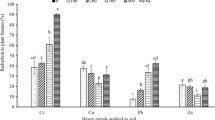
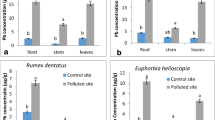
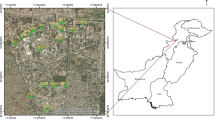
Abstract
Heavy metals present in the soil and water are entering the food chain, which in turn causes severe health hazards. The present study was aimed to explore phytotoxicity of various concentrations of lead acetate, zinc and cadmium (0–8000 ppm) in Atriplex halimus L. Exogenous application of zinc significantly boosted shoot length (67.8%), polyphenoloxidase activity (66.6%), chlorophyll a (55.5%), chlorophyll b (45.9%), chlorophyll t (52.4%) and carotenoid (58.6%) under zinc-6000 ppm compared to the control without zinc treatment, while catalase activity and root length reduced by 45.6 and 14.6%, respectively. In comparison to control, polyphenoloxidase and non-enzymatic antioxidant i.e. carotenoid, chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, chlorophyll t were significantly enhanced while root length and free proline contents in leaves reduced by 45.6 and 53.1% with exogenous application of plomb-8000 ppm. The same treatment of cadmium (6000 and 8000 ppm) enhanced antioxidant enzymes activities but decreased shoot length, root length and photosynthetic pigments as compared to control. The present results suggest that Atriplex halimus L. had potential tolerance mechanism and could be used to bioremediate the trace elements-contaminated soils.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in Vitro. Meth Enzymol 105:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Alamri SA, Siddiqui MH, Al-Khaishany MY, Nasir KM, Ali HM, Alaraidh IA, Mateen M (2018) Ascorbic acid improves the tolerance of wheat plants to lead toxicity. J Plant Interact 13(1):409–419. https://doi.org/10.1080/17429145.2018.1491067
Ali H, Naseer M, Sajad MA (2012) Phytoremediation of heavy metals by Trifolium alexandrinum. Agris Online Pap Econ Inform 2(3):1459–1469. https://doi.org/10.6088/ijes.002020300031
Amjadian K, Sacchi E, Rastegari MM (2016) Heavy metals (HMs) and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in soils of different land uses in Erbil metropolis, Kurdistan Region, Iraq. Environ Monit Assess 188:605. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5623-6
Anderson C, Moreno F, Meech J (2005) A field demonstration of gold phytoextraction technology. Miner Eng 18(4):385–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2004.07.002
Anjum NA, Ahmad I, Válega M, Mohmood I, Gill SS, Tuteja N, Duarte AC, Pereira E (2014) Salt marsh halophyte services to metal–metalloid remediation: Assessment of the processes and underlying mechanisms. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 44(18):2038–2106. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2013.828271
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.24.1.1
Assuncao AGL, Schat H, Aarts MGM (2003) Thlaspi caerulescens, an attractive model species to study heavy metal hyperaccumulation in plants. New Phytol 159(2):351–360. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2003.00820.x
Bai J, Cui B, Wang Q, Gao H, Ding Q (2009) Assessment of heavy metal contamination of roadside soils in Southwest China. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 23:341–347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00477-008-0219-5
Barrs HD, Weatherley PE (1962) A re-examination of the relative turgidity technique for estimating water deficit in leaves. Aust Jnl Of Bio Sci 15(3):413–428. https://doi.org/10.1071/BI9620413
Bhargava A, Carmona FF, Bhargava M, Srivastava S (2012) Approaches for enhanced phytoextraction of heavy metals. J Environ Manag 105:103–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.04.002
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye-binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Chaney R (1993) Zinc phytotoxicity. In: Robson AD (ed) Zinc in soils and plants. Kluwer Academic Publisher, Dordrecht, pp 135–150 https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-0878-2_10
Clemens S, Ma JF (2016) Toxic heavy metal and metalloid accumulation in crop plants and foods. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67:489–512. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-043015-112301
Clemente R, Walker DJ, Pardo T, MartínezFernández D, Bernal MP (2012) The use of a halophytic plant species and organic amendments for the remediation of a trace elements-contaminated soil under semi-arid conditions. J Hazard Mater 223–224:63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.04.048
Corso M, De La Torre VSG (2020) Biomolecular approaches to understanding metal tolerance and hyperaccumulation in plants. Metallomics 12:840–859. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0mt00043d
Dong Y, Chen W, Bai X, Liu F, Wan Y (2019) Effects of exogenous nitric oxide and 24-epibrassinolide on physiological characteristics of peanut under cadmium stress. Pedosphere 29(1):45–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(17)60376-X
Drazkiewicz M (1994) Chlorophyll-occurrence, functions, mechanism of action, effects of internal and external factors. Photosynt 30:321–331
Dreier W, Göring M (1974) Der Einfluss hoher Salzkonzentration auf verschiedene physiologische Parameters von Maiswurzeln. Wiss. Z. Humboldt Univ. Berlin, Reihe/Math. Naturwiss 23:641–644
Ghnaya T, Slama I, Messedi D, Grignon C, Ghorbel MH, Abdelly C (2007) Cd-induced growth reduction in the halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum is significantly improved by NaCl. J Plant Res 120(2):309–316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-006-0042-3
Haghighi M, Kafi M, Pessarakli M, Sheibanirad A, Sharifinia MR (2016) Using kale (Brassica oleracea var. acephala) as a phytoremediation plant species for lead (Pb) and cadmium (Cd) removal in saline soils. J of Plant Nutrition 39(10):1460–1471. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2016.1161768
Hall JL (2002) Cellular mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. J Exp Bot 53(366):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/53.366.1
Hewlett JD, Kramer PJ (1963) The measurement of water deficits in broadleaf plants. Protoplasma 57:381–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01252067
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. California Agricultural Experiment Station, Circular-347 (2nd edit)
Hori K, Wada A, Shibuta T (1997) Changes in phenoloxidase activities of the galls on leaves of Ulmus davidana formed by Tetraneura fusiformis (Homoptera: Eriosomatidae). Appl Entomol Zool 32(2):365–371. https://doi.org/10.1303/aez.32.365
Jabeen R, Ahmad A, Iqbal M (2009) Phytoremediation of heavy metals: physiological and molecular mechanisms. Bot Rev 75(4):339–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12229-009-9036-x
Kabata-Pendias A (2000) Trace elements in soils and plants, 3rd edn. CRC Press LLC, Boca Raton https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420039900
Kabata-Pendias A (2011) Trace elements in soils and plants. CRC press, Boca-Raton https://doi.org/10.1201/b10158
Kadukova J, Manousaki E, Kalogerakis N (2008) Pb and Cd accumulation and phyto-excretion by salt cedar (Tamarix smyrnensis bunge). Int J Phytoremediation 10(1):31–46. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226510701827051
Kirkham MB (2006) Cadmium in plants on polluted soils: effects of soil factors, hyperaccumulation, and amendments. Geoderma 137(1–2):19–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2006.08.024
Krishnaraj S, Dan TV, Saxena PK (2000) A fragrant solution to soil remediation. Int J Phytoremediation 2(2):117–132. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226510008500034
Kulkarni MG, Stirk WA, Southway C, Papenfus HB, Swart PA, Lux A, Vaculík M, Martinka M, Van Staden J (2013) Plant growth regulators enhance gold uptake in Brassica juncea. Int J Phytoremediation 15(2):117–126. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2012.683207
Lamb AE, Anderson CWN, Haverkamp RG (2001) The induced accumulation of gold in the plants Brassica juncea, Berkheya coddii and chicory. Chemstry in New Zealand: 34–36. https://hdl.handle.net/10179/9608
Lamhamdi M, Bakrim A, Aarab A, Lafont R, Sayah F (2011) Lead phytotoxicity on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seed germination and seedlings growth. Comptes Rendus Biol 334(2):118–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crvi.2010.12.006
Latef AAHA, Chao-xing H (2011) Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth, mineral nutrition, antioxidant enzymes activity and fruit yield of tomato grown under salinity stress. Sci Hortic 127(3):228–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2010.09.020
Lefèvre I, Marchal G, Meerts P, Correal E, Lutts S (2009) Chloride salinity reduces cadmium accumulation by the Mediterranean halophyte species Atriplex halimus L. Environ Exp Bot 65(1):142–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2008.07.005
Lefevre I, Marchal G, Ghanem EM, Correal E, Lutts S (2010) Cadmium has contrasting effects on polyethylene glycol—Sensitive and resistant cell lines in the Mediterranean halophyte species Atriplex halimus L. J Plant Physiol 167:365–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2009.09.019
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Meth Enzymol 148:350–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(87)48036-1
Lutts S, Lefèvre I (2015) How can we take advantage of halophyte properties to cope with heavy metal toxicity in salt-affected areas? Ann Bot 115(3):509–528. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcu264
Lutts S, Lefèvre I, Delpérée S, Kivits S, Dechamps C, Robledo A, Correal E (2004) Heavy metal accumulation by the halophyte species Mediterranean saltbush. J Environ Qual 33(4):1271–1279. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2004.1271
Madebo MP, Luo SM, Li W, Zheng YH, Peng J (2021) Melatonin treatment induces chilling tolerance by regulating the contents of polyamine, γ‑aminobutyric acid, and proline in cucumber fruit. J Integr Agric 20(11):3060–3074. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2095-3119(20)63485-2
Mahmud J, Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Rahman A, Fujita M (2017) Relative tolerance of different species of Brassica to cadmium toxicity: coordinated role of antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems. Plant Omics J 10:107. https://doi.org/10.21475/poj.10.02.17.pne409
Malar S, Manikandan R, Favas PJC, Sahi SV, Venkatachalam P (2014) Effect of lead on phytotoxicity, growth, biochemical alterations and its role on genomic template stability in Sesbania grandiflora: a potential plant for phytoremediation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 108:249–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.05.018
Manousaki E, Kalogerakis N (2009) Phytoextraction of Pb and Cd by the Mediterranean saltbush (Atriplex halimus L.): metal uptake in relation to salinity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 16(7):844–854. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-009-0224-3
Manousaki E, Kalogerakis N (2011) Halophytes present new opportunities in phytoremediation of heavy metals and saline soils. Ind Eng Chem Res 50(2):656–660. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie100270x
Manousaki E, Kadukova J, Papadantonakis N, Kalogerakis N (2008) Phytoextraction and phytoexcretion of Cd by the leaves of Tamarix smyrnensis growing on contaminated non-saline and saline soils. Environ Res 106(3):326–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2007.04.004
Mateos-Naranjo E, Castellanos EM, Perez-Martin A (2014) Zinc tolerance and accumulation in the halophytic species Juncus acutus. Environ Exp Bot 100:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2013.12.023
Monneveux P, Nemmar M (1986) Contribution à l’étude de la résistance à la sécheresse chez le blé tendre (Triticum aestivum L.) et chez le blé dur (Triticum durum Desf.): Etude de l’accumulation de la proline au cours du cycle de développement. Agronomie 6:583–590
Nawaz MF, Gul S, Tanvir MA, Akhtar J, Chaudary S, Ahmad I (2016) Influence of NaCl-salinity on Pb-uptake behavior and growth of River Red gum tree (Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh.). Turk J Agric For 40(3):425–432. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1407-73
Nedjimi B, Daoud Y (2009) Cadmium accumulation in Atriplex halimus subsp. schweinfurthii and its influence on growth, proline, root hydraulic conductivity and nutrient uptake. Flora Morphol Distrib Funct Ecol Plant 204(4):316–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.flora.2008.03.004
Parkash V, Singh S (2020) A review on potential plant-based water stress indicators for vegetable crops. Sustainability 12(10):3945. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12103945
Parmar P, Kumari N, Sharma V (2013) Structural and functional alterations in photosynthetic apparatus of plants under cadmium stress. Bot Stud 54:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/1999-3110-54-45
Pourrut B, Shahid M, Dumat C, Winterton P, Pinelli E (2011) Lead uptake, toxicity, and detoxification in plants. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 213:113–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-9860-6_4
Ramirez DA, Yactayo W, Guterrez R, Mares V, De Mendiburu F, Posadas A, Roberto QA (2014) Chlorophyll concentration in leaves is an indicator of potato tuber yield in water-shortage conditions. Sci Hortic 168:202–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.01.036
Rastegari Mehr M, Keshavarzi B, Moore F, Sharifi R, Lahijanzadeh A, Kermani M (2017) Distribution, source identification and health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in urban areas of Isfahan province, Iran. J Afr Earth Sci 132:16–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2017.04.026
Rong-hua L, Pei-guo G, Baum M, Grando S, Ceccarelli S (2006) Evaluation of chlorophyll content and fluorescence parameters as indicators of drought tolerance in barley. Agric Sci China 5:751–757. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1671-2927(06)60120-X
Ruley AT (2004) Effects of Accumulation of Pb and Synthetic Chelators on the Physiology and Biochemistry of Sesbania drummondii (M.S. thesis). Western Kentucky University. USA.
Sarwar N, Imran M, Shaheen MR, Ishaque W, Kamran MA, Matloob A, Rehim A, Hussain S (2017) Phytoremediation strategies for soils contaminated with heavy metals: modifications and future perspectives. Chemosphere 171:710–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.116
Scippa GS, Di Michele M, Onelli E, Patrignani G, Chiatante D, Bray EA (2004) The histone-like protein H1‑S and the response of tomato leaves to water deficit. J Exp Bot 55(394):99–109. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erh022
Sgherri C, Cosi E, Navari-Izzo F (2003) Phenols and antioxidative status of Raphanus sativus grown in copper excess. Physiol Plant 118(1):21–28. https://doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3054.2003.00068.x
Singh HP, Batish DR, Kaur G, Arora K, Kohli RK (2008) Nitric oxide (as sodium nitroprusside) supplementation ameliorates Cd toxicity in hydroponically grown wheat roots. Environ Exp Bot 63:158–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2007.12.005
Souahi H (2021) Impact of lead on the amount of chlorophyll and carotenoids in the leaves of Triticum durum and T. aestivum, Hordeum vulgare and Avena sativa. Biosyst Divers 29(3):207–210. https://doi.org/10.15421/012125
Souahi H, Gharbi A, Gassarellil Z (2017) Growth and physiological responses of cereals species under lead stress. Int J Biosci 11(1):266–273. https://doi.org/10.12692/ijb/11.1.266-273
Souahi H, Gassarellil Z, Gharbi A, Meksem AL (2021a) Comparative growth of cereal species under lead stress. In: Ksibi M et al (ed) Recent advances in environmental science from the Euro-Mediterranean and surrounding regions, 2nd edn. EMCEI 2019. Environmental Science and Engineering. Springer, Cham https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-51210-1_99
Souahi H, Chebout A, Akrout K, Massaoud N, Gacem R (2021b) Physiological responses to lead exposure in wheat, barley and oat. Environ Chall 4:100079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envc.2021.100079
Souahi H, Chebout A, Assal N (2021c) Effects of heavy metals on the germination and radicle growth of halophytes species (Atriplex halimus l.). Studia Univ Vasile Goldis Ser Stiintele Vietii (Life Sci Ser) 31(4):178–186
Souahi H, Gacem R, Chenchouni H (2022) Variation in plant diversity along a watershed in the semi-arid lands of North Africa. Diversity 14(6):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/d14060450
Tian K, Huang B, Xing Z, Hu W (2017) Geochemical baseline establishment and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in greenhouse soils from Dongtai, China. Ecol Indic 72:510–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.08.037
Troll W, Lindsley J (1955) A photometric method for the determination of proline. J Biochem 215:655–660
Trovato M, Mattioli R, Costantino P (2008) Multiple roles of proline in plant stress tolerance and development. Rendiconti Lincei 19(4):325–346. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12210-008-0022-8
Walker DJ, Lutts S (2014) The tolerance of Atriplex halimus L. to environmental stresses. Emirates J Food Agric 26(12):1081–1090. https://doi.org/10.9755/ejfa.v26i12.19116
Wang HL, Tian CY, Jiang L, Wang L (2014) Remediation of heavy metals contaminated saline soils: a halophyte choice? Environ Sci Technol 48(1):21–22. https://doi.org/10.1021/es405052j
Wessolek G, Fahrenhorst C (1994) Immobilization of heavy metals in a polluted soil of a sewage farm by application of a modified aluminosilicate: a laboratory and numerical displacement study. Soil Technol 7(3):221–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/0933-3630(94)90023-X
Wilkins DA (1957) A technique for the measurement of lead tolerance in plants. Nature 180:37–38. https://doi.org/10.1038/180037b0
Wu XX, He J, Zhu ZW, Yang SJ, Zha DS (2014) Protection of photosynthesis and antioxidative system by 24-epibrassinolide in Solanum melongena under cold stress. Biol Plant 58(1):185–188. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10535-013-0377-2
Xue ZC, Li JH, Li DS, Li SZ, Jiang CD, Liu LA, Wang SY, Kang WJ (2018) Bioaccumulation and photosynthetic activity response of sweet sorghum seedling (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) to cadmium stress. Photosynt 56:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11099-018-0835-3
Yang X, Long X, Ye H, He Z, Calvert D, Stoffella P (2004) Cadmium tolerance and hyperaccumulation in a new Znhyperaccumulating plant species (Sedum alfredii Hance). Plant Soil 259:181–189. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:PLSO.0000020956.24027.f2
Zaier H, Ghnaya T, Rejeb KB, Lakhdar A, Rejeb S, Jemal F (2010) Effects of EDTA on phytoextraction of heavy metals (Zn, Mn and Pb) from sludge-amnded soil with Brassica napus. Bioresour Technol 101(11):3978–3983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.01.035
Acknowledgements
Special thanks for the financial support from the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research, through the associated PRFU project (D01N01UN120120190003) and Laboratory of Plant Biology, Faculty of Exact Sciences and Natural and Life Sciences, University of Tebessa for providing necessary facilities and also technical staffs and students for their high commitment and cooperation in conducting the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Hana SOUAHI: conceptualised, designed the study, supervised the work, analysed the data and drafted the manuscript. Abderrezzeq CHEBOUT, Randa FARES and Loubna SÉDAIRIA carried out the research work in the laboratory. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
H. Souahi, A. Chebout, R. Fares and L. Sédairia declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Availability of Data and Materials
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Souahi, H., Chebout, A., Fares, R. et al. Remediation of Agricultural Soil by the Use of Halophytic Crops Under Heavy Metals Conditions in Semi-Arid Environments. Gesunde Pflanzen 75, 1181–1192 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-022-00779-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-022-00779-z