Abstract
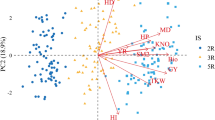
In recent years, the cultivation and consumption of sweet corn has become more popular in the world. Improving seedling establishment and preserving the soil moisture content are crucial in the production of this plant. The purpose of this experiment was to determine the effect of sowing methods and wheat residue mulching on the physiological traits, yield and water productivity of sweet corn under irrigation regimes. Two irrigation levels (100 and 70% of the water requirement), three sowing methods (irrigation after sowing, pre-sowing irrigation after furrow-ridge preparation, and pre-sowing irrigation before furrow-ridge preparation), and four rates of wheat residue mulching (0, 250, 500, and 750 gr m−2) were arranged in a split-split plot based on a randomized complete block design. The results revealed a significant effect for sowing method and residue mulching treatment on plant parameters such as yield, water productivity, total chlorophyll content, carotenoid, and grain carbohydrates. The reduction in water requirement by 30% increased F0 (minimum chlorophyll fluorescence), but pre-sowing irrigation after furrow-ridge preparation and mulching (especially 500 and 750 gr m−2) decreased this trait. Moreover, pre-sowing irrigation after furrow-ridge preparation increased Fv/Fm (variable fluorescence to maximum fluorescence ratio) and grain carbohydrate content. The highest fresh ear and canned grain yield were observed with the pre-sowing irrigation after furrow-ridge preparation and the application of 750 gr m−2 residue mulching. The highest water productivity was obtained when wheat residues (particularly 750 g m−2) were applied and land was prepared with pre-sowing irrigation after furrow-ridge preparation treatment. Overall, the results showed the successful interaction of residue mulching with pre-sowing irrigation in the improvement of physiological indices, yield, and water productivity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad S, Zaheer MS, Ali HH, Erinle KO, Wani SH, Iqbal R, Okone OG, Raza A, Waqas MM, Nawaz M (2021) Physiological and biochemical properties of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under different mulching and water management systems in the semi-arid region of Punjab, Pakistan. Arid Land Res Manag 24:1–6
Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M (1998) Crop Evapotranspiration-guidelines for computing crop water requirements. FAO irrigation and drainage paper, vol 56. FAO, Rome
Andrade FH, Sadras VO, Vega CRC, Echarte L (2005) Physiological determinants of crop growth and yield in maize, sunflower and soybean: their application to crop management, modeling and breeding. J Crop Improv 14:51–101
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1
Brar AS, Buttar GS, Thind HS, Singh KB (2019) Improvement of water productivity, economics and energetics of potato through straw mulching and irrigation scheduling in Indian Punjab. Potato Res 6:1–20
Cai T, Zhang C, Huang Y, Huang H, Yang B, Zhao Z, Zhang J, Jia Z (2015) Effects of different straw mulch modes on soil water storage and water use efficiency of spring maize (Zea mays L.) in the Loess Plateau of China. Plant Soil Environ 61:253–259
Coolong T (2013) Using irrigation to manage weeds: a focus on drip irrigation. Intech: agricultural and biological sciences. In: Soloneski S, Larramendy M (eds) Weed and pest control-conventional and new challenges, vol 14, pp 161–179
Dubey RS (2018) Photosynthesis in plants under stressful conditions. In: Handbook of photosynthesis. CRC Press, pp 629–649
Farooq M, Hussain M, Ul-Allah S, Siddique KH (2019) Physiological and agronomic approaches for improving water-use efficiency in crop plants. Agric Water Manag 219:95–108
Farsiani A, Ghobadi ME, Jalali-Honarm S (2011) The effect of water deficit and sowing date on yield components and seed sugar contents of sweet corn (Zea mays L.). Afr J Agric Res 6:5769–5774
Hajibabaee M, Azizi F, Zargari K (2012) Effect of drought stress on some morphological, physiological and agronomic traits in various foliage corn hybrids. Am Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 12:890–896
Hazrati S, Tahmasebi-Sarvestani Z, Modarres-Sanavy SAM, Mokhtassi-Bidgoli A, Nicola S (2016) Effects of water stress and light intensity on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and pigments of Aloe vera L. Plant Physiol Biochem 106:141–148
Hosseinzadeh SR, Amiri H, Ismaili A (2017) Nutrition and biochemical responses of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) to vermicompost fertilizer and water deficit stress. J Plant Nutr 40:2259–2268
Jin ZM, Wang CH, Liu ZP, Gong WJ (2007) Physiological and ecological characters studies on Aloe vera under soil salinity and seawater irrigation. Process Biochem 42:710–714
Khadem SA, Galavi M, Ramrodi M, Mousavi SR, Rousta MJ, Rezvani-Moghadam P (2010) Effect of animal manure and superabsorbent polymer on corn leaf relative water content, cell membrane stability and leaf chlorophyll content under dry condition. Aust J Crop Sci 4:642–647
Krishna G, Sahoo RN, Singh P, Bajpai V, Patra H, Kumar S, Dandapani R, Gupta VK, Viswanathan C, Ahmad T (2019) Comparison of various modelling approaches for water deficit stress monitoring in rice crop through hyperspectral remote sensing. Agric Water Manag 213:231–244
Li S, Wang Z, Li S, Gao Y, Tian X (2013) Effect of plastic sheet mulch, wheat straw mulch, and maize growth on water loss by evaporation in dryland areas of China. Agric Water Manag 116:39–49
Liang YL, Wu X, Zhu JJ, Zhou MJ, Peng Q (2011) Response of hot pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) to mulching practices under planted greenhouse condition. Agric Water Manag 99:111–120
Mansouri-Far C, Sanavy SAMM, Saberali SF (2010) Maize yield response to deficit irrigation during low-sensitive growth stages and nitrogen rate under semi-arid climatic conditions. Agric Water Manag 97:12–22
Mishra A, Choudhuri M (1999) Effects of salicylic acid on heavy metal-induced membrane deterioration mediated by lipoxygenase in rice. Biol Plant 42:409–415
Mondo VHV, Cicero SM, Dourado-Neto D, Pupim TL, Dias MAN (2013) Seed vigor and initial growth of corn crop. J Seed Sci 35:64–69
Muñoz K, Buchmann C, Meyer M, Schmidt-Heydt M, Steinmetz Z, Diehl D, Thiele-Bruhn S, Schaumann G (2017) Physicochemical and microbial soil quality indicators as affected by the agricultural management system in strawberry cultivation using straw or black polyethylene mulching. Appl Soil Ecol 113:36–44
Nasiri M, Zarehaghi D, Neyshabouri MR (2019) The effect of different levels of pumice mulch and deficit irrigation on the some physiological traits and seed yield of corn (Zea maysL.). J Plant Physiol 13:217–230
Porcar-Castell A, Tyystjärvi E, Atherton J, Van der Tol C, Flexas J, Pfündel EE, Moreno J, Frankenberg C, Berry JA (2014) Linking chlorophyll a fluorescence to photosynthesis for remote sensing applications: mechanisms and challenges. J Exp Bot 65:4065–4095
Rannu RP, Ahmed R, Siddiky A, Ali ASM, Ibn Murad KF, Sarkar PK (2018) Effect of irrigation and mulch on the yield and water use of strawberry. Int J Agron 2018:1–10
Seleiman MF, Al-Suhaibani N, Ali N, Akmal M, Alotaibi M, Refay Y, Dindaroglu T, Abdul-Wajid HH, Battaglia ML (2021) Drought stress impacts on plants and different approaches to alleviate its adverse effects. Plants 10:259
Sepaskhah A (2003) A new outlook to the researches on irrigation efficiency in Islamic Republic of Iran. In: Proceeding of the methods for preventing of wasting of national resources, Tehran, pp 53–62
Sun H, Shao L, Liu XW, Miao WF, Chen SY, Zhang XY (2012) Determination of water consumption and the water-saving potential of three mulching methods in a jujube orchard. Eur J Agron 43:87–95
Szymanek M, Tanaś W, Kassar FH (2015) Kernel carbohydrates concentration in sugary‑1, sugary enhanced and shrunken sweet corn kernels. Agric Agric Sci Procedia 7:260–264
Tafrishi SG, Ayenehband A, Tavakoli H, Khorasani SK, Joleini M (2013) Impacts of drought stress and planting methods on sweet corn yield and water use efficiency. J Plant Physiol Breed 3:23–31
Vaziri Z, Salamat AR, Antesari MR, Moschi M, Heidary N, DehghaniSanich H (2008) Plant Evapotranspiration (Instructions calculate crop water requirement). WG-SDTA, p 270 (in Persian)
Wang XB, Wu HJ, Dai K, Zhang DC, Feng ZH, Zhao QS, Wu XP, Jin K, Cai DX, Oenema O, Hoogmoed WB (2012) Tillage and crop residue effects on rain fed wheat and maize Production in northern China. Field Crop Res 132:106–116
Wasson AP, Richards R, Chatrath R, Misra S, Prasad SS, Rebetzke G, Kirkegaard J, Christopher J, Watt M (2012) Traits and selection strategies to improve root systems and water uptake in water-limited wheat crops. J Exp Bot 63:3485–3498
Widomska J, Welc R, Gruszecki WI (2019) The effect of carotenoids on the concentration of singlet oxygen in lipid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1861:845–851
Xu D, Xu L, Xin X, Yang G, Miao Y (2017) Study on roots morphological properties and distribution of different perennial forages in Hulunber. Acta Agrestia Sin 25:55–60
Yang X, Zhang Q, Li X, Jia X, Wei X, Shao MA (2015) Determination of soil texture by laser diffraction method. Soil Sci Soc Am J 79:1556–1566
Yin W, Fan ZL, Hu FL, Yu AZ, Zhao C, Chai Q, Coulter JA (2019) Innovation in alternate mulch with straw and plastic management bolsters yield and water use efficiency in wheat-maize intercropping in arid conditions. Sci Rep 9:6364
Zhou X, Chen Y, Ouyang Z (2011) Effects of row spacing on soil water and water consumption of winter wheat under irrigated and rainfed conditions. Plant Soil Environ 57:115–121
Zlatev Z, Lidon FC (2012) An overview on drought induced changes in plant growth, water relationsand photosynthesis. Emir J Food Agric 1:57–72
Funding
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
N. Niknam, H. Farajee, M. Movahhedi Dehnavi and A. Yadavi declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature oder sein Lizenzgeber (z.B. eine Gesellschaft oder ein*e andere*r Vertragspartner*in) hält die ausschließlichen Nutzungsrechte an diesem Artikel kraft eines Verlagsvertrags mit dem/den Autor*in(nen) oder anderen Rechteinhaber*in(nen); die Selbstarchivierung der akzeptierten Manuskriptversion dieses Artikels durch Autor*in(nen) unterliegt ausschließlich den Bedingungen dieses Verlagsvertrags und dem geltenden Recht.
About this article
Cite this article
Niknam, N., Farajee, H., Movahhedi Dehnavi, M. et al. Improvement of Physiological Indices and Sweet Corn Performance by Sowing Methods and Wheat Residue Mulching Under Two Irrigation Regimes. Gesunde Pflanzen 75, 2853–2863 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-023-00922-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-023-00922-4