Abstract
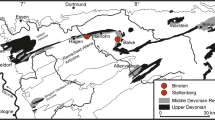
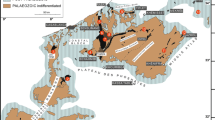
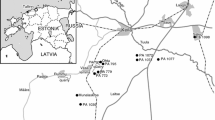
The Brilon-reef complex is one of the biggest Devonian carbonate buildups (~80 km2) of the Rheinisches Schiefergebirge. The Burgberg section is located in the southeastern fore-reef area of the Brilon Reef Complex and exposes a succession of strata (117 m thick), which extends from the Middle Givetian (middle varcus conodont Zone) to the Viséan (bilineatus conodont Zone). Field and microfacies observations led to the definition of nine microfacies that are integrated into a sedimentary model divided into off-reef, intermediate fore-reef, and proximal fore-reef sedimentary domains (SD). The off-reef domain (SD1) is the most distal setting observed and is characterized by fine-grained sediments, dominated by pelagic biota and the local occurrence of gravity-flow deposits. The intermediate fore-reef (SD2) is characterized by a mixture of biota and sediments coming from both deeper-water and shallow-water sources and is influenced by storm and gravity-flow currents. In this domain, Renalcis mound-like structures developed locally. Finally, the proximal fore-reef (SD3) corresponds to the most proximal setting that is strongly influenced by gravity-flow currents derived from the Brilon Reef Complex. The temporal evolution of microfacies in the fore-reef setting of the Burgberg section show five main paleoenvironmental trends influenced by the onset, general development, and demise/drowning of the Brilon Reef Complex. Fore-reef to off-reef lithologies and their temporal changes are from the base to the top of the section: (U1)—fine-grained sediments with large reef debris, corresponding to the initial development of the reef building upon submarine volcaniclastic deposits during the Middle Givetian (middle varcus Zone) and first export of reef debris in the fore-reef setting; (U2)—high increase of reef-derived material in the fore-reef area, corresponding to a significant progradation of the reef from the Middle Givetian to the Early Frasnian (maximum extension of the Brilon Reef Complex to the south, disparilis to the falsiovalis conodont biozones); (U3)—progressive decrease of shallow-water derived material and increase of fine-grained sediments and deep-water biota into the fore-reef setting, corresponding to the stepwise withdrawal of the reef influence; from the Middle to the Late Frasnian (jamieae conodont Zone); (U4)—development of a submarine rise characterized by nodular and cephalopod-bearing limestones extending from the Late Frasnian to the Late Famennian corresponding to the demise and drowning of the Brilon Reef Complex as a result of the Late Frasnian Kellwasser events (upper rhenana and triangularis conodont biozones); (U5)—significant deepening of the Burgberg area starting in the Late Famennian, directly followed by an aggrading trend marked by pelagic shales overlying the nodular limestone deposits.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboussalam ZS (2003) Das” Taghanic-Event” im höheren Mitteldevon von West-Europa und Marokko. Münstersche Forsch Geol Paläont 97:1–332
Aboussalam ZS, Becker RT (2011) The global Taghanic biocrisis (Givetian) in the eastern Anti-Atlas, Morocco. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 304:136–164
Alekseev AS, Kononova LI, Nikishin AM (1996) The Devonian and Carboniferous of the Moscow Syneclise (Russian Platform): stratigraphy and sea level changes. Tectonophysics 268:149–168
Antoshkina AI (2006) Palaeoenvironmental implications of Palaeomicrocodium in Upper Devonian microbial mounds of the Chernyshev Swell, Timan-northern Ural region. Facies 52:611–625
Bacelle L, Bosellini A (1965) Diagrammi per la stima visiva della composizione percentuale nelle rocce sedimentarie. Ann Univ Ferrara Sez 9 Sci Geol Paleont 1:59–62
Bandel K (1974) Deep-water limestones from the Devonian-Carboniferous of the Carnic Alps, Austria. Spec Publ Int Assoc Sediment 1:93–115
Bär P (1968) Die ober-devonisch/unter-karbonische Schichtlücke über dem Massenkalk des Briloner und Messinghäuser Sattels (Ost-Sauerland). N Jb Geol Paläont Abh 131:263–288
Bathurst RGC (1987) Diagenetically enhanced bedding in argillaceous platform limestones: stratified cementation and selective compaction. Sedimentology 34:749–778
Bond DPG, Wignall PB (2008) The role of sea-level change and marine anoxia in the Frasnian–Famennian (Late Devonian) mass extinction. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 263:107–118
Bond DPG, Wignall PB, Racki G (2004) Extent and duration of marine anoxia during the Frasnian-Famennian (Late Devonian) mass extinction in Poland, Germany, Austria and France. Geol Mag 141:173–193
Boulvain F, Cornet P, da Silva AC, Delaite G, Demany B, Humblet M, Renard M, Coen-Aubert M (2004) Reconstructing atoll-like mounds from the Frasnian of Belgium. Facies 50:313–326
Braun R, Oetken S, Königshof P, Kornder L, Wehrmann A (1994) Development and biofacies of reef-influenced carbonates (Lahn-syncline, Rheinisches Schiefergebirge). Cour Forschungsinst. Senckenberg 169:351–386
Brinckmann J (1981) Projekt Rhenoherzynikum: Untersuchung der Metallverteilung in geosynklinalen Sedimenten des Rhenoherzynikums in stratiformen Konzentrationen; Bericht über das Kernbohrprogramm im Briloner Riffkalk-Komplex. Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe
Buggisch W, Flügel E (1992) Mittel- bis oberdevonische Karbonate auf Blatt Weilburg (Rheinisches Schiefergebirge) und in Randgebieten: Initialstadien der Riffentwick-lung auf Vulkanschwellen. Geol Jb Hessen 120:77–97
Buggisch W, Joachimski MM (2006) Carbon isotope stratigraphy of the Devonian of central and southern Europe. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 240:68–88
Casier J, Preat A (2007) Ostracodes et lithofacies du stratotype de la limite Devonien moyen/Devonien superieur (Puech de la Suque, Montagne Noire, France). Bull Soc Geol France 178:293–304
Chen D, Tucker M (2004) Palaeokarst and its implication for the extinction event at the Frasnian–Famennian boundary (Guilin, South China). J Geol Soc Lond 161:895–898
Chen D, Tuker M, Shen Y, Yans J, Preat A (2002) Carbon isotope excursions and sea-level change: implications for the Frasnian–Famennian biotic crisis. J Geol Soc Lond 159:623–626
Clari P, Martire L (1996) Interplay of cementation, mechanical compaction, and chemical compaction in nodular limestones of the Rosso Ammonitico Veronese (Middle-Upper Jurassic, northeastern Italy). J Sediment Res 66:447–458
Clausen CD, Korn D (2008) Höheres Mitteldevon und Oberdevon des nördlichen Rheinischen Schiefergebirges (mit Velberter Sattel und Kellerwald). In: Deutsche Stratigraphische Kommission (eds) Stratigraphie von Deutschland VIII. Devon. Schriftenreihe dtsch Ges Geowiss Heft 52:439–481
Copper P (2002) Silurian and Devonian reefs: 800 million years of global greenhouse between two ice ages. In: Kiessling W, Flügel E, Golonka J (eds) Phanerozoic reef patterns. SEPM Spec Publ, vol 72, pp 181–238
Dickson J (1965) A modified staining technique for carbonates in thin section. Nature 205:587
Dunham RJ (1962) Classification of carbonate rocks according to depositional texture. Mem Am Assoc Petrol Geol 1:108–121
Eder W, Franke W (1982) Death of Devonian reefs. N Jb Geol Paläont Abh 163:241–243
Embry AF, Klovan JE (1972) Absolute water depth limits of Late Devonian paleoecological zones. Geol Rundsch 61:672–686
Erben HK (1962) Zur Analyse und Interpretation der rheinischen und hercynischen Magnafazies im Devon. In: Erben HK (ed) International Arbeitstagung über die Silur/Devon Grenze und die Stratigraphie von Silur und Devon. Symposium Band, Schweizerbart, Stuttgart, pp 42–61
Flügel E (2004) Microfacies analysis of carbonate rocks. Analysis, interpretation and application. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Franke W (1973) Fazies, Bau und Entwicklungsgeschichte des Iberger Riffes (Mitteldevon bis Unterkarbon III NW-Harz, W-Deutschland). Geol Jb A 11:27–31
Geldsetzer HHJ, Goodfellow WD, McLaren DJ (1993) The Frasnian-Famennian extinction event in a stable cratonic shelf setting: Trout River, Northwest Territories, Canada. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 104:81–89
George AD, Powell CMA (1997) Paleokarst in an Upper Devonian reef complex of the Canning basin, western Australia. J Sediment Res 67:935–944
Gingras MK, Pemberton SG, Muelenbachs K, Machel H (2004) Conceptual models for burrow-related, selective dolomitization with textural and isotopic evidence from the Tyndall Stone, Canada. Geobiology 2:21–30
Gischler E (1995) Current and wind induced facies patterns in a Devonian atoll: Iberg Reef, Harz Mts. Germany. Palaios 10:180–189
Gischler E (1996) Late Devonian-early Carboniferous deep-water coral assemblages and sedimentation on a Devonian seamount: Iberg Reef, Harz Mts. Germany. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 123:297–322
Haq BU, Schutter SR (2008) A chronology of Paleozoic sea-level changes. Science 322:64–68
House MR (1985) Correlation of Mid-Palaeozoic ammonoid evolutionary events with global sedimentary perturbations. Nature 313:17–22
Johnson JG (1970) Taghanic onlap and the end of North American Provinciality. Geol Soc Am Bull 81:2077–2106
Johnson JG, Klapper G, Sandberg CA (1985) Devonian eustatic fluctuations in Euramerica. Geol Soc Am Bull 96:567–587
Jux U (1960) Die devonischen Riffe im Rheinischen Schiefergebirge. N Jb Geol Paläont Abh 110:186–258
Königshof P, Gewehr B, Kornder L, Wehrmann A, Braun R, Zankl H (1991) Stromatoporen-Morphotypen aus einem zentralen Riffbereich (Mitteldevon) in der südwestlichen Lahnmulde. Geol Palaeont 25:19–35
Königshof P, Nesbor HD, Flick H (2010) Volcanism and reef development in the Devonian: a case study from the Lahn syncline, Rheinisches Schiefergebirge (Germany). Gondwana Res 17:264–280
Königshof P, Savage N, Lutat P, Sardsu A, Dopieralska J, Belka Z, Racki G (2012) Late Devonian sedimentary record of the Palaeotethys Ocean—the Mae Sariang succession, northwestern Thailand. J Asian Earth Sci 52:146–157. doi:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.03.006
Korn D (1996) Revision of the Late Visean goniatite stratigraphy. Ann Soc Geol Belg 117:205–212
Korn D, Horn K (1997) The Late Visean (early Carboniferous) goniatite stratigraphy in the South Portuguese Zone, a comparison with the Rhenish Massif. Newsl Stratigr 35:97–113
Korn D, Kaufmann B (2009) A high-resolution relative time scale for the Viséan Stage (Carboniferous) of the Kulm Basin (Rhenish Mountains, Germany). Geoll J 44:306–321
Krebs W (1967) Reef development in the Devonian of the eastern Rhenish Slate Mountains, Germany. In: Oswald DH (ed) International symposium on the Devonian system, vol 1. Alberta Society of Petroleum Geologists, Calgary, pp 295–306
Krebs W (1971) Devonian reef limestones in the eastern Rhenish Schiefergebirge. Sedimentology of parts of Central Europe guidebook, 8th international sedimentology congress, Heidelberg, pp 45–81
Krebs W (1974) Devonian carbonate complexes of central Europe. In: Laporte LF (ed) Reefs in time and space. SEPM Spec Publ, vol 18, pp 155–208
Kroner U, Hahn T, Romer RL, Linnemann U (2007) The Variscan orogeny in the Saxo-Thuringian zone—heterogenous overprint of Cadomian/Palaeozoic peri-Gondwana crust. In: Linnemann U, Nance RD, Kraft P, Zulauf G (eds) The evolution of the Rheic Ocean: From Avalonian-Cadomian active margin to Alleghenian-Variscan collision. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap 423:153–172
Logan BV, Semenuik V (1976) Dynamic metamorphism: processes and products in Devonian carbonate rocks, Canning Basin, Western Australia. Geol Soc Australia Spec Publ 138
Machel H-G (1990) Faziesinterpretation des Briloner Riffs mit Hilfe eines Faziesmodells für devonische Riffkarbonate. Geol Jb D 95:43–83
Maletz J (2006) Middle Devonian dendroid graptolites from the Brilon Reef area (Rheinisches Schiefergebirge, Germany). Paläont Z 80:221–229
Malmsheimer KW, Mensink H, Stritzke R (1990) Beginn der Riffschutt-Produktion und Knollenkalk-Sedimentation in Südosten des Briloner Riffes/Ostsauerland. Geol Jb D 95:177–182
Mamet B, Préat A (1985) Sur la présence de Palaeomicrocodium (Algue?, Incertae sedis?) dans le Givétien inférieur de Belgique. Geobios 18:389–395
May A (1993) Stratigraphie, Stromatoporen-Fauna und Palökologie von Korallenkalken aus dem Ober-Eifelium und Unter-Givetium (Devon) des nordwestlichen Sauerlandes (Rheinisches Schiefergebirge). Geol Paläont Westfalen 24:1–93
May A (1994) Microfacies controls on weathering of carbonate building stones: Devonian (northern Sauerland, Germany). Facies 30:193–208
McKerrow WS, Scotese CR (1990) Palaeozoic palaeogeography and biogeography. Geol Soc Lond Mem 12:1–433
Meischner KD (1964) Allodapische Kalke. Turbidite in riff-nahen Sedimentations-Becken. Developm Sediment 3:156–191
Möller NK, Kvingan K (1988) The genesis of nodular limestones in the Ordovician and Silurian of the Oslo Region (Norway). Sedimentology 35:405–420
Nesbor HD (2004) Paläozoischer Intraplattenvulkanismus im östlichen Rheinischen Schiefergebirge—Magmenentwicklung und zeitlicher Ablauf. Geol Jb Hessen 131:145–182
Nicolaus HJ (1963) Zur Stratigraphie und Fauna der crenistria-Zone im Kulm des Rheinischen Schiefergebirges. Beih Geol Jahrb 53:1–246
Paeckelmann W (1922) Der mitteldevonische Massenkalk des Bergischen Landes. Preuss Geol Landesanst Abh 91:1–112
Paeckelmann W (1936) Geologische Karte von Preussen 1: 25000. Blatt Brilon (2659)
Pettijohn FJ, Potter PE, Siever R (1972) Sand and sandstone. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Piecha M (1993) Stratigraphie, Fazies und Sedimentpetrographie der rhythmisch und zyklisch abgelagerten, tiefoberdevonischen Beckensedimente im Rechtsrheinischen Schiefergebirge (Adorf Bänderschiefer). Cour Forsch Inst Senckenberg 163:1–153
Playford PE (1980) Devonian “Great Barrier Reef” of Canning Basin, Western Australia. Am Assoc Petrol Geol Bull 64:814–840
Rabien A (1956) Zur Stratigraphie und Fazies des Ober-Devons in der Waldecker Hauptmulde. Abh Hess LA Bodenforsch 16:1–83
Ribbert K-H, Skupin K, Oesterreich B (2006) Geologische Karte von Preussen und benachbarten Gebieten, von Nordrhein-Westfalen, 1:25000. Blatt Madfeld (4518)
Riding R (1991) Calcareous algae and stromatolites. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Salamon M, Königshof P (2010) Middle Devonian olistostromes in the Rheno-Hercynian (Rheinisches Schiefergebirge)—an indication of back arc rifting on the passive margin of Laurussia? Gondwana Res 17:281–291. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2009.10.004
Sepkoski JJ Jr (1995) Patterns of Phanerozoic extinctions: a perspective from global data bases. In: Walliser OH (ed) Global events and event stratigraphy. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 35–51
Städter T, Koch R (1987) Mikrofazielle und diagenetische Entwicklung einer devonischen Karbonatfolge (Givet) am SW-Rand des Briloner Sattels. Facies 17:215–229
Stow DAV, Piper DJW (1984) Fine-grained sediments: deep water processes and facies. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 15:1–659
Stritzke R (1990) Die Karbonatsedimentation im Briloner Vorriffbereich. Geol Jb D 95:253–315
Sunkel G (1990) Devonischer submariner Vulkanismus im Ostsauerland (Rheinisches Schiefergebirge): Vulkanaufbau, Magmenzusammensetzung und Alteration. Bochumer geol geotechn Arb 34:1–250
Tucker ME (1973) Sedimentology and diagenesis of Devonian pelagic limestones (Cephalopodenkalk) and associated sediments of the Rhenohercynian Geosyncline, West Germany. N Jb Geol Paläont Abh 142:320–350
Tucker ME (1974) Sedimentology of Palaeozoic pelagic limestones: the Devonian Griotte (Southern France) and Cephalopodenkalk (Germany). Spec Publ Int Assoc Sediment 1:71–92
Tucker ME, Wright VP (1990) Carbonate sedimentology. Blackwell, London
von Dechen H (1858) Geologische Karte der Rheinprovinz und der Provinz Westfalen 1: 80.000. (Hrsg.) Kgl Minist Handel Gewerbe öff Arbeit, Sect 18, Berleburg, Berlin
Warnke K (1997) Microbial carbonate production in a starved basin: the crenistria Limestone of the upper Viséan German Kulm facies. Palaeogeogr Palaeoclimatol Palaeoecol 130:209–225
Wehrmann A, Blieck A, Brocke R, Hertweck G, Jansen U, Königshof P, Plodowski G, Schindler E, Schultka S, Wilde V (2005) Palaeoenvironment and palaeoecology of intertidal deposits in a Lower Devonian siliciclastic sequence of the Mosel Region, Germany. Palaios 20:101–120
Wendt J, Aigner T (1985) Facies patterns and depositional environments of Palaeozoic cephalopod limestones. Sediment Geol 44:263–300
Wendt J, Belka Z (1991) Age and depositional environment of Upper Devonian (early Frasnian to early Famennian) black shales and limestones (Kellwasser facies) in the eastern Anti-Atlas, Morocco. Facies 25:51–89
Ziegler AP (1982) Geological atlas of western and central Europe. Shell, Den Haag
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this project from the sedimentary laboratory of the University of Liège is gratefully acknowledged. The authors would like to thank Philippe Claeys and David De Vleeschouwer (Earth System Sciences, Vrije Universiteit Brussel) for the instrumental help provided for the stable isotope measurements. Many thanks to Rüdiger Stritzke for all the information and comments provided for conodont investigation. This paper is a contribution to IGCP 580 “Application of magnetic susceptibility in paleoenvironmental reconstruction” and to IGCP 596 “Climate change and biodiversity patterns in the Mid-Palaeozoic”. Helpful comments from Dr. Thomas Suttner (Karl-Franzens University of Graz, Austria) and an anonymous journal reviewer are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pas, D., Da Silva, AC., Cornet, P. et al. Sedimentary development of a continuous Middle Devonian to Mississippian section from the fore-reef fringe of the Brilon Reef Complex (Rheinisches Schiefergebirge, Germany). Facies 59, 969–990 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10347-012-0351-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10347-012-0351-z