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2168.2002.02080.x
MJ Brooks R Sutton S Sarin (2005) ArticleTitleComparison of Surgical Risk Score, POSSUM and P-POSSUM in higher-risk surgical patients Br J Surg 92 1288–1292 Occurrence Handle15981213 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD2MrhsFeltw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1002/bjs.5058
EJ Hinchey PG Schaal GK Richards (1978) ArticleTitleTreatment of perforated diverticular disease of the colon Adv Surg 12 85–109 Occurrence Handle735943 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSaC3c%2FotlE%3D
A Gray (2000) ArticleTitleUnited Kingdom national confidential enquiry into perioperative deaths Minerva Anestesiol 66 288–292 Occurrence Handle10965704 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3cvmtVWjsg%3D%3D
AJ Senagore AJ Warmuth CP Delaney et al. (2004) ArticleTitlePOSSUM, P-POSSUM, and CR-POSSUM: implementation issues in a United States health care system for prediction of outcome for colon cancer resection Dis Colon Rectum 47 1435–1441 Occurrence Handle15486738 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10350-004-0694-9
G Gmel (2001) ArticleTitleImputation of missing values in the case of a multiple item instrument measuring alcohol consumption Stat Med 20 2369–2381 Occurrence Handle11468769 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MvitVKrsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1002/sim.837
LD Wijesinghe T Mahmood DJ Scott et al. (1998) ArticleTitleComparison of POSSUM and the Portsmouth predictor equation for predicting death following vascular surgery Br J Surg 85 209–212 Occurrence Handle9501818 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7mt1Cguw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2168.1998.00709.x
JA Hanley BJ McNeil (1983) ArticleTitleA method of comparing the areas under receiver operating characteristic curves derived from the same cases Radiology 148 839–843 Occurrence Handle6878708 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiyB2svmtlA%3D
S Lemeshow DW Hosmer SuffixJr (1982) ArticleTitleA review of goodness of fit statistics for use in the development of logistic regression models Am J Epidemiol 115 92–106 Occurrence Handle7055134 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi2C3M%2FovFI%3D
DM Nagorney MA Adson JH Pemberton (1985) ArticleTitleSigmoid diverticulitis with perforation and generalized peritonitis Dis Colon Rectum 28 71–75 Occurrence Handle3971809 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiqC38njt1I%3D
L Auguste E Borrero L Wise (1985) ArticleTitleSurgical management of perforated colonic diverticulitis Arch Surg 120 450–452 Occurrence Handle3985790 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiqC2szotlE%3D
AW Hackford DJ Schoetz SuffixJr JA Coller MC Veidenheimer (1985) ArticleTitleSurgical management of complicated diverticulitis. The Lahey Clinic experience, 1967 to 1982 Dis Colon Rectum 28 317–321 Occurrence Handle3996147 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiqB3czivFQ%3D
ZH Krukowski NA Matheson (1984) ArticleTitleEmergency surgery for diverticular disease complicated by generalized and faecal peritonitis: a review Br J Surg 71 921–927 Occurrence Handle6388723 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiqD2cjotlc%3D
J Vinas-Salas J Villalba-Acosta M Scaramucci et al. (2001) ArticleTitleComplications of colonic diverticular disease. Comparative study of two series Rev Esp Enferm Dig 93 649–658 Occurrence Handle11767489 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38%2FjvVGjuw%3D%3D
PB Boulos (2002) ArticleTitleComplicated diverticulosis Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 16 649–662 Occurrence Handle12406457 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD38nks12jsQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1053/bega.2002.0305
SM Kirson (1988) ArticleTitleDiverticulitis: management patterns in a community hospital South Med J 81 972–977 Occurrence Handle3261454 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BieA3crks1Y%3D
GW Chodak DM Rangel E Passaro SuffixJr (1981) ArticleTitleColonic diverticulitis in patients under age 40: need for earlier diagnosis Am J Surg 141 699–702 Occurrence Handle7246860 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:Bi6B3s%2FgtFY%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0002-9610(81)90081-7
EB Eusebio MM Eisenberg (1973) ArticleTitleNatural history of diverticular disease of the colon in young patients Am J Surg 125 308–311 Occurrence Handle4690116 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSyC3szgs1Q%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/0002-9610(73)90047-0
WH Aldoori EL Giovannucci EB Rimm et al. (1994) ArticleTitleA prospective study of diet and the risk of symptomatic diverticular disease in men Am J Clin Nutr 60 757–764 Occurrence Handle7942584 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqD38bgvVU%3D
WH Aldoori EL Giovannucci EB Rimm et al. (1995) ArticleTitleProspective study of physical activity and the risk of symptomatic diverticular disease in men Gut 36 276–282 Occurrence Handle7883230 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqC1cbhsVw%3D
WH Aldoori EL Giovannucci EB Rimm et al. (1995) ArticleTitleA prospective study of alcohol, smoking, caffeine, and the risk of symptomatic diverticular disease in men Ann Epidemiol 5 221–228 Occurrence Handle7606311 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqA3s%2FhtlM%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/1047-2797(94)00109-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
On behalf of the Association of Coloproctology of Great Britain and Ireland (ACPGBI)., Constantinides, V.A., Tekkis, P.P. et al. Comparison of POSSUM Scoring Systems and the Surgical Risk Scale in Patients Undergoing Surgery for Complicated Diverticular Disease. Dis Colon Rectum 49, 1322–1331 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-006-0522-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10350-006-0522-5