Abstract
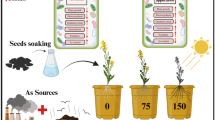
The use of inorganic amendments to immobilize cadmium is an eco-friendly approach. The present study aimed to evaluate sulfur nanoparticles (SNPs) for the mitigation of Cd stress in saffron (Crocus sativus L.). A factorial layout based on a completely randomized design with four replications was conducted in greenhouse conditions. Treatments consisted of Cd concentration (0, 15, 30, and 45 mg kg−1) and sulfur amendments (control, SNPs, and bulk sulfur particles (BSPs) at 100 and 200 mg kg−1). In non-contaminated plants, application of BSPs 200 increased stigma and flower dry weight by 127 and 108%, respectively. At Cd 30 mg kg−1, using BSPs 100 yielded the highest stigma and flower dry weight. More daughter corms were produced by using BSPs 100 in control plants and BSPs 200 or SNPs 100 in 45 mg kg−1 Cd. The highest root dry weight measured in Cd 15 mg kg−1 + SNPs 100 and Cd 45 mg kg−1 + SNPs 200. The fertilization effect of BSPs 200 was reflected in the dry weight of the leaf, daughter corms, root, and daughter corm diameter. Roots accumulated the highest Cd concentration, followed by leaves, corms, and stigma. The bioconcentration factor (BCF) in plant tissues was in descending order (BCFroot > BCFleaves > BCFcorm > BCFstigma). The highest total Cd accumulation was detected in 45 mg kg−1 Cd along with SNPs 200. Overall, saffron seemed to be capable of phytostabilizing in managing Cd toxicity by lowering its translocation to aboveground tissues, especially to the stigma.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhikari S, Ghosh S, Azahar I, Adhikari A, Shaw AK, Konar S, Roy S, Hossain Z (2018) Sulfate improves cadmium tolerance by limiting cadmium accumulation, modulation of sulfur metabolism and antioxidant defense system in maize. Environ Exp Bot 153:143–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.05.008
Ahmad B, Zaid A, Jaleel H, Khan MMA, Ghorbanpour M (2019) Nanotechnology for phytoremediation of heavy metals: Mechanisms of nanomaterial-mediated alleviation of toxic metals. In: Ghorbanpour M, Wani SH (eds) Advances in Phytonanotechnology: from synthesis to application. Academic Press, pp 315–327 https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-815322-2.00014-6
Ahmed T, Noman M, Manzoor N, Shahid M, Abdullah M, Ali L, Wang G, Hashem A, Al-Arjani AF, Alqarawi AA, Abd Allah EF, Li B (2021) Nanoparticle-based amelioration of drought stress and cadmium toxicity in rice via triggering the stress responsive genetic mechanisms and nutrient acquisition. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 209:111829
Alatawi A, Wang X, Maqbool A, Saleem MH, Usman K, Rizwan M, Yasmeen T, Arif MS, Noreen S, Hussain A, Ali S (2022) S‑Fertilizer (Elemental Sulfur) Improves the Phytoextraction of Cadmium through Solanum nigrum L. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(3):1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19031655
An T, Wu Y, Xu B, Zhang S, Deng X, Zhang Y, Deng X, Zhang Y, Siddique KHM, Chen Y (2022) Nitrogen supply improved plant growth and Cd translocation in maize at the silking and physiological maturity under moderate Cd stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 230:113137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113137
Arif MS, Yasmeen T, Abbas Z, Ali S, Rizwan M, Aljarba NH, Alkahtani S, Abdel-Daim MM (2021) Role of exogenous and endogenous hydrogen sulfide (H2S) on functional traits of plants under heavy metal stresses: a recent perspective. Front Plant Sci 11:545453. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.545453
Awasthi G, Nagar V, Mandzhieva S, Minkina T, Sankhla MS, Pandit PP, Aseri V, Awasthi KK, Rajput VD, Bauer T, Srivastava S (2022) Sustainable amelioration of heavy metals in soil ecosystem: existing developments to emerging trends. Minerals 12(1):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12010085
Azizi I, Esmaielpour B, Fatemi H (2020) Effect of foliar application of selenium on morphological and physiological indices of savory (Satureja hortensis) under cadmium stress. Food Sci Nutr 8(12):6539–6549
Bashir H, Ibrahim MM, Bagheri R, Ahmad J, Arif IA, Baig MA, Qureshi MI (2015) Influence of sulfur and cadmium on antioxidants, phytochelatins and growth in Indian mustard. Aob Plants 7:plv1. https://doi.org/10.1093/aobpla/plv001
Cao X, Wang C, Luo X, Yue L, White JC, Elmer W, Dhankher OP, Wang Z, Xing B (2021) Elemental sulfur nanoparticles enhance disease resistance in tomatoes. ACS Nano 15(7):11817–11827. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c02917
Chen L, Hu W, Long C, Wang D (2021) Exogenous plant growth regulator alleviate the adverse effects of U and Cd stress in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) and improve the efficacy of U and Cd remediation. Chemosphere 262:127809
Chen Q, Lu X, Guo X, Pan Y, Yu B, Tang Z, Guo Q (2018) Differential responses to Cd stress induced by exogenous application of Cu, Zn or Ca in the medicinal plant Catharanthus roseus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 157:266–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.03.055
Chen X, Wang J, Shi Y, Zhao MQ, Chi GY (2011) Effects of cadmium on growth and photosynthetic activities in Pakchoi and Mustard. Bot Stud 52:41–46
Cimrin KM, Turan M, Kapur B (2007) Effect of elemental sulfur on heavy metals solubility and remediation by plants in calcareous soils. Fresenius Environ Bull 16(9A):1113–1120
Coakley S, Cahill G, Enright AM, O’Rourke B, Petti C (2019) Cadmium hyperaccumulation and translocation in Impatiens Glandulifera: from foe to Sustainability friend? Sustainability 11(5018):1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11185018
Dhankher OM, Shasti NP, Rosen BP, Fuhrmann M, Meagher RB (2003) Increased cadmium tolerance and accumulation by plants expressing bacterial arsenate reductase. New Phytol 159(2):431–441. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00827.x
Dutta A, Patra A, Jatav HS, Jatav SS, Singh SK, Sathyanarayana E, Verma S, Singh P (2020) Toxicity of cadmium in soil-plant-human continuum and its bioremediation techniques. In: Larramendy ML, Soloneski S (eds) Soil contamination—threats and sustainable solutions. IntechOpen, pp 1–22 https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.94307
El Rasafi T, Oukarroum A, Haddioui A, Song H, Kwon EE, Bolan N, Tack F, Sebastian A, Prasad MNV, Rinklebe J (2022) Cadmium stress in plants: A critical review of the effects, mechanisms, and tolerance strategies. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 52(5):675–726. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1835435
Gajic G, Mitrovic M, Pavlovic P (2020) Feasibility of Festuca rubra L. native grass in phytoremediation. In: Pandey VC, Singh DP (eds) Phytoremediation potential of perennial grasses. Elsevier, pp 115–164 https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-817732-7.00006-7
Ghori NH, Ghori T, Hayat MQ, Imadi SR, Gul A, Altay V, Ozturk M (2019) Heavy metal stress and responses in plants. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16(3):1807–1828. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02215-8
Gong X, Huang D, Liu Y, Zeng G, Wang R, Wan J, Zhang C, Cheng M, Qin X, Xue W (2017) Stabilized nanoscale zerovalent iron mediated cadmium accumulation and oxidative damage of Boehmeria nivea (L.) Gaudich cultivated in cadmium contaminated sediments. Environ Sci Technol 51:11308–11316. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b03164
Grant CA, Buckley WT, Bailey LD, Selles F (1998) Cadmium accumulation in crops. Can J Plant Sci 78:1–17
Gresta F, Lombardo GM, Siracusa L, Ruberto G (2008) Saffron, an alternative crop for sustainable agricultural systems. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 28:95–112
Haider FU, Liqun C, Coulter JA, Cheema SA, Wu J, Zhang R, Wenjun M, Farooq M (2021) Cadmium toxicity in plants: Impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 211:111887. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111887
Huang L, Li W, Tam NFY, Ye Z (2019) Effects of root morphology and anatomy on cadmium uptake and translocation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Environ Sci 75:296–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2018.04.005
Hussain A, Rizwan M, Ali S, Zia ur Rehman MZ, Qayyum MF, Nawaz R, Ahmad A, Asrar M, Ahmad SR, Alsahli AA, Alyemeni MN (2021) Combined use of different nanoparticles effectively decreased cadmium (Cd) concentration in grains of wheat grown in a field contaminated with Cd. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 215:112139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.112139
Ismael MA, Elyamine AM, Moussa MG, Cai M, Zhao X, Hu C (2019) Cadmium in plants: uptake, toxicity, and its interactions with selenium fertilizers. Metallomics 11(2):255–277. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8mt00247a
Javed MT, Saleem MH, Aslam S, Rehman M, Iqbal N, Begum R, Ali S, Alsahli AA, Alyemeni MN, Wijaya L (2020) Elucidating silicon-mediated distinct morpho-physio-biochemical attributes and organic acid exudation patterns of cadmium stressed Ajwain (Trachyspermum ammi L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 157:23–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.10.010
Jia H, Wang X, Shi C, Guo J, Ma P, Ren X, Wei T, Liu H, Li J (2020) Hydrogen sulfide decreases Cd translocation from root to shoot through increasing Cd accumulation in cell wall and decreasing Cd2+ influx in Isatis indigotica. Plant Physiol Biochem 155:605–612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.08.033
Kaya C, Akram NA, Surucu A, Ashraf M (2019) Alleviating effect of nitric oxide on oxidative stress and antioxidant defense system in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants exposed to cadmium and lead toxicity applied separately or in combination. Sci Hortic 255:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2019.05.029
Keyster M, Niekerk L, Basson G, Carelse M, Bakare O, Ludidi N, Klein A, Mekuto L, Gokul A (2020) Decoding heavy metal stress signaling in plants: towards improved food security and safety. Plants 9:1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9121781
Khan MIR, Iqbal N, Masood A, Mobin M, Anjum NA, Khan NA (2015) Modulation and significance of nitrogen and sulfur metabolism in cadmium challenged plants. Plant Growth Regul 78:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-015-0071-9
Koocheki A, Khajeh Hosseini M (2020) Saffron: Science, technology and health. Elsevier, p 580
Kubier A, Wilkin RT, Pichler T (2019) Cadmium in soils and groundwater: A review. Appl Geochem 108:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2019.104388
Li Z, Huang J (2014) Effects of nanoparticle hydroxyapatite on growth and antioxidant system in pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) from cadmium contaminated soil. J Nanomater 470962:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/470962
Li B, Yang L, Wang CQ, Zheng SQ, Xiao R, Guo Y (2019) Effects of organic-inorganic amendments on the cadmium fraction in soil and its accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:13762–13772
Lian J, Zhao L, Wu J, Xiong H, Bao Y, Zeb A, Tang J, Liu W (2020) Foliar spray of TiO2 nanoparticles prevails over root application in reducing Cd accumulation and mitigating Cd-induced phytotoxicity in maize (Zea mays L.). Chemosphere 239:124794
Liang T, Ding H, Wang G, Kang J, Pang H, Lv J (2016) Sulfur decreases cadmium translocation and enhances cadmium tolerance by promoting sulfur assimilation and glutathione metabolism in Brassica chinensis L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 124:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.10.011
Lou L, Kang J, Pang H, Li Q, Du X, Wu W, Chen J, Lv J (2017) Sulfur protects pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) seedlings against cadmium stress by regulating ascorbate-glutathione metabolism. Int J Mol Sci 18:1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081628
Lu Y, Wang QF, Li J, Xiong J, Zhou LN, He SL, Zhang JQ, Chen ZA, He SG, Liu H (2019) Effects of exogenous sulfur on alleviating cadmium stress in tartary buckwheat. Sci Rep 9:7397. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-43901-4
Luo J, Zhang Z (2021) Mechanisms of cadmium phytoremediation and detoxification in plants. Crop J 9(3):521–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2021.02.001
Lwin CS, Seo B, Kim H, Owens G, Kim K (2018) Application of soil amendments to contaminated soils for heavy metal immobilization and improved soil quality—a critical review. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 64(2):156–167. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.2018.1440938
Ma C, Chhikara S, Minocha R, Long S, Musante C, White JC (2015) Reduced silver nanoparticle phytotoxicity in Crambe abyssinica with enhanced glutathione production by overexpressing bacterial gamma-glutamylcysteine synthase. Environ Sci Technol 49:10117–10126
Ma C, Hao Y, Zhao J, Zuverza-Mena N, Meselhy AG, Dhankher OP, Rui Y, White JC, Xing B (2021) Graphitic carbon nitride (C3N4) reduces cadmium and arsenic phytotoxicity and accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Nanomaterials 11(4):839. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11040839
Meselhy MG, Sharma S, Guo Z, Singh G, Yuan H, Tripathi RD, Xing B, Musante C, White JC, Dhankher OP (2021) Nanoscale sulfur improves plant growth and reduces Arsenic toxicity and accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ Sci Technol 55(20):13490–13503. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c05495
Moradi R, Pourghasemian N, Naghizadeh M (2019) Effect of beeswax waste biochar on growth, physiology and cadmium uptake in saffron. J Clean Prod 229:1251–1261
Muradoglu F, Gundogdu M, Ercisli S, Encu T, Balta F, Jaafar H, Zia-Ul-Haq M (2015) Cadmium toxicity affects chlorophyll a and b content, antioxidant enzyme activities and mineral nutrient accumulation in strawberry. Biol Res 48:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40659-015-0001-3
Ng WWC, Wang YC, Ni JJ, Wang ZJ (2021) Quality and yield of Pseudostelaria heterophylla treated with GGBS as pH adjuster against the toxicity of Cd and Cu. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 216:112188
Palansooriya KN, Shaheen SM, Chene SS, Tsange DCW, Hashimotof Y, Houg D, Bolanh NS, Rinklebeb J, Oka YS (2020) Soil amendments for immobilization of potentially toxic elements in contaminated soils: A critical review. Environ Int 134:105046
Paulose B, Chhikara S, Coomey J, Jung H‑I, Vatamaniuk O, Dhankher OP (2013) A γ‑glutamyl cyclotransferase protects Arabidopsis plants from heavy metal toxicity by recycling glutamate to maintain glutathione homeostasis. Plant Cell 25:4580–4595. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.111815
Ragab GA, Saad-Allah KM (2020) Green synthesis of sulfur nanoparticles using Ocimum basilicum leaves and its prospective effect on manganese-stressed Helianthus annuus (L.) seedlings. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 191:110242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110242
Rizwan M, Ali S, Ali B, Adrees M, Arshad M, Hussain A, Zia Ur Rehman M, Waris AA (2019) Zinc and iron oxide nanoparticles improved the plant growth and reduced the oxidative stress and cadmium concentration in wheat. Chemosphere 214:269–277
Saha B, Chowardhara B, Kar S, Devi SS, Awasthi JP, Moulick D, Tanti B, Panda SK (2019) Advances in heavy metal-induced stress alleviation with respect to exogenous amendments in crop plants. In: Hasanuzzaman M, Fotopoulos V (eds) Priming and pretreatment of seeds and seedlings: implication in plant stress tolerance and enhancing productivity in crop plants. Springer, Singapore, pp 313–332
Sebastian A, Nangia A, Prasad M (2018) A green synthetic route to phenolics fabricated magnetite nanoparticles from coconut husk extract: Implications to treat metal contaminated water and heavy metal stress in Oryza sativa L. J Clean Prod 174:355–366
Shanmugaraj BM, Malla A, Ramalingam S (2019) Cadmium stress and toxicity in plants: An overview. In: Hasanuzzaman M, Vara Prasad NM, Fujita M (eds) Cadmium toxicity and tolerance in plants: from physiology to remediation. Academic Press, pp 1–17 https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-814864-8.00001-2
Shehata SM, Badawy RK, Aboulsoud YIE (2019) Phytoremediation of some heavy metals in contaminated soil. Bull Nat Res Cent 43:189. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0214-7
Siddiqui MH, Al-Whaibi MH, Mohammad F, Al-Khaishany MY (2015) Role of Nanoparticles in plants. In: Siddiqui MH, Al-Whaibi MH, Mohammad F (eds) Nanotechnology and plant sciences. Springer, pp 19–35 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14502-0_2
Sirova K, Vaculik M (2022) Toxic effects of cadmium on growth of Aloe ferox Mill. S Afr J Bot 147:1181–1187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2020.12.026
Sterckeman T, Thomine S (2020) Mechanisms of cadmium accumulation in plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 39(4):322–359. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352689.2020.1792179
Subramaniam MN, Goh PS, Lau WJ, Ismail AF (2019) The roles of nanomaterials in conventional and emerging technologies for heavy metal removal: a state of the art review. Nanomaterials 9(4):625. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9040625
Suleiman M, Al Ali A, Hussein A, Hammouti B, Hadda TB, Warad I (2013) Sulfur nanoparticles: synthesis, characterizations and their applications. J Mater Environ Sci 5(6):1029–1033
Sun L, Song K, Shi L, Duan D, Zhang H, Sun Y, Qin Q, Xue Y (2021) Influence of elemental sulfur on cadmium bioavailability, microbial community in paddy soil and Cd accumulation in rice plants. Sci Rep 11(1):11468. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-91003-x
Tabrizi L, Lakzaei M, Motesharezadeh B (2021) The yield potential and growth responses of licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra L.) to mycorrhization under Pb and Cd stress. Int J Phytoremediation 23(3):316–327. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2020.1813076
Turganbay S, Aidarova SB, Turganbay G, Tileuberdi Y, Chen SL (2019) Synthesis and characterization of sulfur nanoparticles with WSP/surfactants mixtures. Int J Biol Chem 12:146–152. https://doi.org/10.26577/ijbch-2019-1-i19
Wang F, Wang L, Wang X, Shi Z (2014) Role of immobilization amendments in phytoremediation of Pb-Cd-contaminated soil using tobacco plants. Chin J Environ Eng 8(2):789–794
Wei X, Cao P, Wang G, Han J (2020) Microbial inoculant and garbage enzyme reduced cadmium (Cd) uptake in Salvia miltiorrhiza (Bge.) under Cd stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 192:110311
Wu Z, Liu S, Zhao J, Wang F, Du Y, Zou SM, Li HM, Wen D, Huang YD (2017) Comparative responses to silicon and selenium in relation to antioxidant enzyme system and the glutathione-ascorbate cycle in flowering Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis var. utilis) under cadmium stress. Environ Exp Bot 133:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.09.005
Wu Z, Naveed S, Zhang C, Ge Y (2020) Adequate supply of sulfur simultaneously enhances iron uptake and reduces cadmium accumulation in rice grown in hydroponic culture. Environ Pollut 262:114327
Xie XY, Li LY, Zheng PS, Zheng WJ, Bai Y, Cheng TF, Liu J (2012) Facile synthesis, spectral properties and formation mechanism of sulfur nanorods in PEG-200. Mater Res Bull 47(11):3665–3669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2012.06.043
Yao A, Liu Y, Luo X, Tang Y, Wang S, Huang X, Qiu R (2021) Mediation effects of different sulfur forms on solubility, uptake and accumulation of Cd in soil-paddy rice system induced by organic carbon and liming. Environ Pollut 279:116862
Yuan H, Liu Q, Zhang Y, Fu J, Wang Y, Sun Y, Tong H (2021a) Effects of sulfur nanoparticles on growth and Pb accumulation in Brassica napus L. seedlings under Pb stress. J Agro Environ Sci 40(3):517–524
Yuan H, Liu Q, Guo Z, Fu J, Sun Y, Gu C, Xing B, Dhankher OP (2021b) Sulfur nanoparticles improved plant growth and reduced mercury toxicity via mitigating the oxidative stress in Brassica napus L. J Clean Prod 318:128589
Yuan H, Liu Q, Fu J, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Sun Y, Tong H, Dhankher OP (2023) Co-exposure of sulfur nanoparticles and Cu alleviate Cu stress and toxicity to oilseed rape Brassica napus L. J Environ Sci 124:319–329
Zhang D, Du G, Chen D, Shi G, Rao W, Li X, Jiang Y, Liu S, Wang D (2019) Effect of elemental sulfur and gypsum application on the bioavailability and redistribution of cadmium during rice growth. Sci Total Environ 657:1460–1467
Zhao F, Tausz M, De Kok LJ (2008) Role of sulfur for plant production in agricultural and natural ecosystems. In: Hell R, Dahl C, Knaff DB, Leustek T (eds) Sulfur metabolism in phototropic organisms. Springer, pp 425–443
Zhou P, Adeel M, Shakoor N, Guo M, Hao Y, Azeem I, Li M, Liu M, Rui Y (2021) Application of nanoparticles alleviates heavy metals stress and promotes plant growth: an overview. Nanomaterials 11:26. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano11010026
Zia-ur-Rehman M, Khalid H, Rizwan M, Ali S, Sohail MI, Usman M, Umair M (2019) Inorganic amendments for the remediation of cadmium contaminated soils. In: Hasanuzzaman M, Vara Prasad MN, Nahar K (eds) Cadmium tolerance in plants: agronomic, genetic, molecular and omic approaches. Academic Press, pp 113–141 https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-815794-7.00004-7
Zulfiqar U, Jiang W, Xiukang W, Hussain S, Ahmad M, Maqsood MF, Ali N, Ishfaq M, Kaleem M, Haider FU, Farooq N, Naveed M, Kucerik J, Brtnicky M, Mustafa A (2022) Cadmium Phytotoxicity, tolerance, and advanced remediation approaches in agricultural soils; A comprehensive review. Front Plant Sci 13:773815. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.773815
Acknowledgements
The authors wish their sincere appreciation to Dr. Jason C. White and Yi Wang from the Connecticut Agricultural Experiment Station, New Haven, CT 06504, USA, for supporting this research by ICP-OES analysis. Their comments and suggestions highly improved this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
L. Tabrizi, M. Hashemi and O.P. Dhankher declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The authors L. Tabrizi, O.P. Dhankher and M. Hashemi contributed equally to this work.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tabrizi, L., Dhankher, O.P. & Hashemi, M. Alleviation of Cadmium Stress in Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) with Nanoscale and Bulk Sulfur Amendment. Journal of Crop Health 76, 357–370 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-023-00961-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-023-00961-x