Abstract
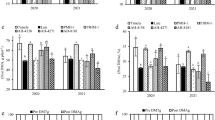
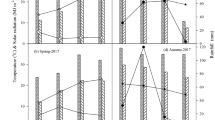
Maize (Zea mays L.) is important for grain and fodder; its optimal production ensures food security. The seasonal shift of monsoon rain is becoming a threat to high maize production in Pakistan. This study addressed changes in phases of the crop lifecycle and their effects on yield. The experiment was conducted in 2017 and 2018 at the Agronomy Research Farm of the University of Agriculture Peshawar, Pakistan, as split plot in randomized complete block design with three replications. Sowing timing (ST) from June 6 to July 16 with 10-day intervals was the factor in main plots, and N rate (NR) 160, 180, 200, and 220 kg ha−1 was the factor in subplots. Results revealed significant changes (p < 0.05) in the crop lifecycle, with a significant decrease in the reproductive versus the vegetative phase of growth for each 10-day delay from June 16. Likewise, a decrease in grain yield was observed by limiting NR from 200 kg ha−1, with no change (p < 0.05) from 220 kg ha−1. A decrease in yield caused by delayed sowing was mainly due to low floret fertilization with fewer grains per row and limited grain weight overall due to fewer days of reproductive growth, which affected grain yield accordingly. High NR of 200 kg ha−1 is advantageous for crops facing flood irrigation with a heavy monsoon season for harvesting optimal production. The study concludes that maize planted after wheat (or any other crop) should be planted early in the season, in June, to avoid monsoon rain damage for optimum density and to ensure high production with healthy traits for future food security.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas G, Ahmad S, Hussain M, Fatima Z, Hussain S, Iqbal P, Farooq M (2020) Sowing date and hybrid choice matters production of maize–maize system. Int J Plant Prod 14(4):583–595
Adhikari K, Bhandari S, Aryal K, Mahato M, Shrestha J (2021) Effect of different rates of nitrogen on growth and yield of hybrid maize (Zea mays L.) varieties. J Agric Nat Res 4(2):48–62
Ahmad I, Wajid SA, Ahmad A, Cheema MJM, Judge J (2018) Assessing the impact of thermo-temporal changes on the productivity of spring maize under semi-arid environment. Int J Agric Biol 20:2203–2210
Ahmed P, Saikia M (2020) Influence of sowing dates for higher productivity of rabi maize. A Review. Int J Recent Sci Res 11(04):38267–38271
Ahsan M, Hussain MM, Farooq J, Khaliq I, Farooq A, Ali Q, Kashif M (2011) Physio-genetic behavior of maize seedlings at water deficit conditions. Cerceta Agron Moldova 146:41–49
Ahsan M, Farooq A, Khaliq I, Ali Q, Aslam M, Kashif M (2013) Inheritance of various yield contributing traits in maize (Zeamays L.) at low moisture condition. Afri J Agric Res 8:413–420
Akmal M, Rehman MH, Farhatullah, Akbar H (2010) Response of maize varieties to nitrogen application for leaf area profile, crop growth, yield and yield components. Pak J Bot 42(3):1941–1947
Albacete AA, Andújar CM, Alfocea FP (2014) Hormonal and metabolic regulation of source–sink relations under salinity and drought: from plant survival to crop yield stability. Biotechnol Adv 32(1):12–30
Alexandratos N, Bruinsma J (2012) World agriculture towards 2030/2050: the 2012 revision
Ali S, Liu Y, Ishaq M, Shah T, Ilyas A, Din IU (2017) Climate change and its impact on the yield of major food crops: evidence from Pakistan. Foods 6(39):50
Ali W, Ali M, Ahmad Z, Iqbal J, Anwar S, Khan MH, Kamal A (2018) Influence of sowing dates on varying maize (Zea mays L.) varieties grown under agro-climatic condition of Peshawar, Pakistan. Eur J Exp Biol 8(6):35–36
Arshad AA, Raza MA, Zhangn Y, Zhang L, Wang X, Ahmed M, Habib-ur-Rehman (2021) Impact of climate warming on cotton growth and yields in China and Pakistan: A regional perspective. Agriculture 11(2):97
Atibioke OA, Ogunlade I, Abiodun AA, Ogundele BA, Omodaraand MA, Ade AR (2012) Effects of farmers’ demographic factors on the adoption of grain storage technologies developed by Nigerian stored products research institute (NSPRI): A case study of selected villages in Ilorin West LGA of Kwara State. Res Humanit Soc Sci 2(6):56–63
Begam A, Ray M, Roy DC, Sujit A (2018) Performance of hybrid maize (Zea mays L.) in different rates and time of nitrogen application in Indo-Gangetic plains of eastern India. J Exp Biol Agric Sci 6(6):929–935
Bisbis MB, Gruda N, Blanke M (2018) Potential impacts of climate change on vegetable production and product quality—A review. J Clean Prod 170:1602–1620
Blandino M, Battisti M, Vanara F, Reyneri A (2022) The synergistic effect of nitrogen and phosphorus starter fertilization sub-surface banded at sowing on the early vigor, grain yield and quality of maize. Eur J Agron 137:126509
Cavalcante VS, Prado RDM, Vasconcelos RL, Almeida HJ, Silva TRD (2019) Growth and nutritional efficiency of watermelon plants grown under macronutrient deficiencies. Hortic Sci 54(4):738–742
Chakraborty P, Dwivedi P (2021) Seed priming and its role in mitigating heat stress responses in crop plants. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 21(2):1718–1734
Chen L (2019) Invasive plants in coastal wetlands: patterns and mechanisms. In: Wetlands: ecosystem services, restoration and wise use, pp 97–128
Chen FJ, Fang ZG, Gao Q, Ye YL, Jia LL, Yuan LX, Mi GH, Zhang FS (2013) Evaluation of the yield and nitrogen use efficiency of the dominant maize hybrids grown in North and Northeast China. Sci China Life Sci 56:552–560. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-013-4462-8
D’Andrea KE, Parco M, Maddonni GA (2022) Maize prolificacy under contrasting plant densities and N supplies: II. Growth per plant, biomass partitioning to apical and sub-apical ears during the critical period and kernel setting. Field Crop Res 284:108557
Dawadi DR, Sah SK (2012) Growth and yield of hybrid maize (Zea mays L.) in relation to planting density and nitrogen rates during winter season in Nepal. Tropic Agric Res 23(3):218–227
Foster T, Brozović N (2018) Simulating crop-water production functions using crop growth models to support water policy assessments. Ecol Econ 152:9–21
Gaile Z (2012) Response to sowing timing under agro-climatic condition of latvia. Zemdirbyste Agric 99:31–40
Gazengel K, Aigu Y, Lariagon C, Humeau M, Gravot A, Dauleux MJM, Daval S (2021) Nitrogen supply and host-plant genotype modulate the transcriptomic profile of plasmodiophorabrassicae. Front Microbiol 12:1795
Geng G, Cakmak I, Ren T, Lu Z, Lu J (2021) Effect of magnesium fertilization on seed yield, seed quality, carbon assimilation and nutrient uptake of rapeseed plants. Field Crop Res 264:108082
Giunta F, Prunddu G, Motzu R (2009) Radiation interception and biomass and nitrogen. Field Crop Res 110:76–84
Godswill AG, Somtochukwu IV, Ikechukwu AO, Kate EC (2020) Health benefits of micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) and their associated deficiency diseases: A systematic review. Int J Food Sci 3(1):1–32
Hanif M, Ali J (2014) Climate scenarios 2001–2014 Districts Haripur, Sawabi, Attock and Chakwal-Pakistan. Publication, Inter-Cooperation Pakistan, pp 27
Hammad HM, Ahmad A, Wajid A, Akhter J (2011) Maize response to time and rate of nitrogen application. Pak J Bot 43(4):1935–1942
Hammer GL, McLean G, Van Oosterom E, Chapman S, Zheng B, Wu A, Jordan D (2020) Designing crops for adaptation to the drought and high-temperature risks anticipated in future climates. Crop Sci 60(2):605–621
Hu J, Ren B, Dong S, Liu P, Zhao B, Zhang J (2021) Poor development of spike differentiation triggered by lower photosynthesis and carbon partitioning reduces summer maize yield after water logging. Eur Exp Biol 8(2):411–416
Hu Y, Ma P, Duan C, Wu S, Feng H, Zou Y (2020) Black plastic film combined with straw mulching delays senescence and increases summer maize yield in northwest China. Agri Water Manag 231:106031
Huang S, Lv L, Zhu J, Li Y, Tao H, Wang P (2018) Extending growing period is limited to offsetting negative effects of climate changes on maize yield in the North China Plain. Field Crop Res 215:66–73
Hunt JR, Hayman PT, Richards RA, Passioura JB (2018) Opportunities to reduce heat damage in rain-fed wheat crops based on plant breeding and agronomic management. Field Crop Res 224:126–138
Hütsch BW, Schubert S (2021) Can nutrient-utilization efficiency be improved by reduced fertilizer supply to maize plants treated with the plant growth regulator paclobutrazol. J Agron Crop Sci 207(5):884–900
Jebril J, Wang D, Rozeboom K, Tess T (2021) Grain sink removal increases stalk juice yield, sugar accumulation, and biomass in sweet sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench). Ind Crops Prod 173:114089
Kearney J (2010) Food consumption trends and drivers. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 365(1554):2793–2807
Khan HZ, Iqbal S, Iqbal A, Akbar N, Jones DL (2011) Response of maize (Zea mays L.) varieties to different rates of nitrogen. Crop Environ 2(2):15–19
Khan ZH, Khalil SK, Ikramullah MA, Iqbal A, Islam B, Ali K, Shah F (2019) Physical characteristics of cobs and kernels in sweet corn under varying planting environments. Fresenius Environ Bull 28:6568
Kibe AM, Singh S, Kalra N (2006) Water nitrogen relationships for wheat growth and productivity in late sown conditions. Agric Water Manag 84(3):221–228
Kozlov K, Singh A, Berger J, Bishop-von E, Wettberg A, Kahraman A, Aydogan, Samsonova M (2019) Non-linear regression models for time to flowering in wild chickpea combine genetic and climatic factors. BMC Plant Biol 19(2):1–14
Kundu A, Ganguli S, Pal A (2022) Genomic designing towards biotic stress resistance in Mungbean and Urdbean. In: Genomic designing for biotic stress resistant pulse crops. Springer, Cham, pp 381–414
Li J, Xu X, Lin G, Wang Y, Liu Y, Zhang M, Zhang Y (2018) Micro-irrigation improves grain yield and resource use efficiency by co-locating the roots and N‑fertilizer distribution of winter wheat in the North China Plain. Sci Total Environ 643:367–377
Liaqat W, Akmal M, Ali J (2018) Sowing date effect on production of high yielding maize varieties. Sarhad J Agric 34(1):102–113
Lindström K, Mousavi SA (2020) Effectiveness of nitrogen fixation in rhizobia. Microb Biotechnol 13(5):1314–1335
Lippmann R, Babben S, Menger A, Delker C, Quint M (2019) Development of wild and cultivated plants under global warming conditions. Curr Biol 29(24):1326–1338
Liu Y, Qin Y, Ge Q (2019) Spatiotemporal differentiation of changes in maize phenology in China from 1981 to 2010. J Geogr Sci 29(3):351–362
Lizaso JI, Ramos MR, Rodríguez L, Leal CG, Oliveira JA, Lorite IJ, Rodríguez A (2018) Impact of high temperatures in maize: Phenology and yield components. Field Crop Res 216:129–140
Martiniello P, Teixeira da Silva JA (2011) Physiological and bio-agronomical aspects involved in growth and yield components of cultivated forage species in mediterranean environments: A review. Eur J Plant Sci Biotechnol 5:64–98
Maryam AB, Khorasani SK, Shojaei SH, Golbashy M (2011) A study on effects of planting dates on growth and yield of 18 corn hybrids (Zea mays L.). Am J Exp Agric 1(3):110–120
Mitiku BT (2021) Genetic variability and associations among yield and yield related traits in maize (Zea mays L.) inbred lines developed for moisture stress tolerance in Ethiopia. Doctoral dissertation, Jimma University
Mo F, Wang JY, Li FM, Nguluu SN, Ren HX, Zhou H, Xiong YC (2017) Yield-phenology relations and water use efficiency of maize (Zea mays L.) in ridge-furrow mulching system in semiarid east African Plateau. Sci Rep 7(1):1–14
Mohsin AU, Ahmad AUH, Farooq M, Ullah S (2014) Influence of zinc application through seed treatment and foliar spray on growth, productivity and grain quality of hybrid maize. J Anim Plant Sci 24(5):1494–1503
Monga D, Basu S (2019) Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of industrial dye by g‑C3N4/TiO2 nanocomposite: Role of shape of TiO2. Adv Powder Technol 30(5):1089–1098
Nasielski J, Deen B (2019) Nitrogen applications made close to silking: Implications for yield formation in maize. Field Crop Res 243:107621
Ngoune TL, Mutengwa CS (2019) Estimation of maize (Zea mays L.) yield per harvest area: appropriate methods. Agronomy 10(1):29
Pauzon C, Hryha E, Forêt P, Nyborg L (2019) Effect of argon and nitrogen atmospheres on the properties of stainless steel 316 L parts produced by laser-powder bed fusion. Mater Des 179:107873
Pico LBO, Zhang C, Vyn TJ (2021) The central role of ear nitrogen uptake in maize endosperm cell and kernel weight determination during the lag period. Field Crop Res 273:108285
Post AK, Knapp AK (2020) The importance of extreme rainfall events and their timing in a semi-arid grassland. J Ecol 108(6):2431–2443
Prasad PVV, Staggenborg SA, Ristic Z (2008) Response of crops to limited water: Understanding and modeling water stress effects on plant growth processes. In: Impacts of drought and/or heat stress on physiological, developmental, growth, and yield processes of crop plants, pp 301–355
Priyadarshini P, Choudhury S, Tilgam J, Bharati A, Sreeshma N (2021) Nitrogen fixing cereal: A rising hero towards meeting food security. Plant Physiol Biochem 167:912–920
Qaseem MF, Qureshi R, Shaheen H (2019) Effects of pre-anthesis drought, heat and their combination on the growth, yield and physiology of diverse wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genotypes varying in sensitivity to heat and drought stress. Sci Rep 9(1):1–12
Qin Z, Myers DB, Ransom CJ, Kitchen NR, Liang SZ, Camberato JJ, Shanahan JF (2018) Application of machine learning methodologies for predicting corn economic optimal nitrogen rate. Agron J 110(6):2596–2607. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2018.03.0222
Rahimi JM, Akbari GA, Alahdadi I, Soufizadeh S, Kumar U, Parsons D (2021) Phenotypic traits, grain yield and yield components of maize cultivars under combinations of management practices in semi-arid conditions of Iran. Int J Plant Prod 15(3):459–471
Rahman KM, Zhang D (2018) Effects of fertilizer broadcasting on the excessive use of inorganic fertilizers and environmental sustainability. Sustainability 10(3):759
Ravier C, Meynard JM, Cohan JP, Gate P, Jeuffroy MH (2017) Early nitrogen deficiencies favor high yield, grain protein content and N use efficiency in wheat. Eur J Agron 89:16–24
Richards RA, Cavanagh CR, Riffkin P (2019) Selection for erect canopy architecture can increase yield and biomass of spring wheat. Field Crop Res 244:107649
Saddique Q, Cai H, Ishaque W, Chen H, Chau HW, Chattha MU, He J (2019) Optimizing the sowing date and irrigation strategy to improve maize yield by using CERES (Crop Estimation through Resource and Environment Synthesis) maize model. Agronomy 9(2):109
Shah A, Akmal M, Asim M, Farhatullah, Raziuddin, Rafi A (2012) Maize growth and yield in Peshawar under changing climate. Pak J Bot 44(6):1933–1938
Shah L, Yahya M, Shah SMA, Nadeem M, Ali A, Ma C (2019) Improving lodging resistance: using wheat and rice as classical examples. Int J Mol Sci 20(17):4211
Shrestha U, Amgain LP, Karki TB, Dahal KR, Shrestha J (2016) Effect of sowing dates and maize cultivars in growth and yield of maize along with their agro-climatic Indices in Nawalparasi, Nepal. JAS 3(1):57–62
Siyar S, Sami S, Muhammad Z, Majeed A (2020) Seed priming, implication in agriculture to manage salinity stress in crops. In: New frontiers in stress management for durable agriculture, p 269
Sun K, Liu XS, Qin TJ, Jiang F, Cai TJ, Shen YL, Li HL (2021) Relative abundance of invasive plants more effectively explains the response of wetland communities to different invasion degrees than phylogenetic evenness. J Plant Ecol 12(40):45–51
Tedersoo L, Bahram M, Zobel M (2020) How mycorrhizal associations drive plant population and community biology. Science. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba1223
Thomson JD (2019) Progressive deterioration of pollination service detected in a 17-year study vanishes in a 26-year study. New Phytol 224(3):1151–1159
Tirado-Corbalá R, Gao S, Ayars JE, Wang D, Phenea CJ, Phene RC (2019) Carbon and nitrogen dynamics affected by drip irrigation methods and fertilization practices in a pomegranate orchard. Horticulturae 5(4):77
Wang Y, Yao Z, Zhan Y, Zheng X, Zhou M, Yan G, Bahl KB (2021) Potential benefits of liming to acid soils on climate change mitigation and food security. Glob Change Biol 27(12):2807–2821
Wolfe DW, DeGaetano AT, Peck GM, Carey M, Ziska LH, Cox JL, Hollinger DY (2018) Unique challenges and opportunities for northeastern US crop production in a changing climate. Clim Change 146(1):231–245
Funding
The authors greatly acknowledge the financial support of the Higher Education Commission (HEC) Islamabad in the form of the indigenous 5000 scholarship program for postgraduate students in the universities of Pakistan. Mr Abdullah Shah was among those who have qualified for financial support from HEC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A. Shah worked on data recording, compilation, and draft MS preparation. M. Akmal designed the experiment and edited the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
A. Shah and M. Akmal declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shah, A., Akmal, M. Yield and Healthy Trait Harvest of Maize with Adjustment of Sowing Timing and N Rate in a Monsoon Region under the Changing Climate. Gesunde Pflanzen 75, 1157–1167 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-022-00773-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-022-00773-5