Abstract
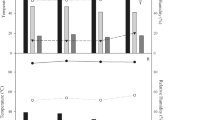
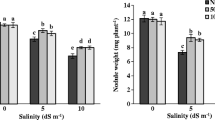
Hypoxia can reduce cellular respiration, ATP synthesis and crop yield and increase production of reactive oxygen species. The use of biostimulants in agriculture has been growing considerably and its use is associated as a strategy to increase crop productivity and plant resistance against abiotic stress. This study aimed to verify the influence of the application of biostimulants on the development and yield of soybean crop grown under hypoxia under field conditions. The treatments were composed of different biostimulants, being the control (no application), Lysine, Tryptophan, Methionine, Betaine-glycine, Histidine, Arginine, Leucine, Aparagine, Alanine, Glutamic acid, Proline, Phenylamine, Serine, Valine, Amino acid extract and algae extract, applied via foliar in soybean cultivated under hypoxia totaling 17 treatments. Hypoxia significantly reduced chlorophyll concentration, number of branches, shoot fresh weight and yield of soybean plants. The use of serine, proline, valine, algae and, amino acid extracts, methionine, arginine and betaine-glycine is promising to increase soybean tolerance to hypoxia by improving physiological parameters, development and yield of plants. Our results contribute to increase knowledge about the influence of biostimulants in combating the stress caused by hypoxia in the soybean crop and can be used as a strategy in agriculture to increase food production in the face of climate change and population growth in order to guarantee food security.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelaal KA, Attia KA, Alamery SF, El-Afry MM, Ghazy AI, Tantawy DS, Hafez YM (2020) Exogenous application of proline and salicylic acid can mitigate the injurious impacts of drought stress on barley plants associated with physiological and histological characters. Sustainability 12(5):1736. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051736
Alfosea-Simón M, Zavala-Gonzalez EA, Camara-Zapata JM, Martínez-Nicolás JJ, Simón I, Simón-Grao S, García-Sánchez F (2020) Effect of foliar application of amino acids on the salinity tolerance of tomato plants cultivated under hydroponic system. Sci Hortic 272:109509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109509
Ali Q, Haider MZ, Shahid S, Aslam N, Shehzad F, Naseem J, Hussain SM (2019) Role of amino acids in improving abiotic stress tolerance to plants. In: Plant tolerance to environmental stress. CRC Press, pp 175–204
Ali S, Abbas Z, Seleiman MF, Rizwan M, Yava Şİ, Alhammad BA, Kalderis D (2020) Glycine betaine accumulation, significance and interests for heavy metal tolerance in plants. Plants 9(7):896. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9070896
AlKahtani MD, Hafez YM, Attia K, Rashwan E, Husnain LA, AlGwaiz HI, Abdelaal KA (2021) Evaluation of silicon and proline application on the oxidative machinery in drought-stressed sugar beet. Antioxidants 10(3):398. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox10030398
Batista-Silva W, Heinemann B, Rugen N, Nunes-Nesi A, Araújo WL, Braun HP, Hildebrandt TM (2019) The role of amino acid metabolism during abiotic stress release. Plant Cell Environ 42(5):1630–1644. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13518
Bulgari R, Franzoni G, Ferrante A (2019) Biostimulants application in horticultural crops under abiotic stress conditions. Agronomy 9(6):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9060306
Campos JVL, Oliveira Cunha LM, do Nascimento V, de Figueiredo P, Ferrari S (2022) Can foliar application of nutrients increase the productive potential of peanuts? Gesunde Pflanz. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-022-00739-7
Carara GDL, Cunha MLO, do Nascimento V, Dos Santos BB, Prado EP, Ferrari S (2022) Effects of application of silicon doses and irrigation on the photosynthetic parameters of cotton. Gesunde Pflanz. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-022-00699-y
Cunha MLO, de Oliveira Lca LCA, Silva VM, Montanha GS, Dos Reis AR (2022) Selenium increases photosynthetic capacity, daidzein biosynthesis, nodulation and yield of peanuts plants (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Physiol Biochem 190:231–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.08.006
Drobek M, Frąc M, Cybulska J (2019) Plant biostimulants: Importance of the quality and yield of horticultural crops and the improvement of plant tolerance to abiotic stress—A review. Agronomy 9(6):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9060335
El Moukhtari A, Cabassa-Hourton C, Farissi M, Savouré A (2020) How does proline treatment promote salt stress tolerance during crop plant development? Front Plant Sci 11:1127. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.01127
Ferrari S, Cunha MLO, do Valle Polycarpo G, Zied DC, de Oliveira Lca LCA, Júnior EF (2022a) Genotypic variation in grain nutritional content and agronomic traits of upland rice: strategy to reduce hunger and malnutrition. Cereal Res Commun. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42976-022-00257-2
Ferrari S, do Valle Polycarpo G, Vargas PF, Fernandes AM, Luís Oliveira Cunha M, Pagliari P (2022b) Mix of trinexapac-ethyl and nitrogen application to reduce upland rice plant height and increase yield. Plant Growth Reg 96(1):209–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-021-00770-0
Foyer CH (2018) Reactive oxygen species, oxidative signaling and the regulation of photosynthesis. Environ Exp Bot 154:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2018.05.003
Haghighi M, Saadat S, Abbey L (2020) Effect of exogenous amino acids application on growth and nutritional value of cabbage under drought stress. Sci Hortic 272:109561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109561
Hammad SA, Ali OA (2014) Physiological and biochemical studies on drought tolerance of wheat plants by application of amino acids and yeast extract. Ann Agric Sci 59(1):133–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2014.06.018
Hasanuzzaman M, Parvin K, Bardhan K, Nahar K, Anee TI, Masud AAC, Fotopoulos V (2021) Biostimulants for the regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolism in plants under abiotic stress. Cells 10(10):2537. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10102537
Khan N, Ali S, Zandi P, Mehmood A, Ullah S, Ikram M, Babar MA (2020) Role of sugars, amino acids and organic acids in improving plant abiotic stress tolerance. Pak J Bot 52(2):355–363. https://doi.org/10.30848/PJB2020-2(24)
León J, Castillo MC, Gayubas B (2021) The hypoxia-reoxygenation stress in plants. J Exp Bot 72(16):5841–5856. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eraa591
Loreti E, Perata P (2020) The many facets of hypoxia in plants. Plants 9(6):745. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9060745
Matysiak K, Kierzek R, Siatkowski I, Kowalska J, Krawczyk R, Miziniak W (2020) Effect of exogenous application of amino acids l‑arginine and glycine on maize under temperature stress. Agronomy 10(6):769. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10060769
Mittler R, Zandalinas SI, Fichman Y, Van Breusegem F (2022) Reactive oxygen species signalling in plant stress responses. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-022-00499-2
Nephali L, Piater LA, Dubery IA, Patterson V, Huyser J, Burgess K, Tugizimana F (2020) Biostimulants for plant growth and mitigation of abiotic stresses: A metabolomics perspective. Metabolites 10(12):505. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10120505
Peña Calzada K, Olivera Viciedo D, Habermann E, Calero Hurtado A, Lupino Gratão P, De Mello Prado R, Rodríguez JC (2022) Exogenous application of amino acids mitigates the deleterious effects of salt stress on soybean plants. Agronomy 12(9):2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12092014
Pucciariello C, Perata P (2017) Flooding stress tolerance in plants. In: Plant stress physiology. CABI, Wallingford, pp 155–177
Rampazzo MV, Cunha MLO, de Oliveira LCA, Silva VM, Lanza MGDB, de Melo AAR, dos Reis AR (2022) Physiological roles of nickel on antioxidant and nitrogen metabolism increasing the yield of sugarcane plants. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-022-01045-x
Rasheed R, Yasmeen H, Hussain I, Iqbal M, Ashraf MA, Parveen A (2020) Exogenously applied 5‑aminolevulinic acid modulates growth, secondary metabolism and oxidative defense in sunflower under water deficit stress. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 26(3):489–499. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-019-00756-3
Sadak MS, Abdelhamid MT (2015) Influence of amino acids mixture application on some biochemical aspects, antioxidant enzymes and endogenous polyamines of Vicia faba plant grown under seawater salinity stress. Gesunde Pflan 67(3):119–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-015-0344-2
Salvatierra A, Pimentel P, Almada R, Hinrichsen P (2016) Exogenous GABA application transiently improves the tolerance to root hypoxia on a sensitive genotype of Prunus rootstock. Environ Exp Bot 125:52–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2016.01.009
Seifikalhor M, Niknam V, Aliniaeifard S, Didaran F, Tsaniklidis G, Fanourakis D, Li T (2022) The regulatory role of γ‑Aminobutyric acid in chickpea plants depends on drought tolerance and water scarcity level. Sci Rep 12(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-10571-8
Silva VM, Tavanti RFR, Gratão PL, Alcock TD, Dos Reis AR (2020) Selenate and selenite affect photosynthetic pigments and ROS scavenging through distinct mechanisms in cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) walp) plants. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 201:110777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110777
Yakhin OI, Lubyanov AA, Yakhin IA, Brown PH (2017) Biostimulants in plant science: a global perspective. Front Plant Sci 7:2049. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.02049
Yang Z, Chang Z, Sun L, Yu J, Huang B (2014) Physiological and metabolic effects of 5‑aminolevulinic acid for mitigating salinity stress in creeping bentgrass. PLoS One 9(12):e116283. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0116283
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
R. de Andrade Silva, W. Lessa Silva, L. Farias Damasceno, M. Luís Oliveira Cunha, N. Angelica Carvalho Mendes and L. Aparecido Manzani Lisboa declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature oder sein Lizenzgeber (z.B. eine Gesellschaft oder ein*e andere*r Vertragspartner*in) hält die ausschließlichen Nutzungsrechte an diesem Artikel kraft eines Verlagsvertrags mit dem/den Autor*in(nen) oder anderen Rechteinhaber*in(nen); die Selbstarchivierung der akzeptierten Manuskriptversion dieses Artikels durch Autor*in(nen) unterliegt ausschließlich den Bedingungen dieses Verlagsvertrags und dem geltenden Recht.
About this article
Cite this article
de Andrade Silva, R., Lessa Silva, W., Farias Damasceno, L. et al. Physiological and Productive Role of Biostimulants in Alleviating Hypoxia Stress in Soybean Grown Under Field Conditions. Gesunde Pflanzen 75, 2713–2721 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-023-00896-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-023-00896-3