Abstract
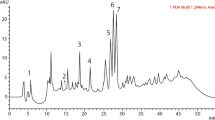
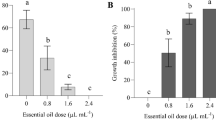
One of the most significant diseases is the bacterial blight of beans caused by Xanthomonas phaseoli pv. phaseoli. In the present study, different concentrations of clove oil were evaluated on in vitro growth inhibition of X.s phaseoli pv. phaseoli (Xap3), whereas its in vivo effects on disease severity, and bacterial colony-forming units, were investigated. While a considerable inhibition of in vitro growth was seen, the pathogen’s growth was significantly inhibited as the concentration was raised. Higher concentrations (10, 12, 14 µL/mL) effectively inhibited the growth as the growth of 26.6, 27.1, and 28.2 mm, respectively, was recorded. After 4 and 12 days of application, foliar application (1%) of clove oil in the greenhouse showed a significant reduction in disease severity (60% and 50% respectively). After 4 days, the population of colony-forming units on bean leaves was lower (0.5 × 106) and a gradual increase (5.0 × 106) after 16 days was recorded in clove oil-treated plants that were significantly lower than in infected control. A total of 18 chemical compounds including alkaline, alkane, isomer, alcohol, fatty acids acetates, and terpene were found during GC-MS analysis. The main component, eugenol (64.82%), which is an ally chain substituted guaiacol molecule and an efficient scavenger of reactive oxygen radicals responsible for cell proliferation, was detected in a higher amount. These results confer the application of clove oil can provide an alternative to chemical fungicides to mitigate this disease and therefore, future studies should focus on the field application of clove oil.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abo-Elyousr KAM (2006) Induction of systemic acquired resistance against common blight of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. phaseoli. Egyp J Phyto 34:41–50
Abo-Elyousr KAM, Hadeel MMKB, Mohamed H, Saad AMA, Yasser SM (2019) Biological control of the tomato wilt caused by Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganensis using formulated plant growth-promoting bacteria. Egyp J Biol Pest Control 29:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41938-019-0152-6
Abo-Elyousr KAM, Najeeb MA, Ahmed WMA, Sergio RR, Khamis Y (2020) Plant extract treatments induce resistance to bacterial spot by tomato plants for a sustainable system. Hortic 6:36. https://doi.org/10.3390/horticulturae6020036
Alighiri D, Eden WT, Cahyono E, Supardi KI (2018) Quality improvement by batch vacuum distillation and physicochemical characterization of clove leaf oil in Central Java, Indonesia. J Phys Conf Ser 983:12163. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/983/1/012163
Alma MH, Ertas M, Nitz S, Kollmannsberger H (2007) Chemical composition and content of essential oil from the bud of cultivated Turkish clove (Syzigium aromaticum L.). BioRes 2:265–269. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.2.2.265-269
Amelia B, Saepudin E, Cahyana AH, Rahayu DU, Sulistyoningrum AS, Haib J (2016) GC-MS Analysis of Clove (Syzygium aromaticum) Bud Essential Oil from Java and Manado. Int Symp Current Progress Math Sc 1862:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4991186
Amira MH, Amal ME (2007) Impact of salicylic acid and paclobutrazol exogenous application on the growth, yield and nodule formation of common bean. Aus J Basic App Sci 1(4):834–840
Baysal Ö (2001) The induced resistance against fire blight by the plant activator BTH (Bion) or plant extracts of Hedera helix leaves and studies on the mode of action. PhD Thesis. Georg-August-Universität Göttingen, Göttingen
Bowers JH, Locke JC (2000) Effect of botanical extracts on the population density of Fusarium oxysporum in soil and control of Fusarium wilt in the greenhouse. Plant Dis 84:300–305
Burt S (2004) Essential oils: their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods—A review. Int J Food Microbiol 94(3):223–253. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.03.022
Cansian RL, Vanin AB, Orlando T, Piazza SP, Puton BMS, Cardoso RI, Gonçalves IL, Honaiser TC, Paroul N, Oliveira D (2017) Toxicity of clove essential oil and its ester eugenyl acetate against Artemia salina. Braz J Biol 77(1):155–161. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.12215
Carlos FJ, Cristiano MT, Camila FPN, Adrise MN, Claudio MPP, Flávio RMG (2016) Insecticide activity of clove essential oil on bean weevil and maize weevil. Rev Bras Eng Agric Ambient 20(1):72–77. https://doi.org/10.1590/1807-1929/agriambi.v20n1p72-77
Castellanos LM, Olivas NA, Ayala-Soto J, Contreras CMD, Ortega MZ, Salas FS, Hernández-Ochoa L (2020) In Vitro and In Vivo Antifungal Activity of Clove (Eugenia caryophyllata) and Pepper (Piper nigrum L.) Essential Oils and Functional Extracts Against Fusarium oxysporum and Aspergillus niger in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Int J Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1702037
Castro-Guerrero NA, Isidra-Arellano MC, Mendoza-Cozatl DG, Valdés-López O (2016) Common bean: a legume model on the rise for unraveling responses and adaptations to iron, zinc, and phosphate deficiencies. Front Plant Sci 7:600. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00600
Cellini A, Fiorentini L, Buriani G, Yu J, Donati I, Cornish DA, Novak B, Costa G, Vanneste JL, Spinelli F (2014) Elicitors of the salicylic acid pathway reduce incidence of bacterial canker of kiwifruit caused by Pseudomonas syringae pv. actinidae. Ann App Biol 165:441–453. https://doi.org/10.1111/aab.12150
Da Silva EG, Moura AB, Deuner CC, Farias DR (2008) Study of biocontrol mechanisms of bacterial bean blight by bacteria. Rev Cer 55:377–383
Dihazi A, Fatima J, Jamila Z, Majida H, Ismail H (2003) Effect of salicylic acid on phenolic compounds related to date palm resistance to Fusarium oxysporum F. sp. albedinis. Phytopathol Medit 42:9–16
El-Mougy SN, Nadia GE, Abdel-kader MM (2007) Control of wilt and root rot incidence in phaseolus vulgaris L. By some plant volatile compounds. J Plant Prot Res 47:255–265
Ferreira CF, Pereira MG, Santos ADS, Rodrigues R, Bressan-Smith RE, Pio-Viana A, Daher REF (2003) Resistance to common bacterial blight in Phaseolus vulgaris L. recombinant inbred lines under natural infection of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. phaseoli. Euphytica 134:43–46. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026131626592
Fikire L (2004) Effects of intercropping and cultivar mixtures on bean diseases and yield. Eth Inst Agri Res 8:71–81
Gomez KA, Gomez AA (1984) Statistical procedures for agriculture research, 2nd edn. John Willey, New York
Gruľová D, Caputo L, Elshafie HS, Baranová B, De Martino L, Sedlák V, Gogaľová Z, Poráčová J, Camele I, De Feo V (2020) Thymol chemotype Origanum vulgare L. Essential oil as a potential selective bio-based herbicide on monocot plant species. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25030595
Halfeld-Vieira BA, Romeiro RS, Mizubuti ESG (2004) Isolation methods of tomato phylloplane bacteria aiming specific populations and implications as biocontrol agents. Fitopatol Bras 29:638–643. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-41582004000600007
Hu Q, Meifang Z, Shuyong W (2018) Progress on the antimicrobial activity research of clove oil and eugenol in the food antisepsis field. J Food Sci 83(6):1476–1483. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.14180
Huang Q, Lakshman DK (2010) Effect of clove oil on plant pathogenic bacteria and bacterial wilt of tomato and geranium. J Plant Pathol 92(3):701–707
Imran M, Esmat FA, Abo-Elyousr KAM, Nashwa MAS, Muhammad MMK, Muhammad WY (2021) Characterization and sensitivity of Botrytis cinerea to Benzimidazole and SDHI fungicides and illustration of resistance profile. Aus Plant Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-021-00803-2
Imran M, Abo-Elyousr KAM, Mousa M, Saad MM (2022) A study on the synergetic effect of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and dipotassium phosphate on Alternaria solani causing early blight disease of tomato. Eur J Plant Pathol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-021-02384-8
Jha AB, Ashokkumar K, Diapari M, Ambrose SJ, Zhang H, Tar’an B (2015) Genetic diversity of folate profiles in seeds of common bean, lentil, chickpea and pea. J Food Compos Anal 42:134–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2015.03.006
Khan MSA, Zahin M, Hasan S, Husain FM, Ahmad I (2009) Inhibition of quorum sensing regulated bacterial functionsby plant essential oils with special reference to clove oil. Letters in Applied Microbiology 49:354–360
Kishore GK, Pande S (2004) Natural fungicides for management of phytopathogenic fungi. Ann Rev Phytopathol 3:331–356
Kishore GK, Pande S, Harish S (2007) Evaluation of essential oils and their components for broad-spectrum antifungal activity and control of late leaf spot and crown rot diseases in peanut. Plant Dis 91:375–379. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-91-4-0375
Kumar P, Veeresh L, Pushpa D, Aprajita K, Pooja S, Bharati SM, Jyotsana S, Kapuganti JG, Girigowda M (2021) Greenhouse and field experiments revealed that clove oil can effectively reduce bacterial blight and increase yield in pomegranate. Food Energy Secur 10:e305. https://doi.org/10.1002/fes3.305
Kumar V, Mathela CS, Tewari AK, Bisht KS (2014) In vitro inhibition activity of essential oils from some Lamiaceae species against phytopathogenic fungi. Pest Biochem Physiol 114:67–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2014.07.001
Linde JH, Combrinck S, Regnier TJ, Virijevic S (2010) Chemical composition and antifungal activity of the essential oils of Lippia rehmannii from South Africa. South Afr J Bot 76:37–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2009.06.011
Lindow SE, Brandl MT (2003) Microbiology of the phyllosphere. App Env Microbiol 69:1875–1883. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.4.1875-1883.2003
Louws FJ, Campbell HL, Cuppels DA, Jones JB, Shoemaker PB, Sahin F, Miller SA (2001) Field control of bacterial spot and bacterial speck of tomato using a plant activator. Plant Dis 85:481–488. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS.2001.85.5.481
Lucas GC, Alves E, Pereira RB, Zacaroni AB, Perina FJ, Souza RM (2012a) Indian clove essential oil in the control of tomato bacterial spot. J Plant Pathol 94:45–51
Lucas GC, Eduardo A, Ricardo BP, Fabiano JP, Ricardo M (2012b) Antibacterial activity of essential oils on Xanthomonas vesicatoria and control of bacterial spot in tomato. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 47(3):351–359. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-204X2012000300006
Luke DB, Murray BI, Mahesh KU (2006) Phytotoxicity of clove oil and its primary constituent eugenol and the role of leaf epicuticular wax in the susceptibility to these essential oils. Weed Sci 54:833–837. https://doi.org/10.1614/WS-06-039R.1
Marian T, Walaa K (2018) Antifungal activities of clove oil against root rot and wilt pathogens of tomato plants. Am Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 18(3):105–114
Medice R, Alves E, Assis RT, Magno MR Jr, Lopes EA et al (2007) Essential oils used in the control of asian soybean rust Phakopsora pachyrhizi Syd. & P. Syd. Cienc. Agrotecnologia 31:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1413-70542007000100013
Memmou F, Mahboub R (2012) Composition of essential oil from fresh flower of clove. J Sci Res Pharm 1:33–35
Nejad MS, Özgüneş H, Başaran N (2017) Pharmacological and toxicological properties of eugenol. Turk J Pharm Sci 14(2):201–206. https://doi.org/10.4274/tjps.62207
Piper P, Calderon CO, Hatzixanthis K, Mollapour M (2001) Weak acid adaptation: the stress response that confers resistance to organic acid food preservatives. Microbiology 47:2635–2642. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-147-10-2635
Polatoğlu K, Demirci B, Başer KHC (2016) High amounts of n‑alkanes in the composition of Asphodelus aestivus Brot. Flower essential oil from Cyprus. J Oleo Sci 65:867–870. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess15197
Popovic T, Starovic M, Aleksic G, Zivkovic S, Josic D, Ignjatov M, Milovanovic P (2012) Response of different beans against common bacterial blight disease caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. Phaseoli. Bulg J Agr Sci 18:701–707
Rodríguez O, Sánchez R, Verde M, Núñez M, Ríos R, Chávez A (2014) Obtaining the essential oil of Syzygium aromaticum, identification of eugenol and its effect on Streptococcus mutans. J Oral Res 3(4):218–224. https://doi.org/10.17126/joralres.2014.051
Sallam NMS (2011) Biological control of common blight of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. phaseoli by using the bacterium Rahnella aquatilis. Arch Phyt Plant Prot 44(20):1966–1975. https://doi.org/10.1080/03235408.2010.544469
Sallam NMA, Ali EFA., Abo-Elyousr KAM, Bereika MFF, Seleim MAA (2021) Thyme oil treatment controls bacterial wilt disease symptoms by inducing antioxidant enzyme activity in Solanum tuberosum. Journal of Plant Pathology 103(2):563–572. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-021-00808-2
Santos JL, Aparicio I, Alonso E (2007) Occurrence and risk assessment of pharmaceutically active compounds in wastewater treatment plants. A case study: Seville city (Spain). Environment International 33:596–601
Sharma A, Naveen KS, Ankit S, Arti K, Saurabh D, Satyawati S, Bishwajit K (2018) Clove and lemongrass oil based non-ionic nano emulsion for suppressing the growth of plant pathogenic Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici. Ind Crops Prod 123:353–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.06.077
Sikkema J, deBont JA, Poolman B (1994) Interactions of cyclic hydrocarbons with biological membranes. J Biol Chem 269(11):8022–8028. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(17)37154-5
Silva LC, Debonaa D, Aucique-Péreza CE, Oliveiraa JR, Ribeiro-Júniorb JI, Brása VV, Rodrigues FA (2020) Physiological and antioxidant insights into common bean resistance to common bacterial blight. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 111:101505
Srinivasan T, Kumar KRR, Meur G, Kirti P (2009) Heterologous expression of Arabidopsis npr1 (atnpr1) enhances oxidative stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco plants. Biotechnol Lett 31(9):1343–1351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0022-5
Tsuda K, Tsuji G, Higashiyama M, Ogiyama H, Umemura K, Mitomi M, Yasuyuki K, Kosaka Y (2016) Biological control of bacterial soft rot in Chinese cabbage by Lactobacillus plantarum strain BY under field conditions. Biol Control 100:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2016.05.010
Uknes S, Mauch MB, Moyer M, Potter S, Williams S (1992) Acquired resistance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 4:645–656. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.4.6.645
Wang W, Fang Y, Imran M, Hu Z, Zhang S, Huang Z, Liu X (2021) Characterization of the field Fludioxonil resistance and its molecular basis in Botrytis cinerea from shanghai province in China. Microorganisms 9:266. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9020266
Wei C, Shixing Z, Kai S, Chi Z, Hua S (2020) Chemical profile and phytotoxic action of Onopordum acanthium essential oil. Sci Rep 10:13568. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-70463-7
Wenqiang G, Li S, Yan R, Tang S, Quan C (2007) Comparison of essential oils of clove buds extracted with supercritical carbon dioxide and other three traditional extraction methods. Food Chem 101(4):1558–1564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.04.009
Whitehead NA, Barnard AM, Slater H, Simpson NJ, Salmond GP (2001) Quorum-sensing in gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:365–404
Yang QQ, Ren-You G, Ying-Ying G, Dan Z, Harold C (2018) Polyphenols in common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.): chemistry, analysis, and factors affecting composition comprehensive. Rev Food Sci Food Safty 17:1518–1539. https://doi.org/10.1111/1541-4337.12391
Zhang C, Imran M, Liu M, Li Z, Gao H, Duan H, Zhou S, Liu X (2020) Two point mutations on CYP51 combined with induced expression of the target gene appeared to mediate pyrisoxazole resistance in Botrytis cinerea. Front Microbiol 11:1396. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01396
Zhang C, Imran M, Xiao L, Hu Z, Li G, Zhang F, Liu X (2021) Difenoconazole resistance shift in Botrytis cinerea from tomato in China associated with inducible expression of CYP51. Plant Dis 105(2):400–407. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-03-20-0508-RE
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Taif University Researchers Supporting Project number (TURSP-2020/64), Taif University, Taif, Saudi Arabia for providing the financial support and research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally in the manuscript, K.A.M.A suggested the idea of the work and contributed to data curation and their validation. M.I performed the experiments and prepared the draft and contributed to the formal analysis of the data. K.A.M.A, N.M.A, E.F.A, M.S.A, H.M.K.M.B and N.M.A.S contributed to the reviewing and editing the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
M. Imran, K.A. M. Abo-Elyousr, M.S. AL-Harbi, E.F. Ali, N.M. A. Sallam and H.M. M. Khalil Bagy declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical standards
Our manuscript is original research and it is not submitted to full or in parts to other journal for publication. The research did not involve any studies with human participants or animal as experimental model. All authors have reviewed the manuscript and approved the final version of manuscript before submission.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Imran, M., Abo-Elyousr, K.A.M., AL-Harbi, M.S. et al. Antibacterial Efficacy of Clove Essential Oil Against Xanthomonas phaseoli pv. phaseoli and Its Influence on Pathogen Responses in Bean. Gesunde Pflanzen 75, 431–440 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-022-00721-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-022-00721-3