Abstract
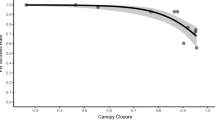
We have assessed behavioural and environmental factors influencing the success of global positioning system (GPS) fixes recorded from 15 collared free-ranging female Mediterranean mouflon (Ovis gmelini musimon x Ovis sp.). We have demonstrated that fix success was 8% lower in resting animals (0.81, 95% CI = 0.79–0.84) than in active animals (0.89, 95% CI = 0.86–0.91) at an average temperature (13.8°C), but was similar and relatively constant at lower temperatures. When temperatures increased above the average temperature, fix success strongly decreased in resting animals (0.44, 95% CI = 0.36–0.52 at 30°C) as compared to active animals (0.76, 95% CI = 0.65–0.85). These results probably involved behavioural changes in habitat use of mouflon, as temperature and activity strongly influence the use of cover in ungulates. We also found that the success of GPS fixes was influenced by habitat types, increasing from 0.76 to 0.93 (under average sky openness of 33%) along a continuum going from forested to open areas. After controlling for differences in vegetation, sky openness had a positive effect on fix success (from 0.76 to 0.97 in evergreen oak forest). Our approach based on free-ranging animals and using a robust interpolation procedure should provide biologists with a more reliable method to account for bias in GPS studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrados C, Girard I, Gendner J-P, Janeau G (2002) GPS location accuracy improvement due to selective availability removal. C R Biol 325:1–6. doi:10.1016/S1631-0691(02)01414-2
Agresti A (2002) Categorical data analysis, 3rd edn. Wiley, Hoboken, New Jersey
Auvray F (1983) Recherches sur l'éco-éthologie du Mouflon (Ovis ammon musimon, Schreber, 1782) dans le massif du Caroux-Espinouse (Hérault) en vue de définir de nouveaux sites d'accueil. Dissertation, Univ Sciences et Techniques du Languedoc, Montpellier, France
Bates D, Sarkar D (2007) lme4: linear mixed-effects models using S4 classes. R package version 0.99875-0
Bon R, Cugnasse J-M, Dubray D, Gibert P, Houard T, Rigaud P (1991) Le mouflon de Corse. Rev Ecol (Terre Vie) 6(Suppl):67–110
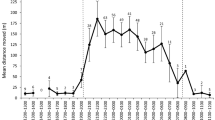
Bourgoin G, Garel M, Van Moorter B, Dubray D, Maillard D, Marty E, Gaillard J-M (2008) Determinants of seasonal variation in activity patterns of mouflon. Can J Zool 86:1410–1418. doi:10.1139/Z08-128
Bowman JL, Kochanny CO, Demarais S, Leopold BD (2000) Evaluation of a GPS collar for white-tailed deer. Wildl Soc Bull 28:141–145
Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2001) Kullback–Leibler information as a basis for strong inference in ecological studies. Wildl Res 28:111–119. doi:10.1071/WR99107
Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2002) Model selection and multimodel inference: a practical information-theoretic approach, 3rd edn. Springer, New York
Cain JW, Krausman PR, Jansen BD, Morgart JR (2005) Influence of topography and GPS fix interval on GPS collar performance. Wildl Soc Bull 33:926–934. doi:10.2193/0091-7648(2005)33[926:IOTAGF]2.0.CO;2
Calenge C (2006) The package adehabitat for the R software: a tool for the analysis of space and habitat use by animals. Ecol Modell 197:516–519. doi:10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2006.03.017
Cargnelutti B, Coulon A, Hewison AJM, Goulard M, Angibault J-M, Morellet N (2007) Testing global positioning system performance for wildlife monitoring using mobile collars and known reference points. J Wildl Manage 71:1380–1387. doi:10.2193/2006-257
Chessel D, Dufour A-B, Thioulouse J (2004) The ade4 package—I: one-table methods. R News 4:5–10
Cransac N, Valet G, Cugnasse J-M, Rech J (1997) Seasonal diet of mouflon (Ovis gmelini): comparison of population sub-units and sex-age classes. Rev Ecol (Terre Vie) 52:21–36
D'Eon RG (2003) Effects of a stationary GPS fix-rate bias on habitat-selection analysis. J Wildl Manage 67:858–863. doi:10.2307/3802693
D'Eon RG, Delparte D (2005) Effects of radio-collar position and orientation on GPS radio-collar performance, and the implications of PDOP in data screening. J Appl Ecol 42:383–388. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2005.01010.x
D'Eon RG, Serrouya R, Smith G, Kochanny CO (2002) GPS radiotelemetry error and bias in mountainous terrain. Wildl Soc Bull 30:430–439
DeCesare NJ, Squires JR, Kolbe JA (2005) Effect of forest canopy on GPS-based movement data. Wildl Soc Bull 33:935–941. doi:10.2193/0091-7648(2005)33[935:EOFCOG]2.0.CO;2
Di Orio AP, Callas R, Schaefer RJ (2003) Performance of two GPS telemetry collars under different habitat conditions. Wildl Soc Bull 31:372–379
Dussault C, Courtois R, Ouellet J-P, Huot J (1999) Evaluation of GPS telemetry collar performance for habitat studies in the boreal forest. Wildl Soc Bull 27:965–972
Dussault C, Ouellet J-P, Courtois R, Huot J, Breton L, Jolicoeur H (2005) Linking moose habitat selection to limiting factors. Ecography 28:619–628. doi:10.1111/j.2005.0906-7590.04263.x
Edenius L (1997) Field test of a GPS location system for moose Alces alces under Scandinavian boreal conditions. Wildl Biol 3:39–43
Faliu L, Cugnasse J-M, Auvray F, Orliac D, Rech J (1990) Le régime alimentaire du mouflon de Corse (Ovis ammon musimon) dans le massif du Caroux-Espinouse d'après l'analyse du contenu de 125 panses. Rev Méd Vét 141:545–556
Frair J, Nielsen SE, Merrill EH, Lele SR, Boyce MS, Munro RHM, Stenhouse GB, Beyer HL (2004) Removing GPS collar bias in habitat selection studies. J Appl Ecol 41:201–212. doi:10.1111/j.0021-8901.2004.00902.x
Garel M, Loison A, Gaillard J-M, Cugnasse J-M, Maillard D (2004) The effects of a severe drought on mouflon lamb survival. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 271(Suppl):S471–S473. doi:10.1098/rsbl.2004.0219
Garel M, Cugnasse J-M, Gaillard J-M, Loison A, Gilbert P, Douvre P, Dubray D (2005) Reproductive output of female mouflon (Ovis gmelini musimon x Ovis sp.): a comparative analysis. J Zool (Lond) 266:65–71. doi:10.1017/S0952836905006667
Gelman A, Hill J (2007) Data analysis using regression and multilevel/hierarchical models. Cambridge University Press, UK
Graves TA, Radandt TG (2004) GPS collar fix success in the Purcell Mountains. Appendix 1. In: Kasworm WF, Carriles H, Radandt TG (eds) Cabinet-Yaak grizzly bear recovery area 2003 research and monitoring progress report. US Fish and Wildlife Service, Missoula, Montana, USA
Graves TA, Waller JS (2006) Understanding the causes of missed global positioning system telemetry fixes. J Wildl Manage 70:844–851. doi:10.2193/0022-541X(2006)70[844:UTCOMG]2.0.CO;2
Hansen MC, Riggs RA (2008) Accuracy, precision, and observation rates of global positioning system telemetry collars. J Wildl Manage 72:518–526. doi:10.2193/2006-493
Hebblewhite M, Percy M, Merrill EH (2007) Are all global positioning system collars created equal? Correcting habitat-induced bias using three brands in the central Canadian Rockies. J Wildl Manage 71:2026–2033. doi:10.2193/2006–238
Hofmann RR (1989) Evolutionary steps of ecophysiological adaptation and diversification of ruminants: a comparative view of their digestive system. Oecologia 78:443–457. doi:10.1007/BF00378733
Hulbert IAR, French J (2001) The accuracy of GPS for wildlife telemetry and habitat mapping. J Appl Ecol 38:869–878. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2664.2001.00624.x
Ihaka R, Gentleman R (1996) R: a language for data analysis and graphics. J Comput Graph Stat 5:299–314. doi:10.2307/1390807
Janeau G, Adrados C, Joachim J, Gendner J-P, Pépin D (2004) Performance of differential GPS collars in temperate mountain forest. C R Biol 327:1143–1149. doi:10.1016/j.crvi.2004.07.014
Langbein J, Scheibe KM, Eichhorn K (1997) Seasonal changes in the circadian behaviour patterns in European mouflons (Ovis ammon musimon Pallas, 1811). Z Saugetierkd 62:117–123
Lewis JS, Rachlow JL, Garton EO, Vierling LA (2007) Effects of habitat on GPS collar performance: using data screening to reduce location error. J Appl Ecol 44:663–671. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2007.01286.x
Lotek Engineering Inc (2003) Small and midsize animals—GPS location system—GPS 3300—user's manual. Lotek Engineering, Inc., Newmarket, Ontario, Canada
Mahoney SH, Virgl JA (2003) Habitat selection and demography of a nonmigratory woodland caribou population in Newfoundland. Can J Zool 81:321–334. doi:10.1139/z02-239
Moen R, Pastor J, Cohen Y (2001) Effects of animal activity on GPS telemetry location attempts. Alces 37:207–216
Moen R, Pastor J, Cohen Y (1996a) Interpreting behavior from activity counters in GPS collars on moose. Alces 32:101–108
Moen R, Pastor J, Cohen Y, Schwartz CC (1996b) Effects of moose movement and habitat use on GPS collar performance. J Wildl Manage 60:659–668. doi:10.2307/3802085
Mysterud A, Østbye E (1999) Cover as a habitat element for temperate ungulates: effects on habitat selection and demography. Wildl Soc Bull 27:385–394
Nams VO (1989) Effects of radiotelemetry error on sample size and bias when testing for habitat selection. Can J Zool 67:1631–1636. doi:10.1139/z89-233
Rempel RS, Rodgers AR, Abraham KF (1995) Performance of a GPS animal location under boreal forest canopy. J Wildl Manage 59:543–551. doi:10.2307/3802461
Rumble MA, Lindzey F (1997) Effects of forest vegetation and topography on global positioning system collars for elk. Proceedings of ACSM/ASPRS Annual Convention and Exposition Technical Papers, 4, pp 492–501
Sager-Fradkin KA, Jenkins KJ, Hoffman RA, Happe RA, Beecham JJ, Wright RG (2007) Fix success and accuracy of global positioning system collars in old-growth temperate coniferous forests. J Wildl Manage 71:1298–1308. doi:10.2193/2006-367
Santosa Y (1990) Utilisation de paramètres éco-éthologiques pour la mise au point d'une méthode d'étude quantitative des populations de grands mammifères : exemple du mouflon (Ovis ammon musimon) du Caroux-Espinouse. Dissertation, Univ Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France
Sigrist P, Coppin P, Hermy M (1999) Impact of forest canopy on quality and accuracy of GPS measurements. Int J Remote Sens 20:3595–3610. doi:10.1080/014311699211228
Thiebaut B (1971) La transition climatique dans le massif de l'Agoût. Vie Milieu Ser C-Biologie Terrestre 22:167–206
Venables WN, Ripley BD (2002) Modern applied statistics with S, 4th edn. Springer, New York
Visscher DR (2006) GPS measurement error and resource selection functions in a fragmented landscape. Ecography 29:458–464. doi:10.1111/j.0906-7590.2006.04648.x
White GC, Garrott RA (1986) Effects of biotelemetry triangulation error on detecting habitat selection. J Wildl Manage 50:509–513. doi:10.2307/3801114
Zweifel-Schielly B, Suter W (2007) Performance of GPS telemetry collars for red deer Cervus elaphus in rugged Alpine terrain under controlled and free-living conditions. Wildl Biol 13:299–312. doi:10.2981/0909-6396(2007)13[299:POGTCF]2.0.CO;2
Acknowledgements
All the experiments were performed in agreement with the current French laws on wildlife and animal welfare. We are grateful to the Office National de la Chasse et de la Faune Sauvage (SD 34, BMI LR and DER) for their technical and data support (especially E. Marty for the field management of the study) and Y. Soubeyran for producing our vegetation map. We gratefully acknowledge the Groupement d'Intérêt Environmental et Cynégétique, the Office National des Forêts and the trainees of Fagairolles for collecting data. We would also like to thank J.-P. Gendner (CNRS, Strasbourg, France) and G. Janeau (IRGM-INRA, Toulouse, France) for differentially correcting GPS data and to B. Van Moorter for recording the activity of mouflon. We thank IN2P3 (Villeurbanne, France) for access to computer resources. We also thank O. Bantus and W. Renaud (Lotek Wireless Inc.) for technical support. We are grateful to Chantal Kirouac for the English improvement. G. Bourgoin and M. Garel were financed by the Office National de la Chasse et de la Faune Sauvage and the Fédération Départementale des Chasseurs de l'Hérault.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Kierdorf
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bourgoin, G., Garel, M., Dubray, D. et al. What determines global positioning system fix success when monitoring free-ranging mouflon?. Eur J Wildl Res 55, 603–613 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-009-0284-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-009-0284-1